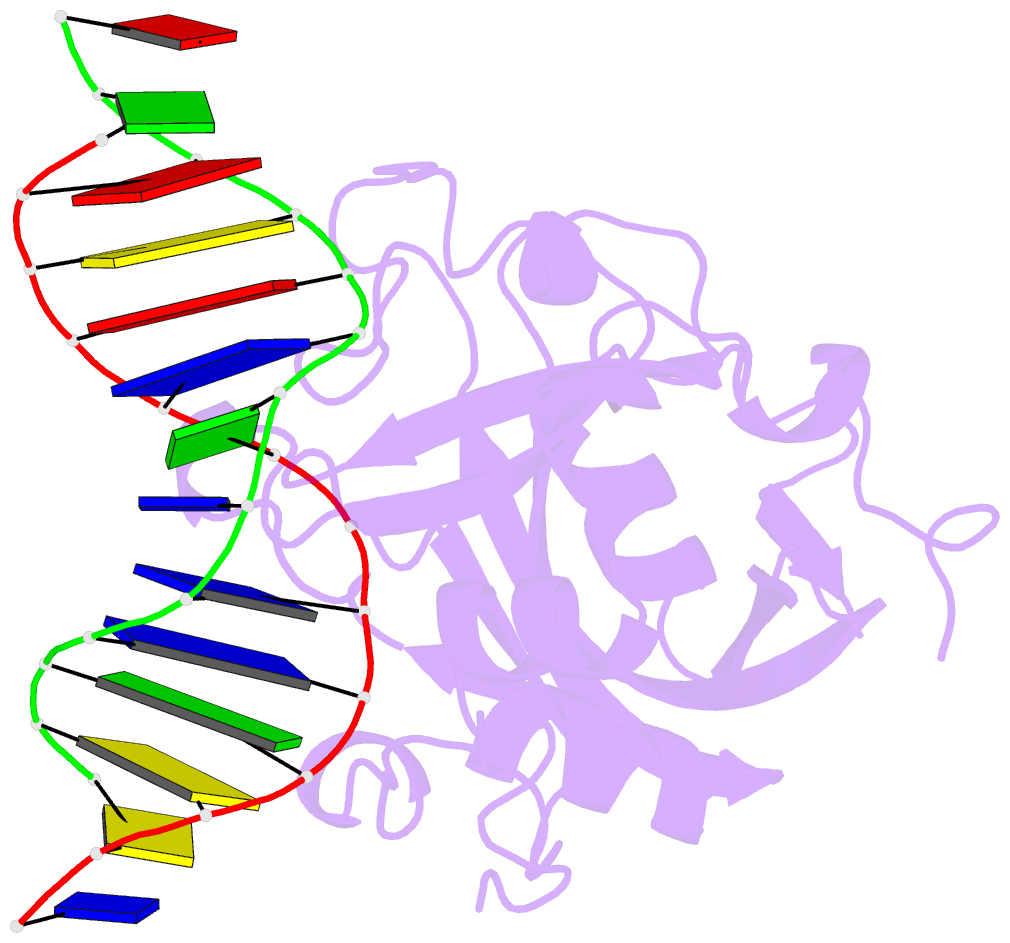
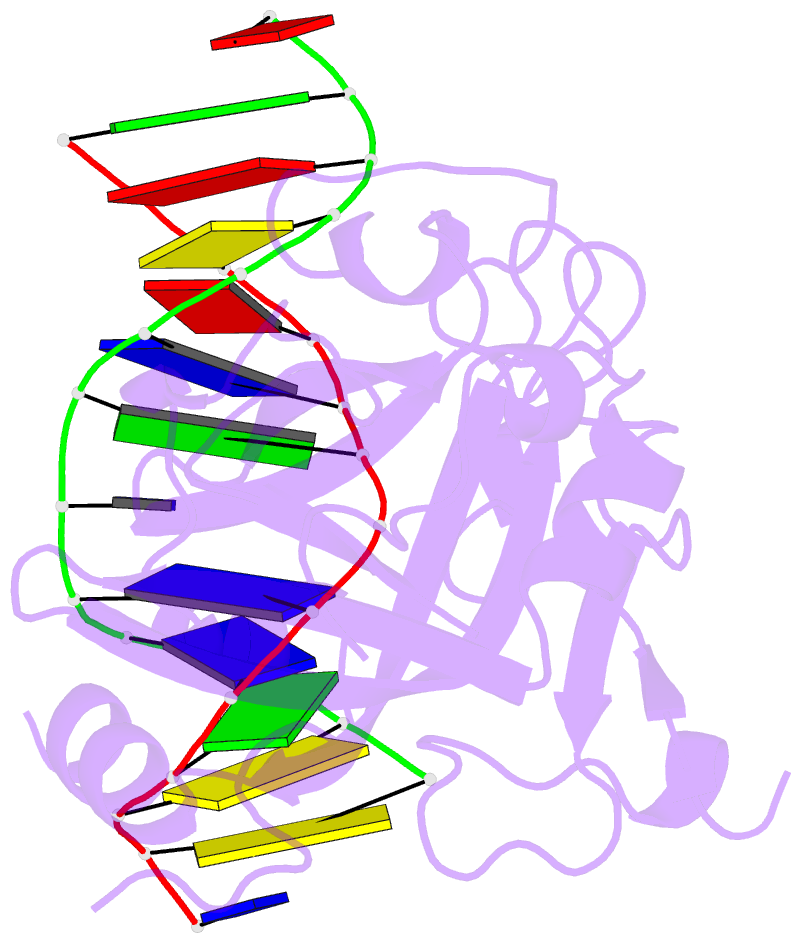
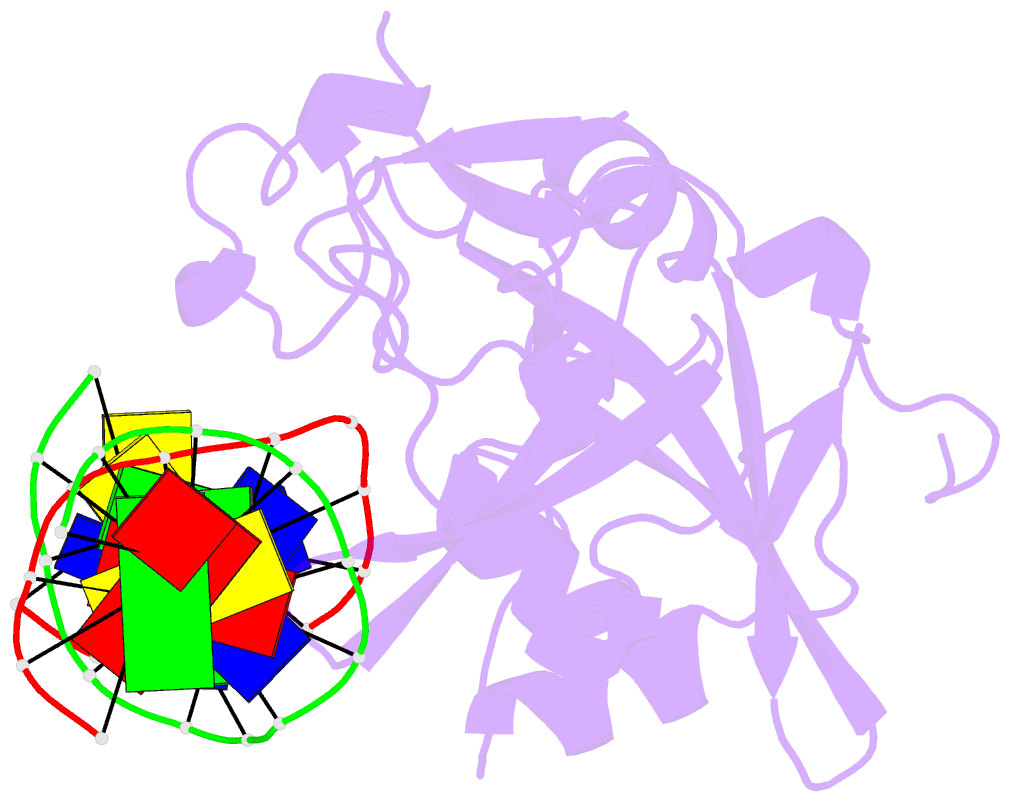
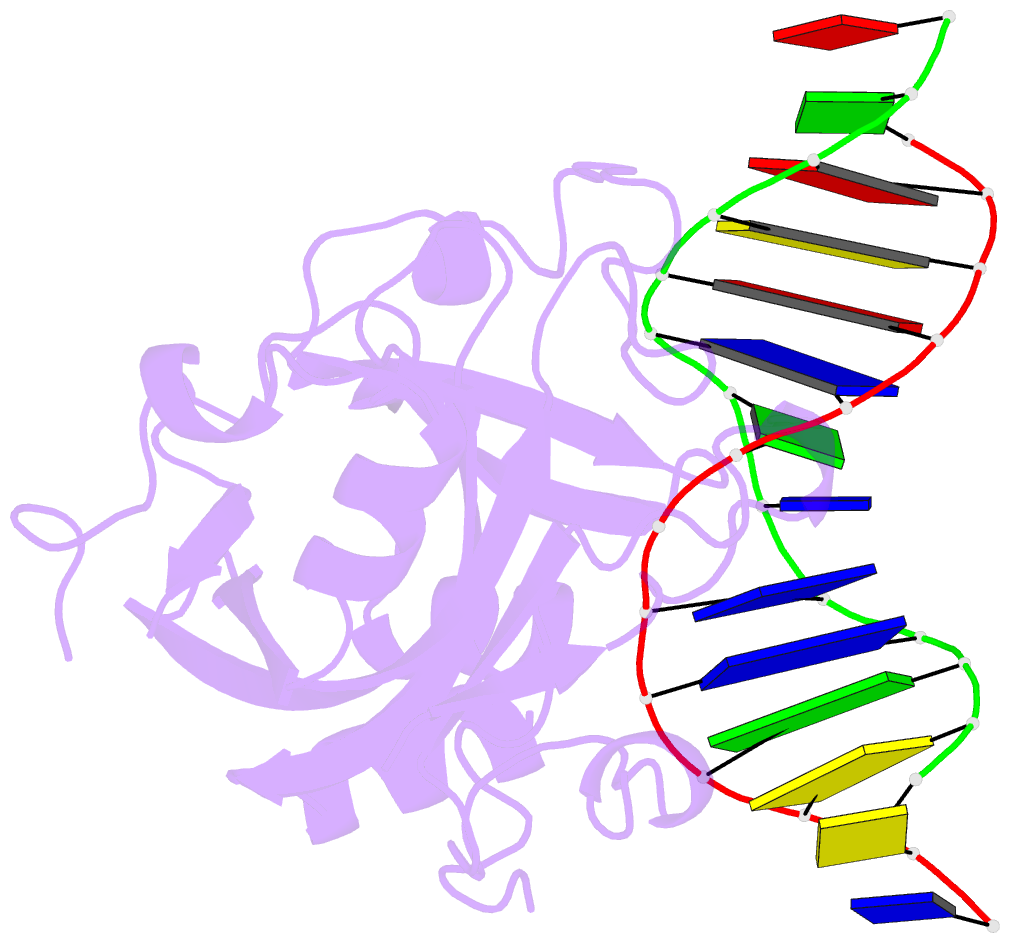
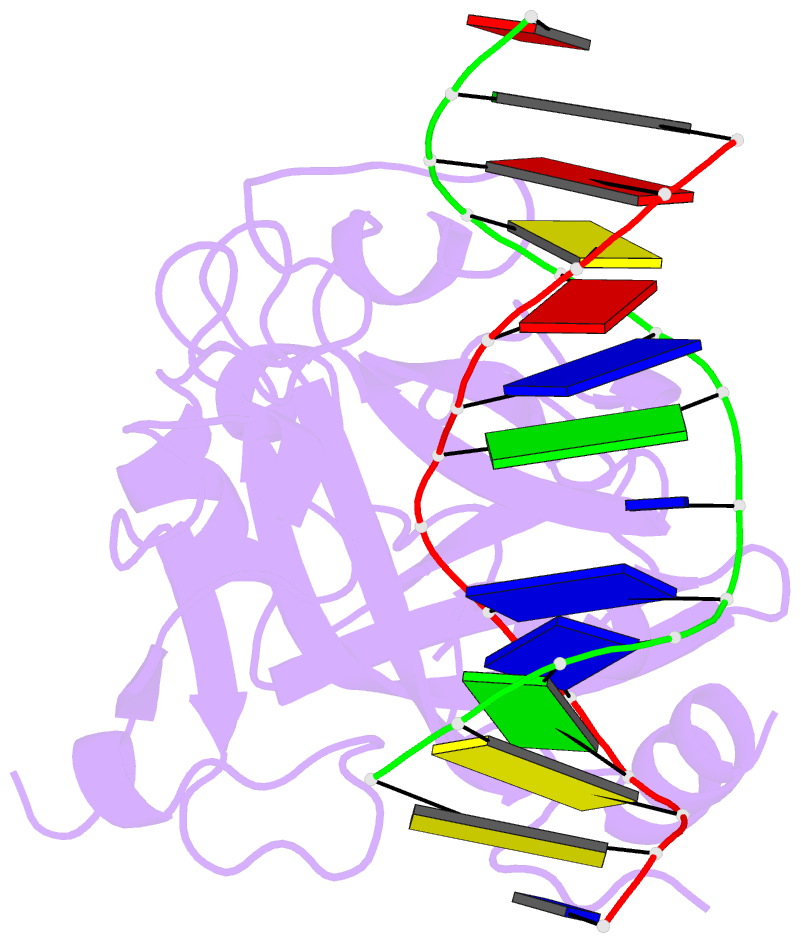
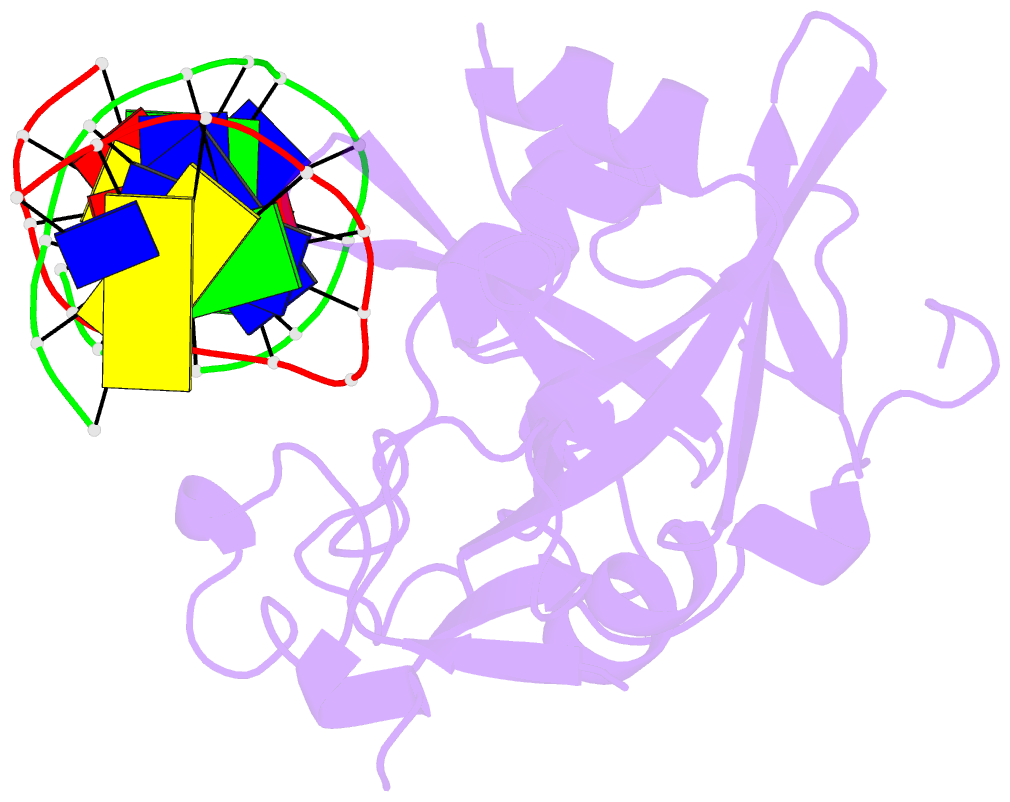
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 1bnk; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- hydrolase-DNA
- Method
- X-ray (2.7 Å)
- Summary
- Human 3-methyladenine DNA glycosylase complexed to DNA
- Reference
- Lau AY, Scharer OD, Samson L, Verdine GL, Ellenberger T (1998): "Crystal structure of a human alkylbase-DNA repair enzyme complexed to DNA: mechanisms for nucleotide flipping and base excision." Cell(Cambridge,Mass.), 95, 249-258. doi: 10.1016/S0092-8674(00)81755-9.
- Abstract
- DNA N-glycosylases are base excision-repair proteins that locate and cleave damaged bases from DNA as the first step in restoring the genetic blueprint. The human enzyme 3-methyladenine DNA glycosylase removes a diverse group of damaged bases from DNA, including cytotoxic and mutagenic alkylation adducts of purines. We report the crystal structure of human 3-methyladenine DNA glycosylase complexed to a mechanism-based pyrrolidine inhibitor. The enzyme has intercalated into the minor groove of DNA, causing the abasic pyrrolidine nucleotide to flip into the enzyme active site, where a bound water is poised for nucleophilic attack. The structure shows an elegant means of exposing a nucleotide for base excision as well as a network of residues that could catalyze the in-line displacement of a damaged base from the phosphodeoxyribose backbone.