Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 1dnk; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- hydrolase-DNA
- Method
- X-ray (2.3 Å)
- Summary
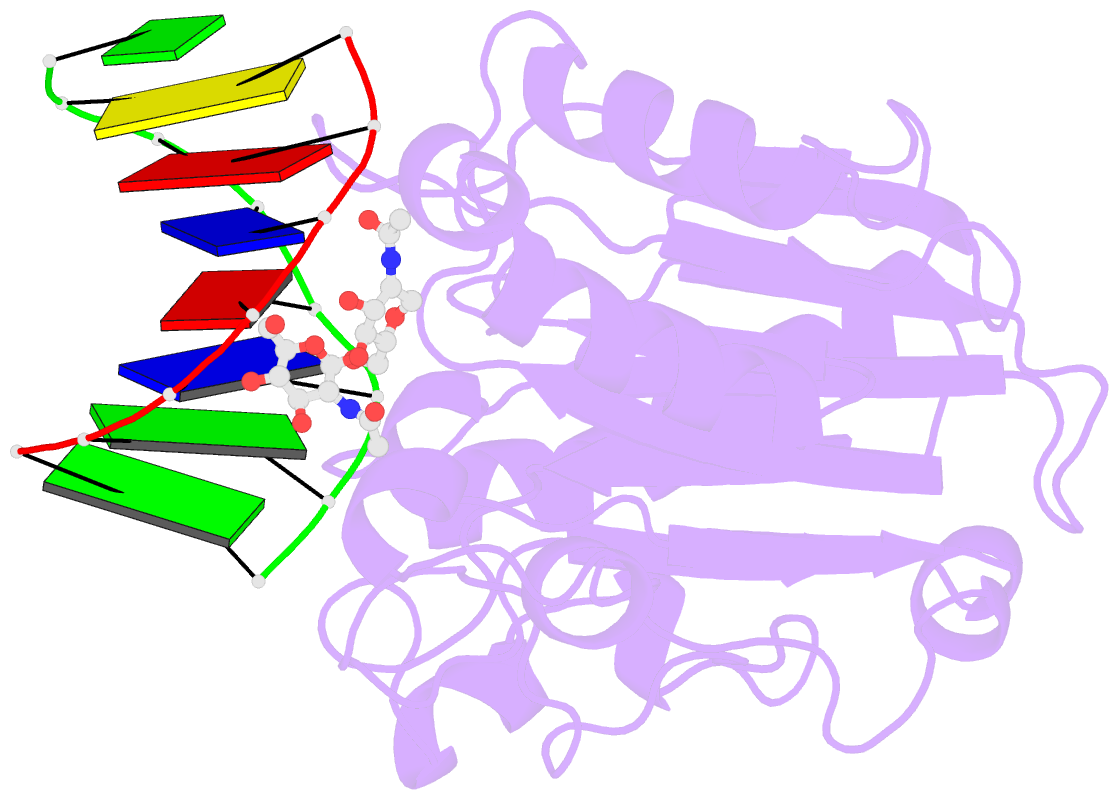
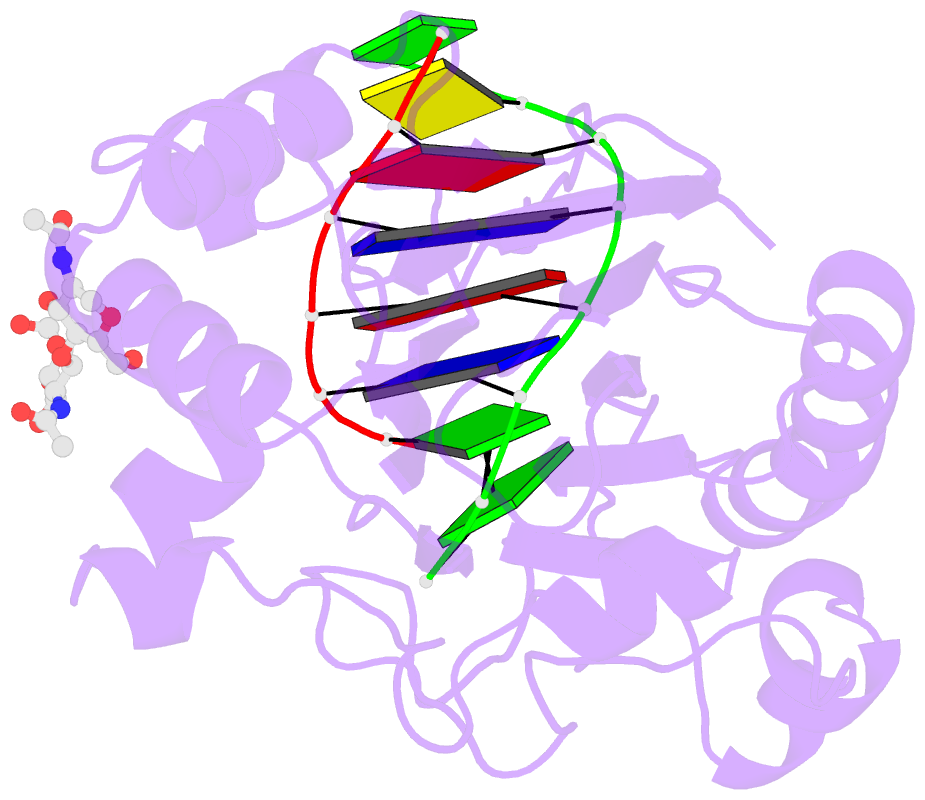
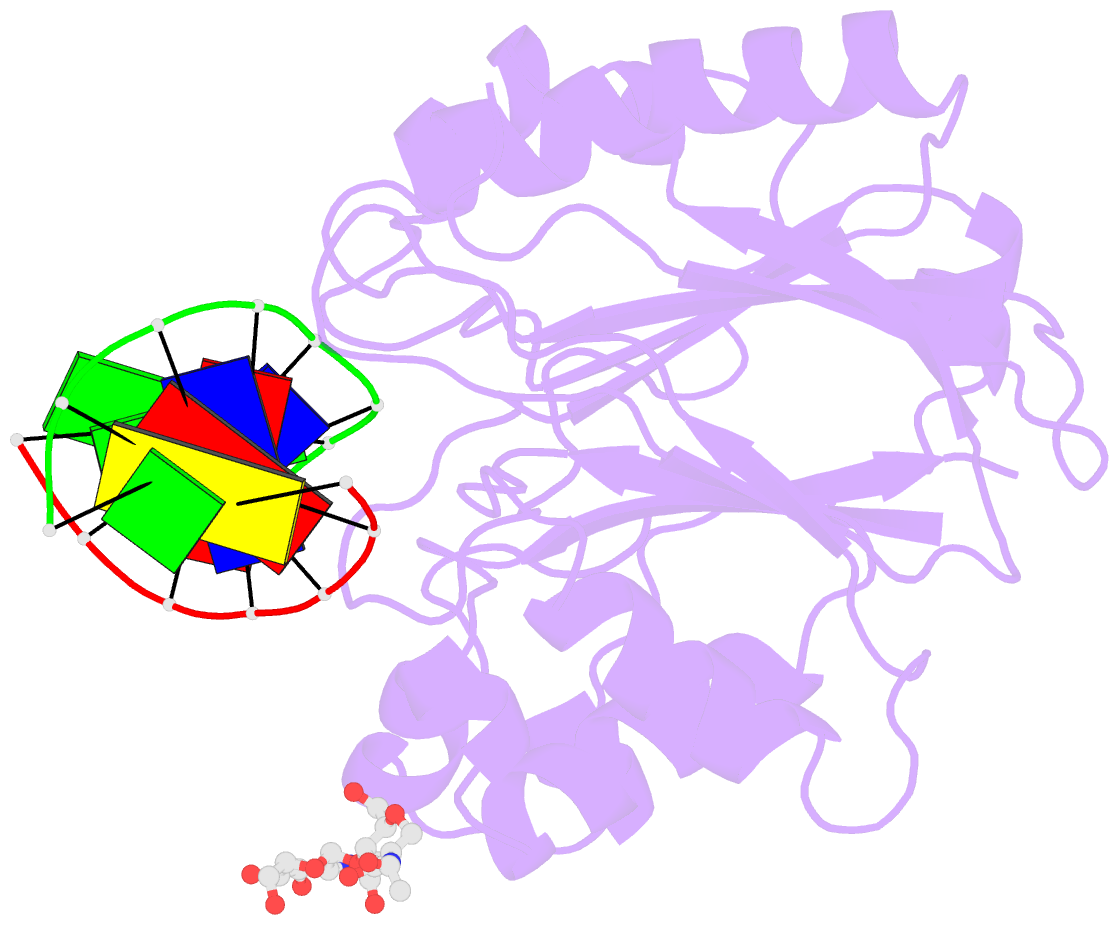
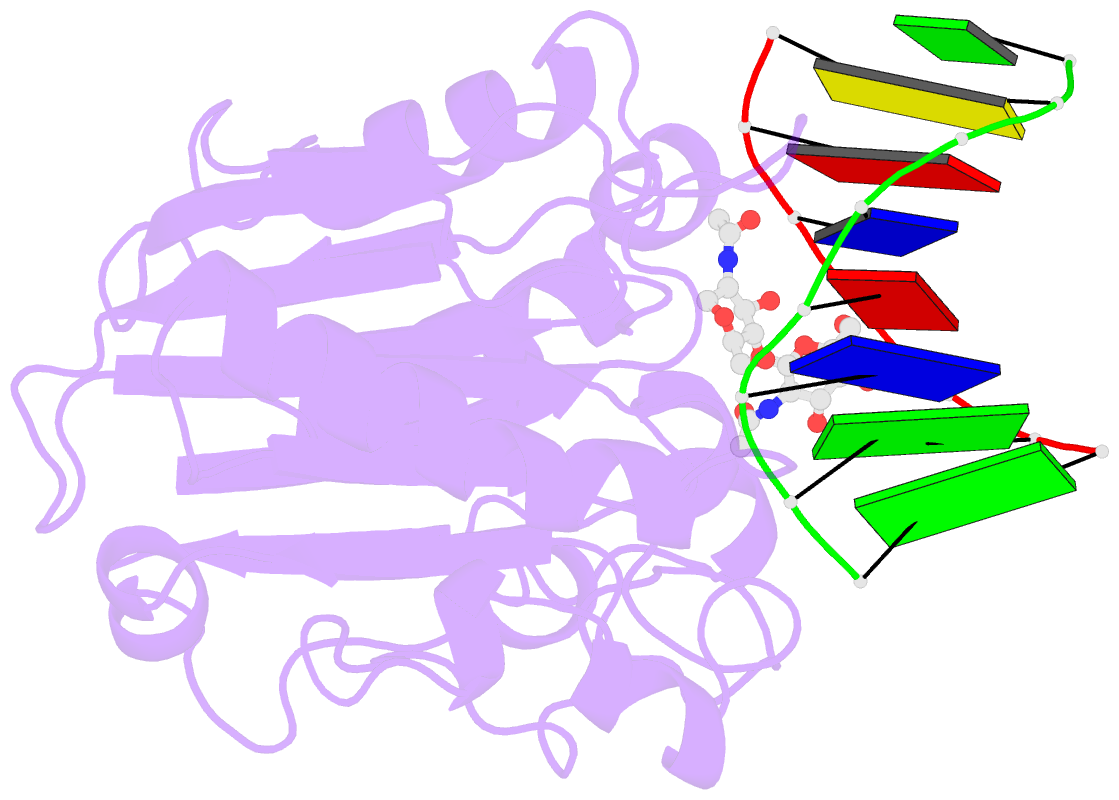
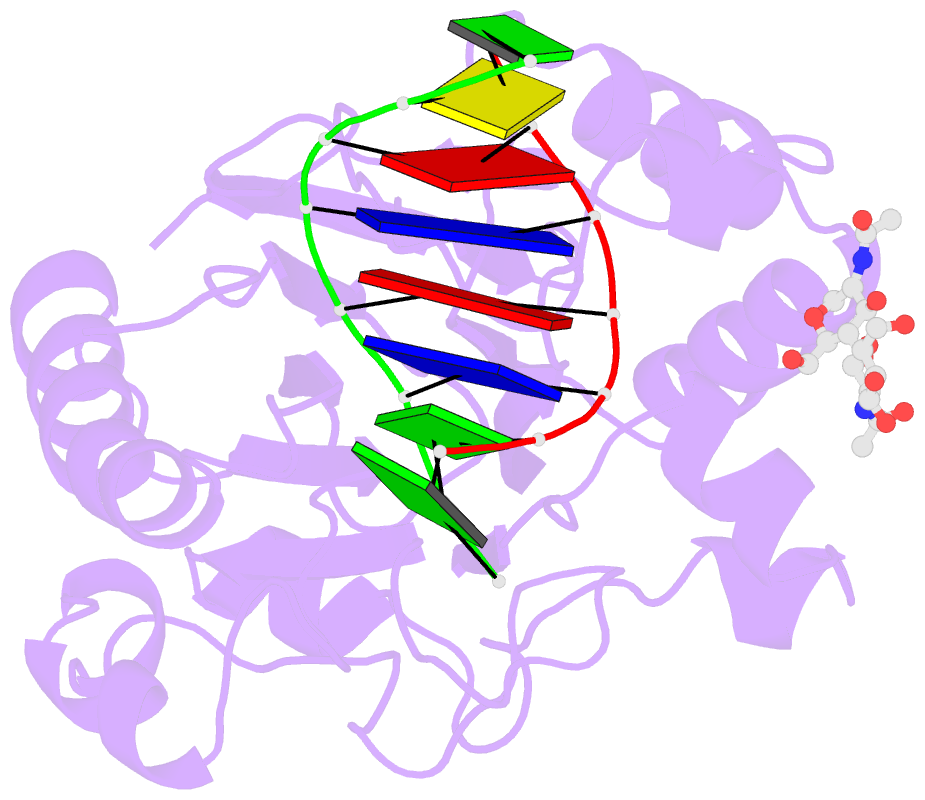
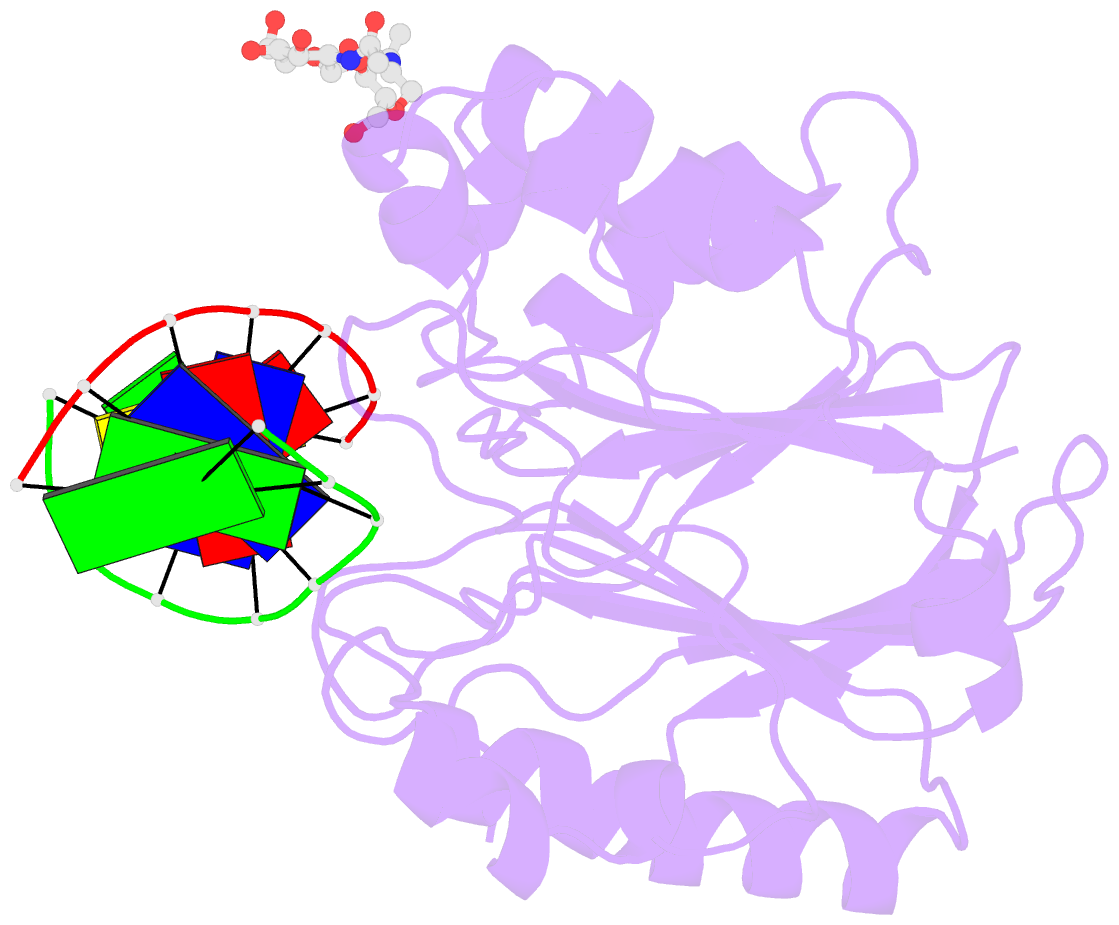
- The x-ray structure of the dnase i-d(ggtatacc)2 complex at 2.3 angstroms resolution
- Reference
- Weston SA, Lahm A, Suck D (1992): "X-ray structure of the DNase I-d(GGTATACC)2 complex at 2.3 A resolution." J.Mol.Biol., 226, 1237-1256. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)91064-V.
- Abstract
- The crystal structure of a complex between DNase I and the self-complementary octamer duplex d(GGTATACC)2 has been solved using the molecular replacement method and refined to a crystallographic R-factor of 18.8% for all data between 6.0 and 2.3 A resolution. In contrast to the structure of the DNase I-d(GCGATCGC)2 complex solved previously, the DNA remains uncleaved in the crystal. The general architecture of the two complexes is highly similar. DNase I binds in the minor groove of a right-handed DNA duplex, and to the phosphate backbones on either side over five base-pairs, resulting in a widening of the minor groove and a concurrent bend of the DNA away from the bound enzyme. There is very little change in the structure of the DNase I on binding the substrate. Many other features of the interaction are conserved in the two complexes, in particular the stacking of a deoxyribose group of the DNA onto the side-chain of a tyrosine residue (Y76), which affects the DNA conformation and the binding of an arginine side-chain in the minor groove. Although the structures of the DNA molecules appear at first sight rather similar, detailed analysis reveals some differences that may explain the relative resistance of the d(GGTATACC)2 duplex to cleavage by DNase I: whilst some backbone parameters are characteristic of a B-conformation, the spatial orientation of the base-pairs in the d(GGTATACC)2 duplex is close to that generally observed in A-DNA. These results further support the hypothesis that the minor-groove width and depth and the intrinsic flexibility of DNA are the most important parameters affecting the interaction. The disposition of residues around the scissile phosphate group suggests that two histidine residues, H134 and H252, are involved in catalysis.