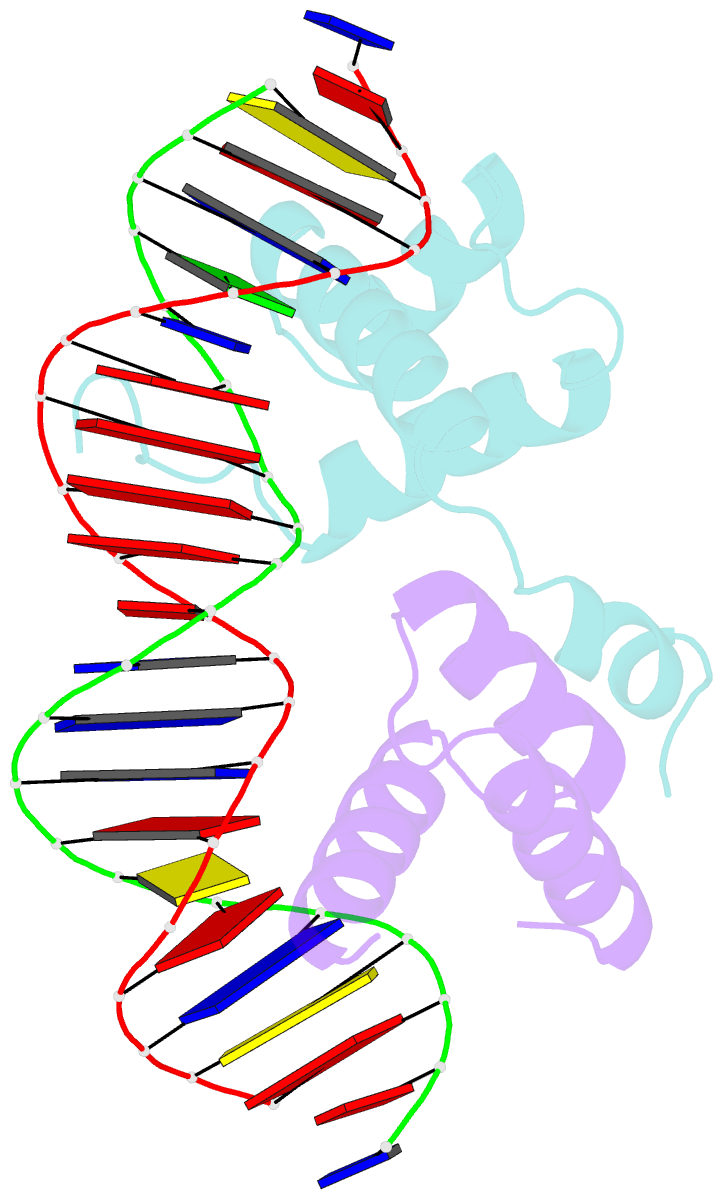
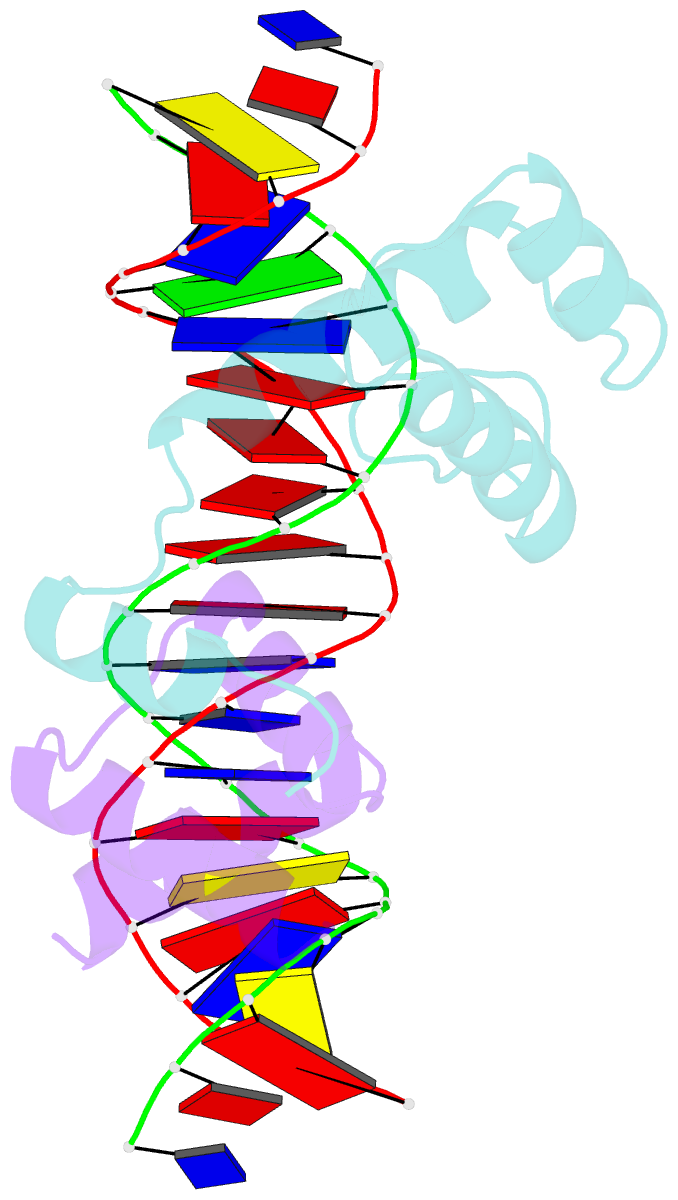
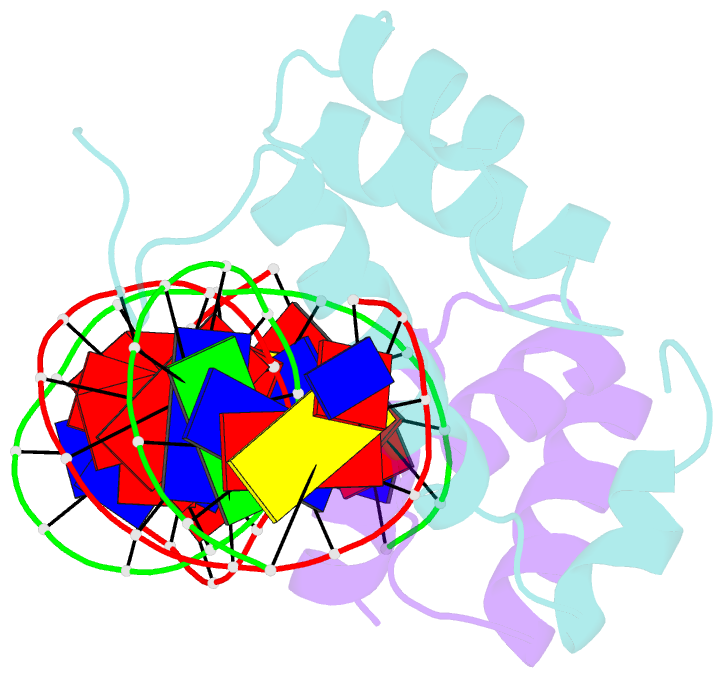
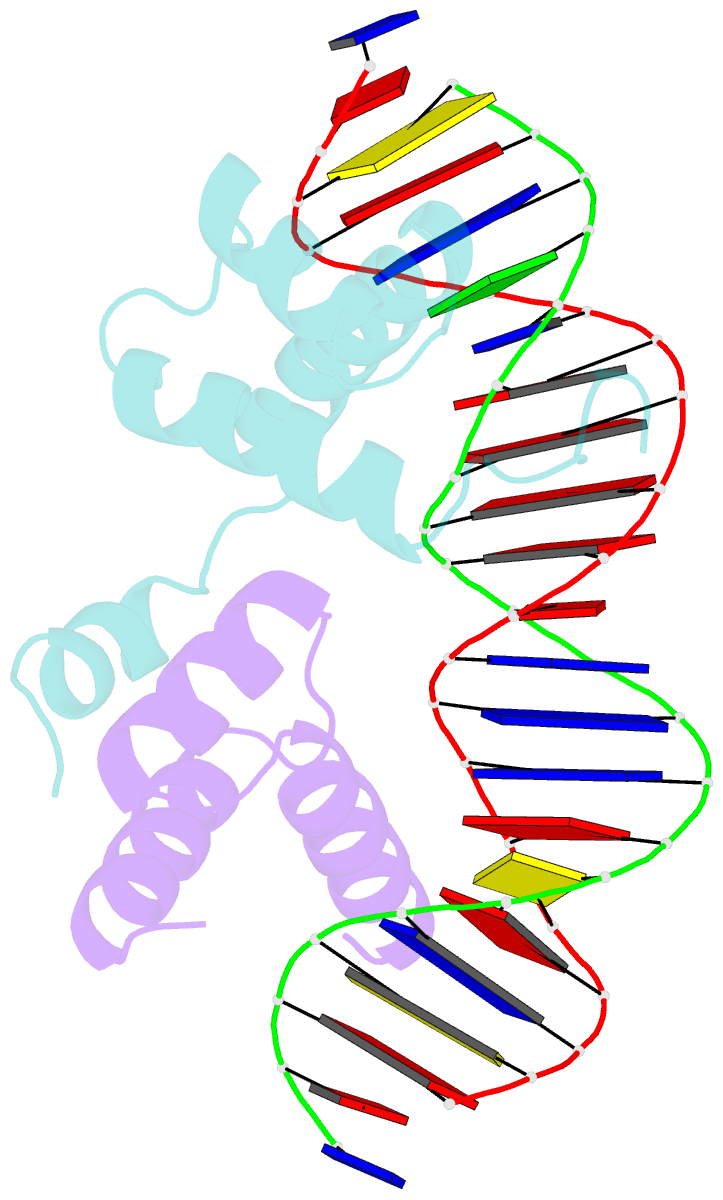
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 1akh; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- DNA binding protein-DNA
- Method
- X-ray (2.5 Å)
- Summary
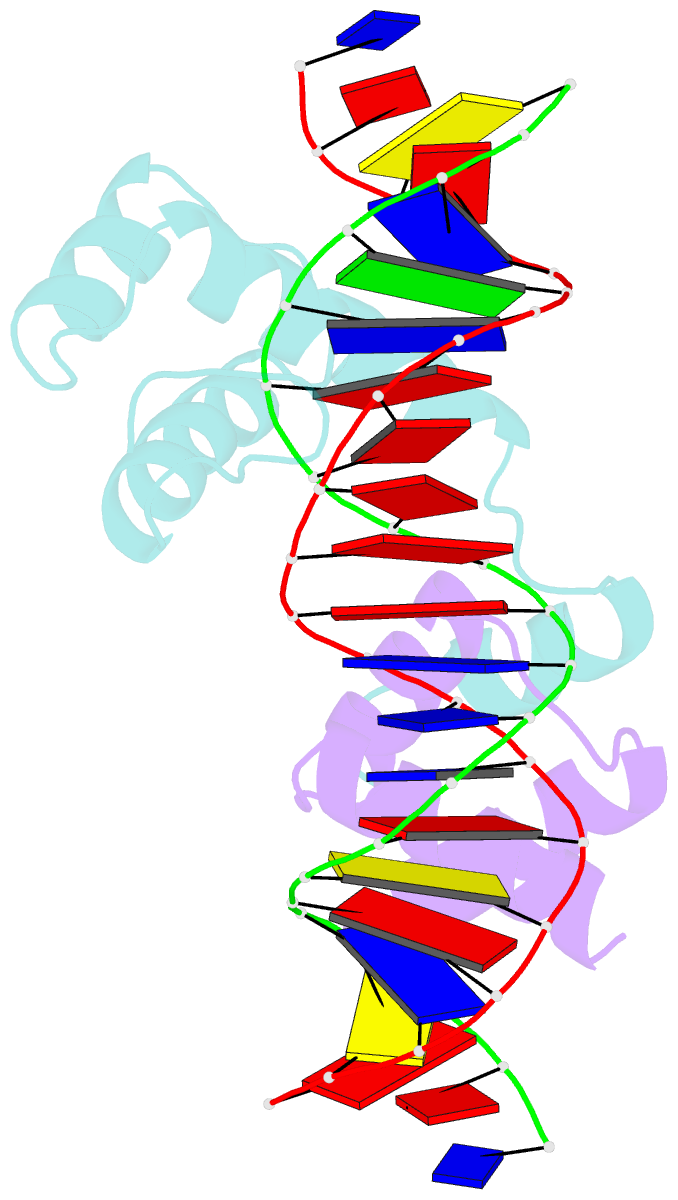
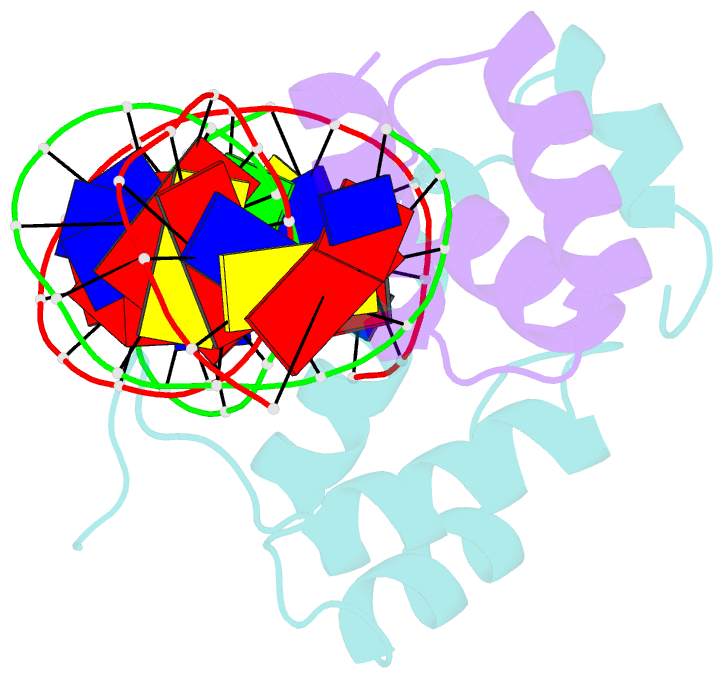
- Mat a1-alpha2-DNA ternary complex
- Reference
- Li T, Jin Y, Vershon AK, Wolberger C (1998): "Crystal structure of the MATa1/MATalpha2 homeodomain heterodimer in complex with DNA containing an A-tract." Nucleic Acids Res., 26, 5707-5718. doi: 10.1093/nar/26.24.5707.
- Abstract
- The crystal structure of the heterodimer formed by the DNA binding domains of the yeast mating type transcription factors, MATa1 and MATalpha2, bound to a 21 bp DNA fragment has been determined at 2.5 A resolution. The DNA fragment in the present study differs at four central base pairs from the DNA sequence used in the previously studied ternary complex. These base pair changes give rise to a (dA5).(dT5) tract without changing the overall base composition of the DNA. The resulting A-tract occurs near the center of the overall 60 degrees bend in the DNA. Comparison of the two structures shows that the structural details of the DNA bend are maintained despite the DNA sequence changes. Analysis of the A5-tract DNA subfragment shows that it contains a bend toward the minor groove centered at one end of the A-tract. The observed bend is larger than that observed in the crystal structures of A-tracts embedded in uncomplexed DNA, which are straight and have been presumed to be quite rigid. Variation of the central DNA base sequence reverses the two AT base pairs contacted in the minor groove by Arg7 of the alpha2 N-terminal arm without significantly altering the DNA binding affinity of the a1/alpha2 heterodimer. The Arg7 side chain accommodates the sequence change by forming alternate H bond interactions, in agreement with the proposal that minor groove base pair recognition is insensitive to base pair reversal. Furthermore, the minor groove spine of hydration, which stabilizes the narrowed minor groove caused by DNA bending, is conserved in both structures. We also find that many of the water-mediated hydrogen bonds between the a1 and alpha2 homeodomains and the DNA are highly conserved, indicating an important role for water in stabilization of the a1/alpha2-DNA complex.