Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 1ddl; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- virus-RNA
- Method
- X-ray (2.7 Å)
- Summary
- Desmodium yellow mottle tymovirus
- Reference
- Larson SB, Day J, Canady MA, Greenwood A, McPherson A (2000): "Refined structure of desmodium yellow mottle tymovirus at 2.7 A resolution." J.Mol.Biol., 301, 625-642. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.2000.3983.
- Abstract
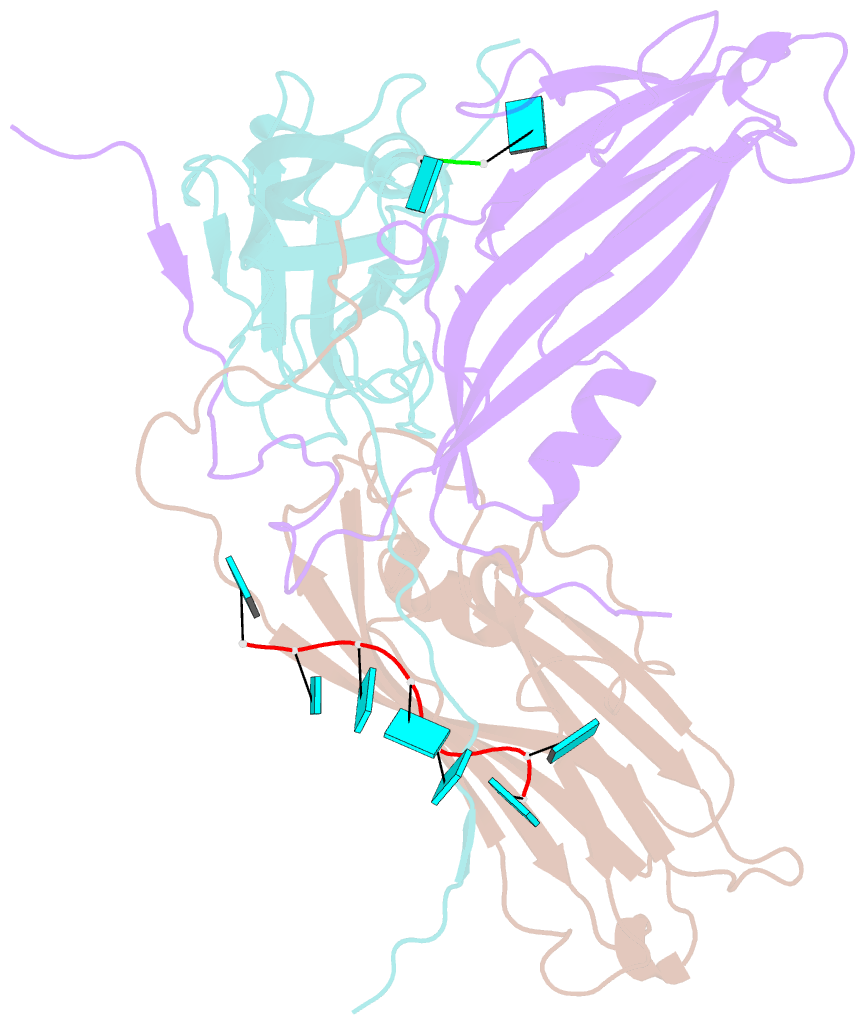
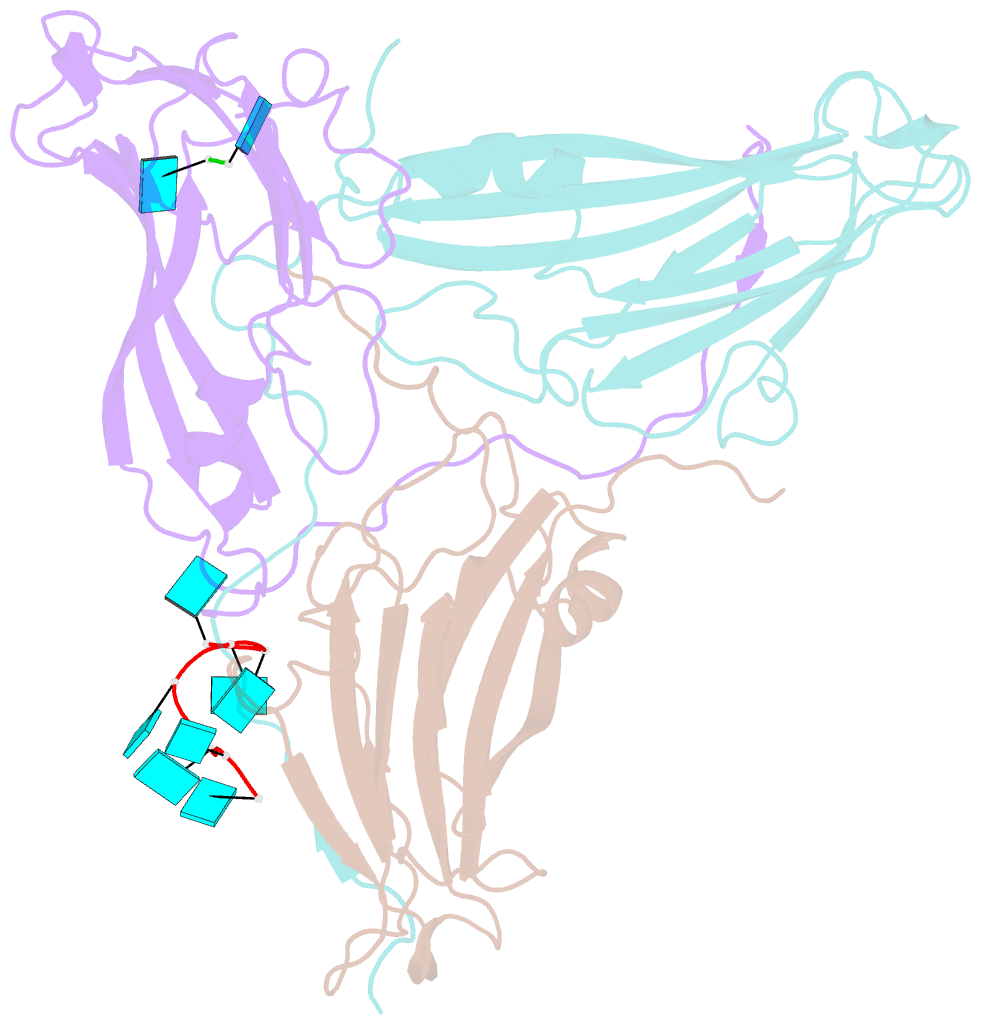
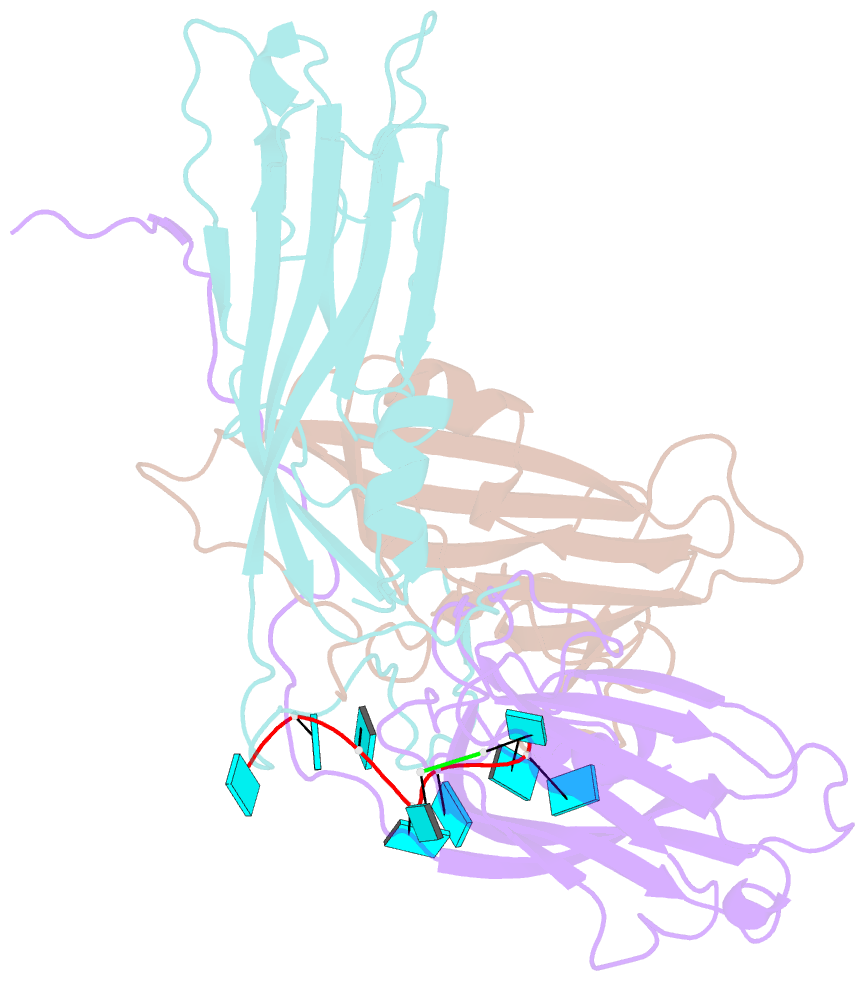
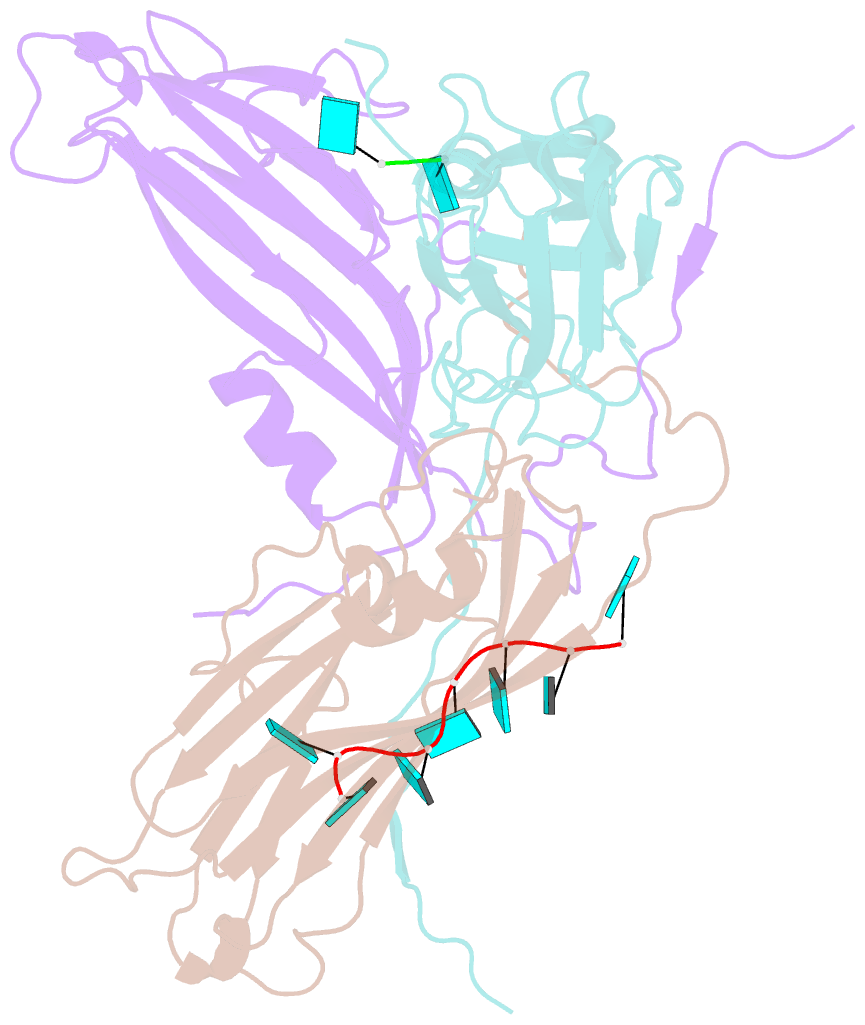
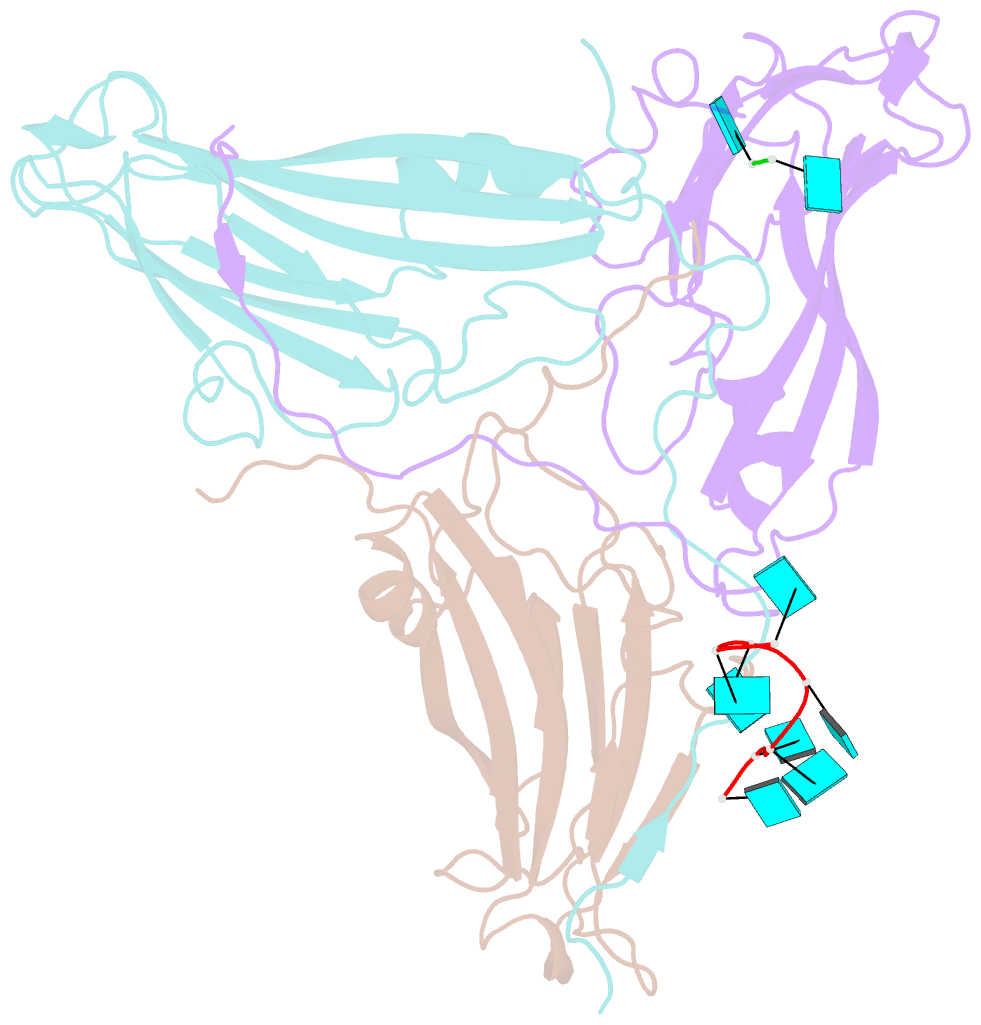
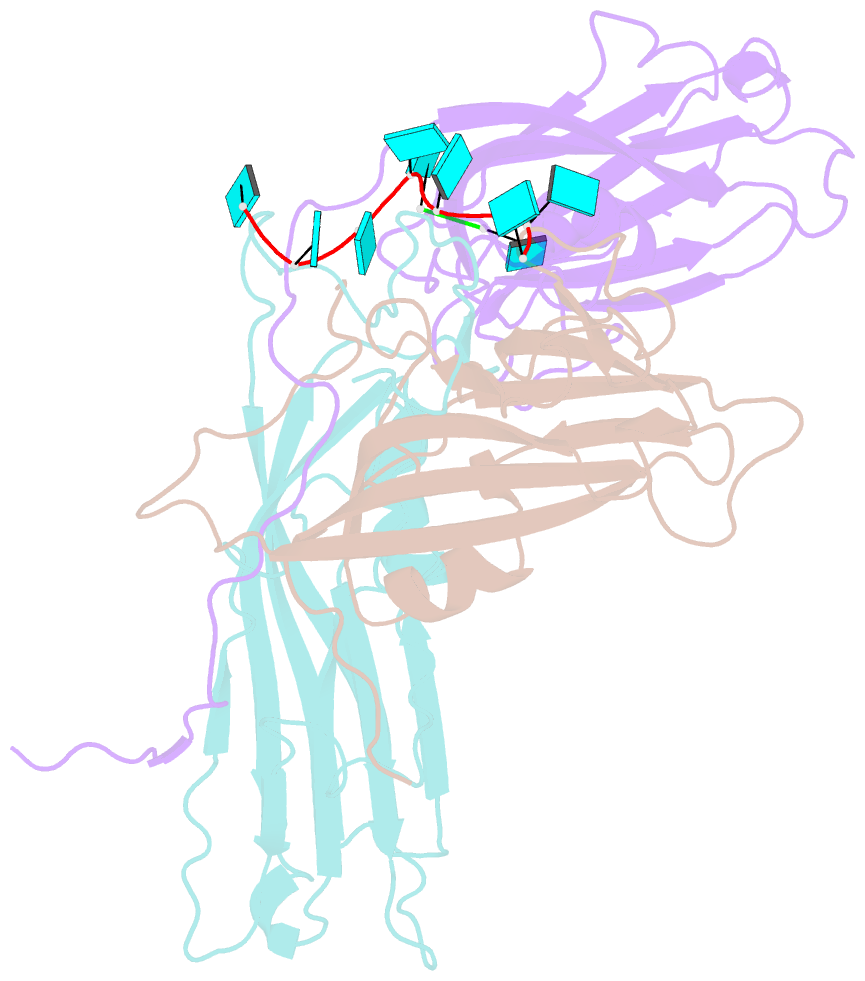
- Desmodium yellow mottle virus is a 28 nm diameter, T=3 icosahedral plant virus of the tymovirus group. Its structure has been solved to a resolution of 2.7 A using X-ray diffraction analysis based on molecular replacement and phase extension methods. The final R value was 0.151 (R(free)=0.159) for 134,454 independent reflections. The folding of the polypeptide backbone is nearly identical with that of turnip yellow mosaic virus, as is the arrangement of subunits in the virus capsid. However, a major difference in the disposition of the amino-terminal ends of the subunits was observed. In turnip yellow mosaic virus, those from the B and C subunits comprising the hexameric capsomeres formed an annulus about the interior of the capsomere, while the corresponding N termini of the pentameric capsomere A subunits were not visible at all in electron density maps. In Desmodium yellow mottle tymovirus, amino termini from the A and B subunits combine to form the annuli, thereby resulting in a much strengthened association between the two types of capsomeres and an, apparently, more stable capsid. The first 13 residues of the C subunit were invisible in electron density maps. Two ordered fragments of single-stranded RNA, seven and two nucleotides in length, were observed. The ordered water structure of the virus particle was delineated and required 95 solvent molecules per protein subunit.