Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 1c7u; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- transcription-DNA
- Method
- NMR
- Summary
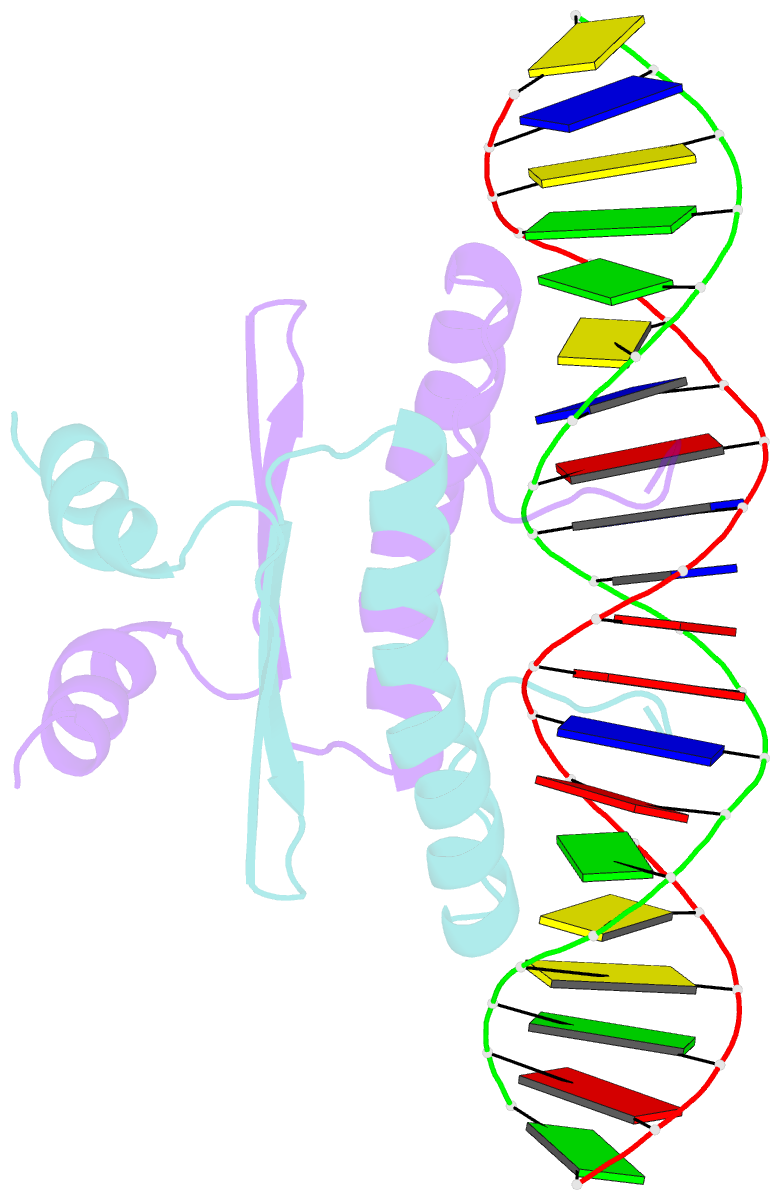
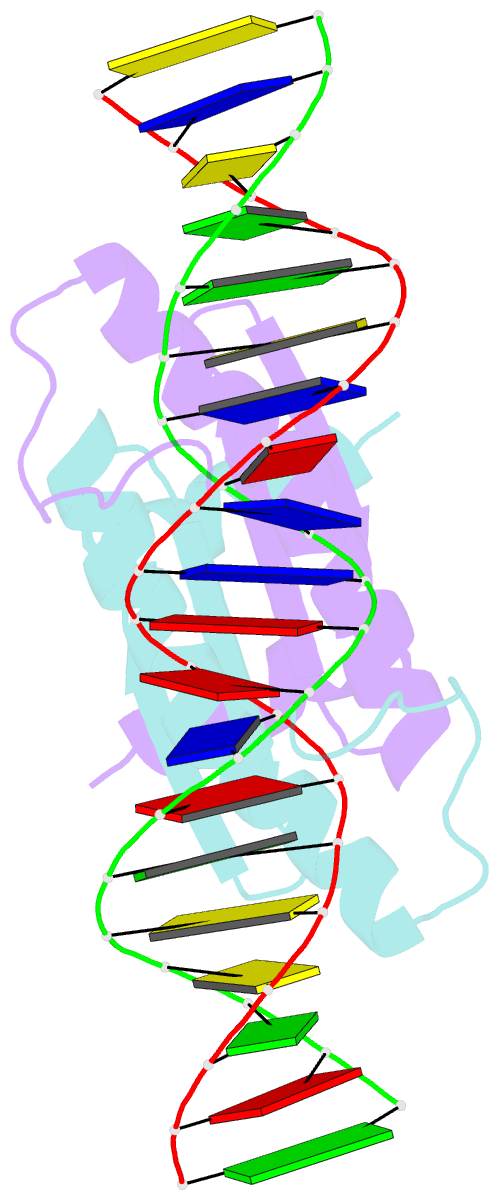
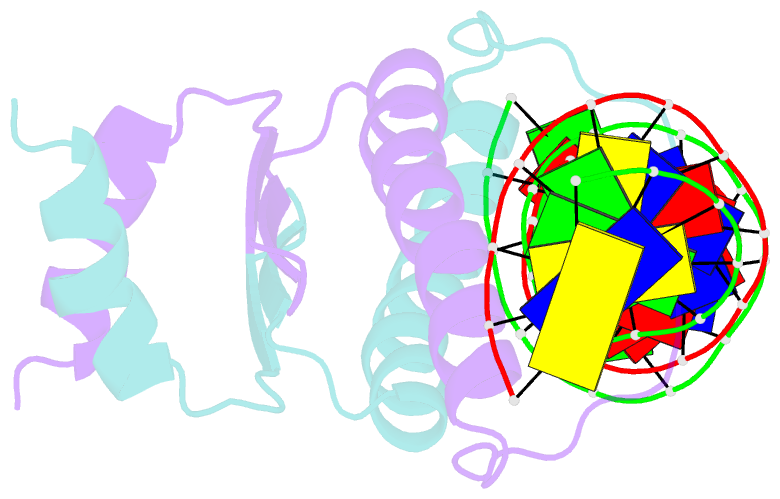
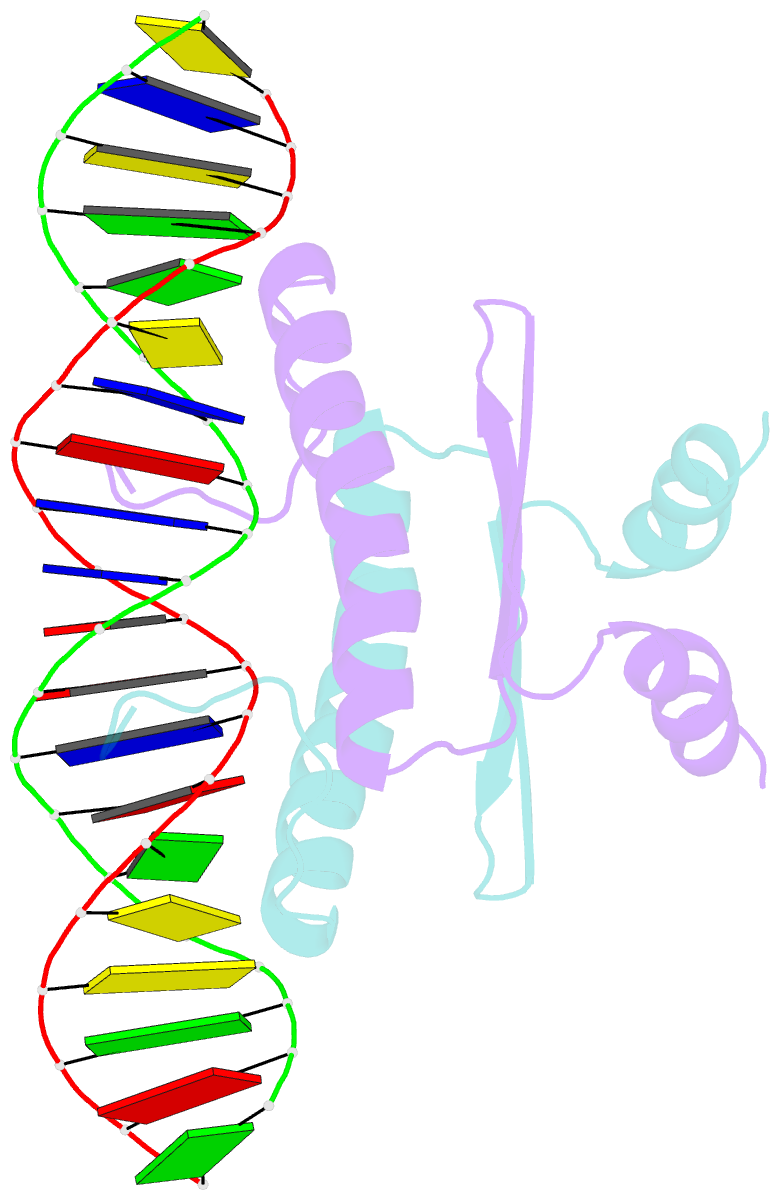
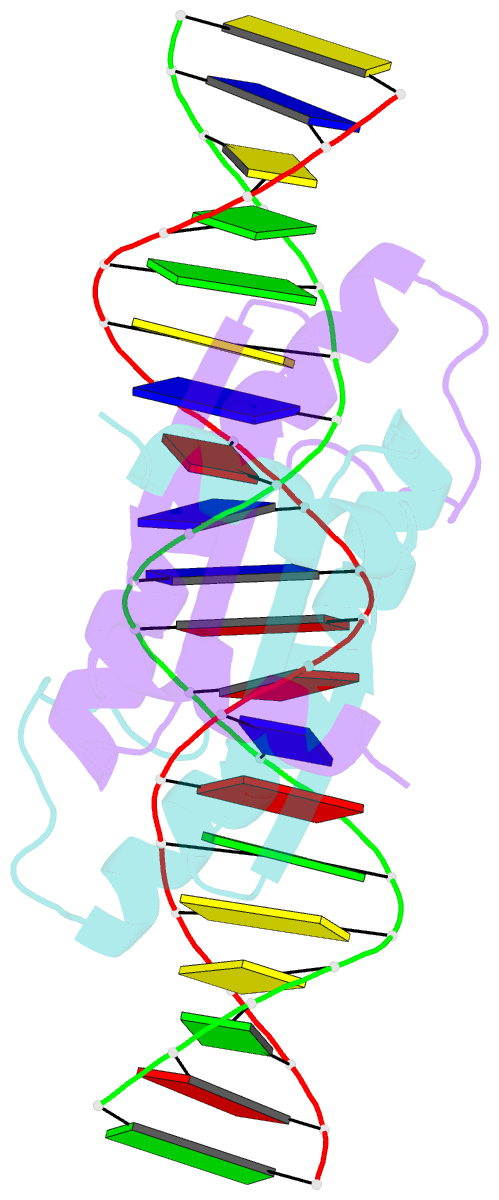
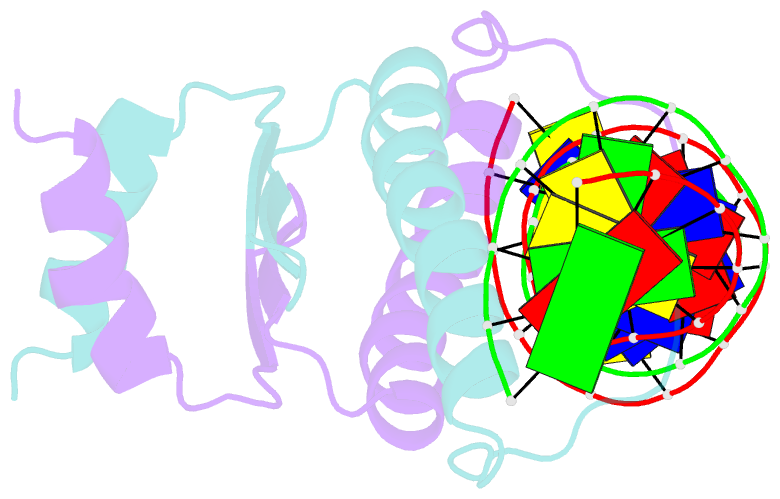
- Complex of the DNA binding core domain of the transcription factor mef2a with a 20mer oligonucleotide
- Reference
- Huang K, Louis JM, Donaldson L, Lim FL, Sharrocks AD, Clore GM (2000): "Solution structure of the MEF2A-DNA complex: structural basis for the modulation of DNA bending and specificity by MADS-box transcription factors." Embo J., 19, 2615-2628. doi: 10.1093/emboj/19.11.2615.
- Abstract
- The solution structure of the 33 kDa complex between the dimeric DNA-binding core domain of the transcription factor MEF2A (residues 1-85) and a 20mer DNA oligonucleotide comprising the consensus sequence CTA(A/T)(4)TAG has been solved by NMR. The protein comprises two domains: a MADS-box (residues 1-58) and a MEF2S domain (residues 59-73). Recognition and specificity are achieved by interactions between the MADS-box and both the major and minor grooves of the DNA. A number of critical differences in protein-DNA contacts observed in the MEF2A-DNA complex and the DNA complexes of the related MADS-box transcription factors SRF and MCM1 provide a molecular explanation for modulation of sequence specificity and extent of DNA bending ( approximately 15 versus approximately 70 degrees ). The structure of the MEF2S domain is entirely different from that of the equivalent SAM domain in SRF and MCM1, accounting for the absence of cross-reactivity with other proteins that interact with these transcription factors.