Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 1dc1; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- hydrolase-DNA
- Method
- X-ray (1.7 Å)
- Summary
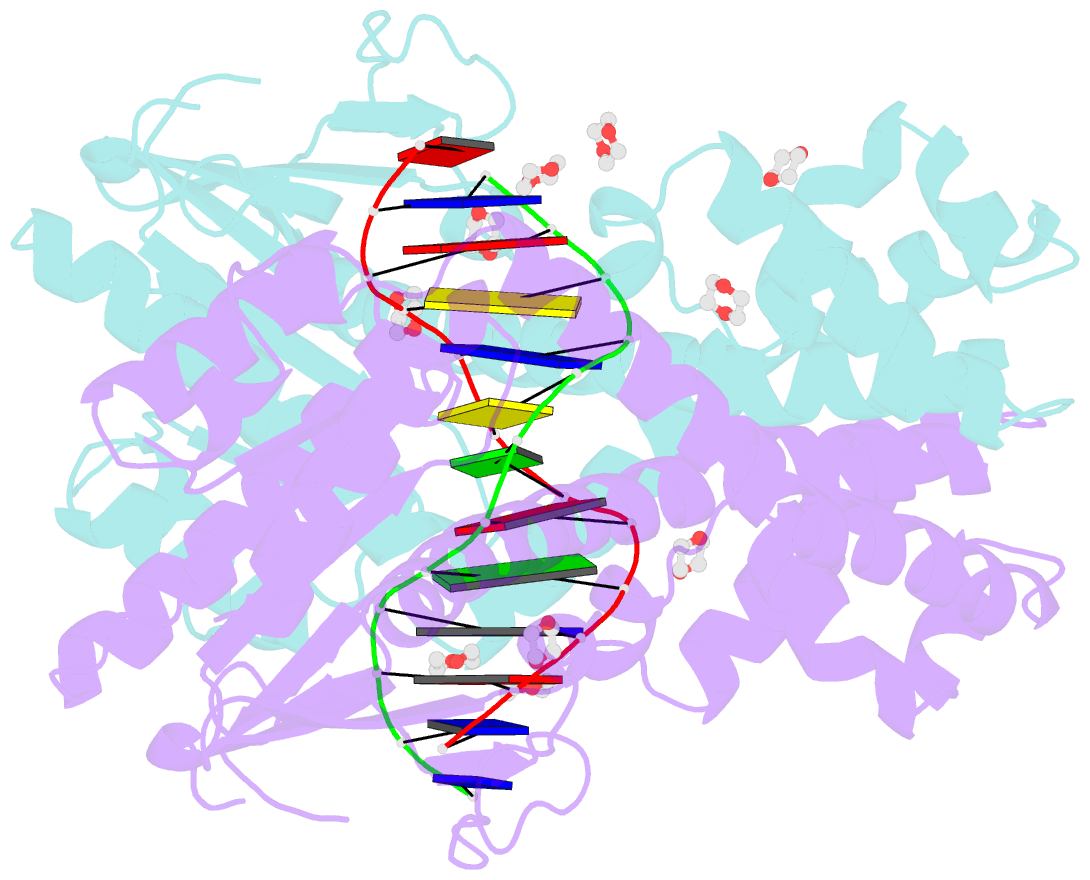
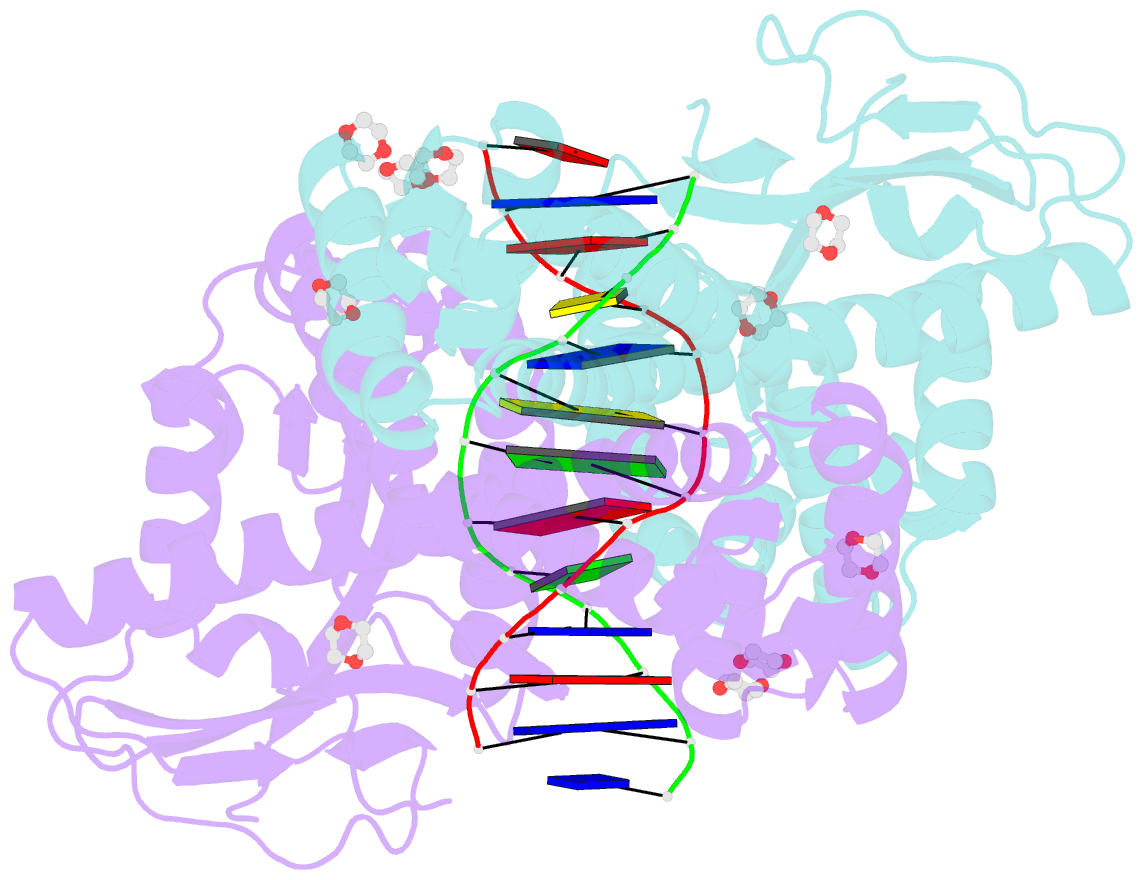
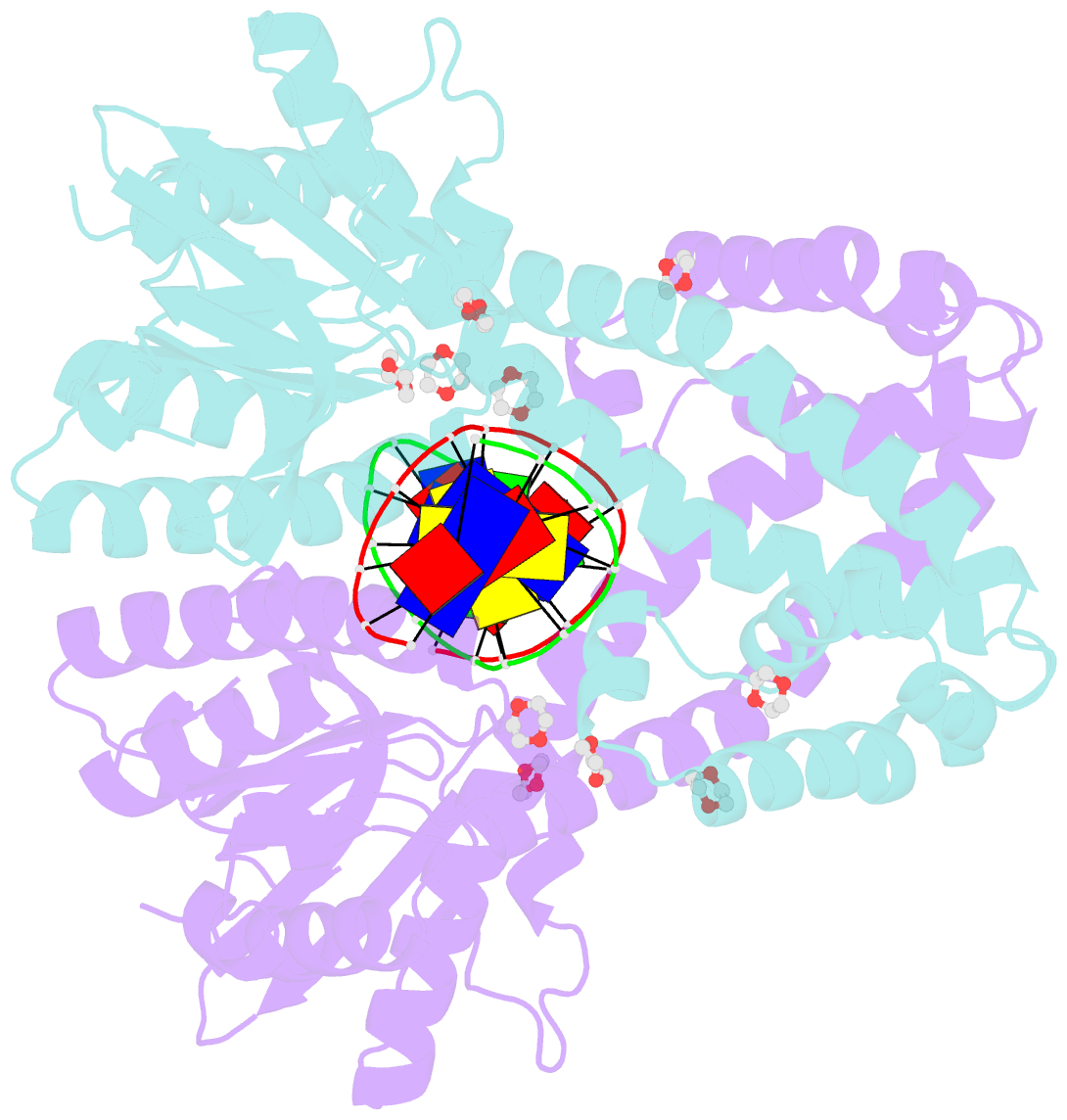
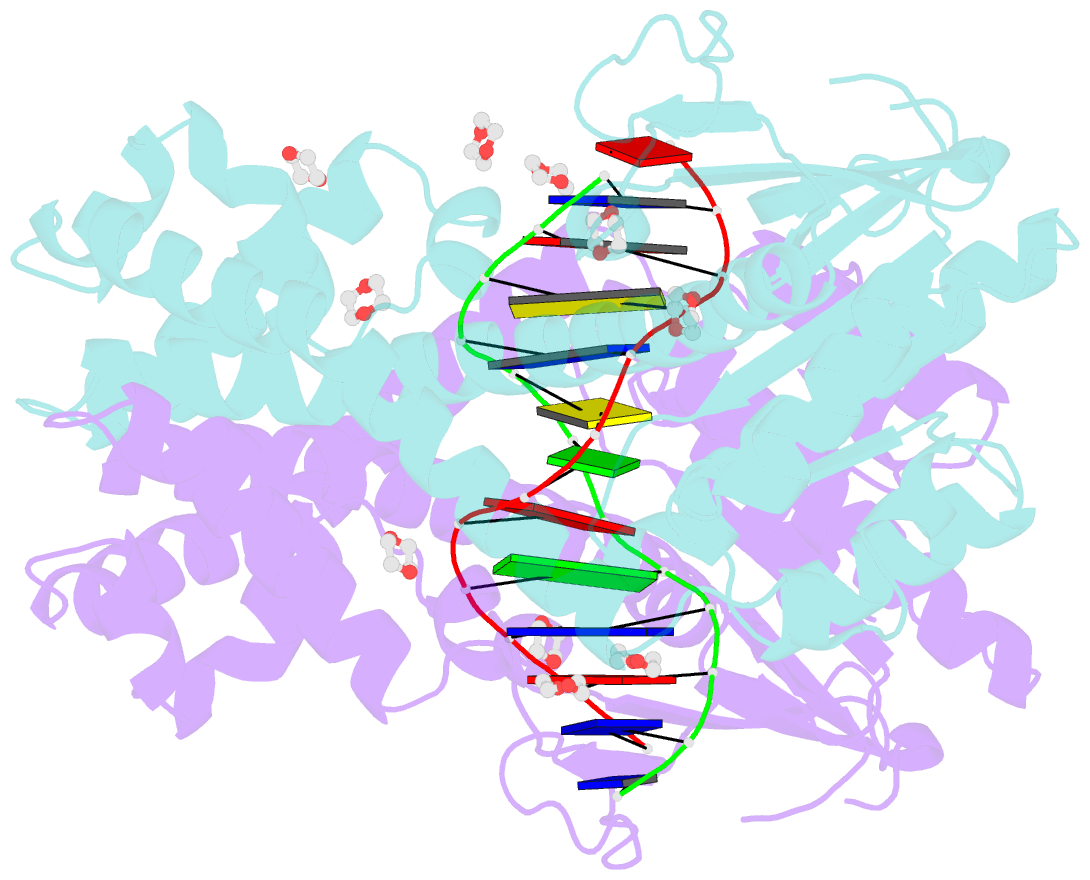
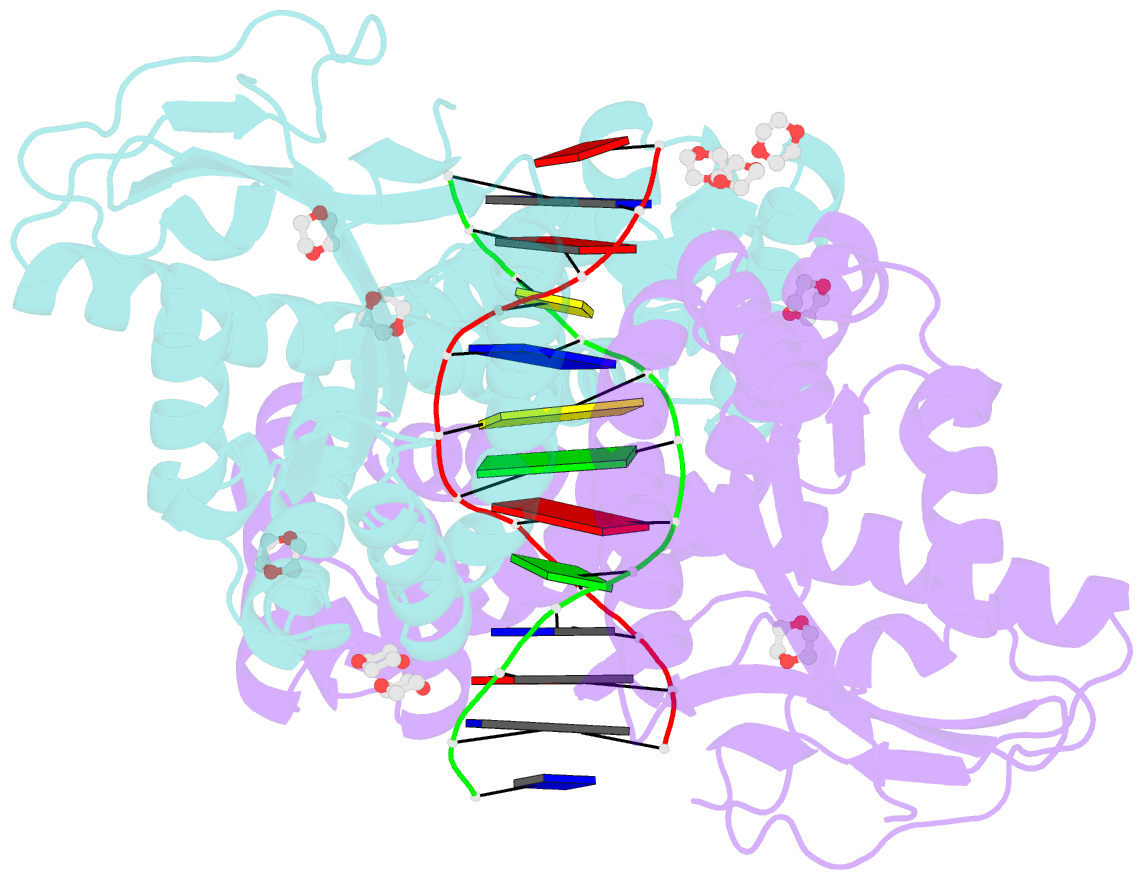
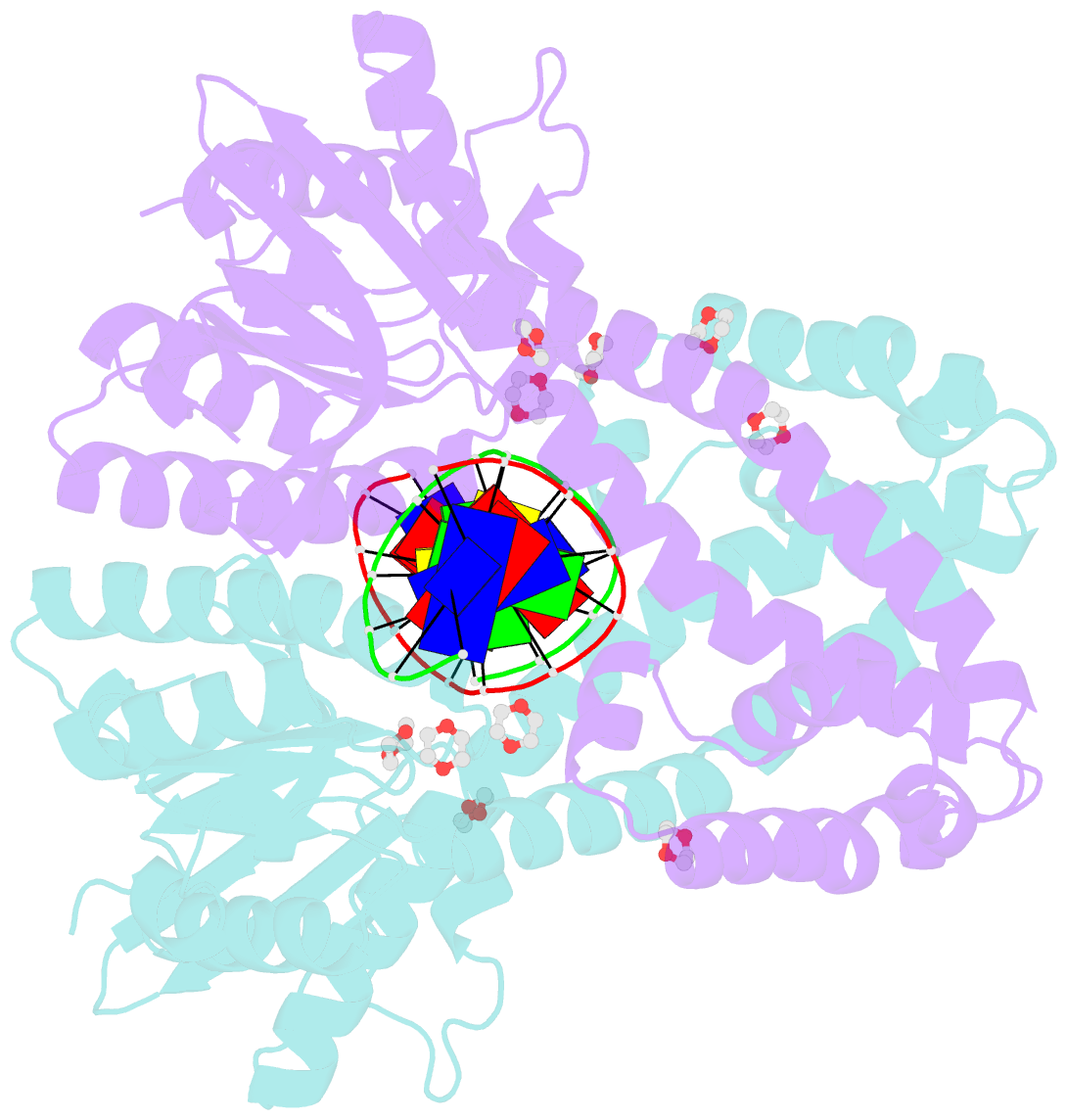
- Restriction enzyme bsobi-DNA complex structure: encirclement of the DNA and histidine-catalyzed hydrolysis within a canonical restriction enzyme fold
- Reference
- van der Woerd MJ, Pelletier JJ, Xu S, Friedman AM (2001): "Restriction enzyme BsoBI-DNA complex: a tunnel for recognition of degenerate DNA sequences and potential histidine catalysis." Structure, 9, 133-144. doi: 10.1016/S0969-2126(01)00564-0.
- Abstract
- Background: Restriction endonucleases form a diverse family of proteins with substantial variation in sequence, structure, and interaction with recognition site DNA. BsoBI is a thermophilic restriction endonuclease that exhibits both base-specific and degenerate recognition within the sequence CPyCGPuG.
Results: The structure of BsoBI complexed to cognate DNA has been determined to 1.7 A resolution, revealing several unprecedented features. Each BsoBI monomer is formed by inserting a helical domain into an expanded EcoRI-type catalytic domain. DNA is completely encircled by a BsoBI dimer. Recognition sequence DNA lies within a 20 A long tunnel of protein that excludes bulk solvent. Interactions with the specific bases are made in both grooves through direct and water-mediated hydrogen bonding. Interaction with the degenerate position is mediated by a purine-specific hydrogen bond to N7, ensuring specificity, and water-mediated H bonding to the purine N6/O6 and pyrimidine N4/O4, allowing degeneracy. In addition to the conserved active site residues of the DX(n)(E/D)ZK restriction enzyme motif, His253 is positioned to act as a general base.
Conclusions: A catalytic mechanism employing His253 and two metal ions is proposed. If confirmed, this would be the first example of histidine-mediated catalysis in a restriction endonuclease. The structure also provides two novel examples of the role of water in protein-DNA interaction. Degenerate recognition may be mediated by employing water as a hydrogen bond donor or acceptor. The structure of DNA in the tunnel may also be influenced by the absence of bulk solvent.