Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 1esg; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- hydrolase-DNA
- Method
- X-ray (1.9 Å)
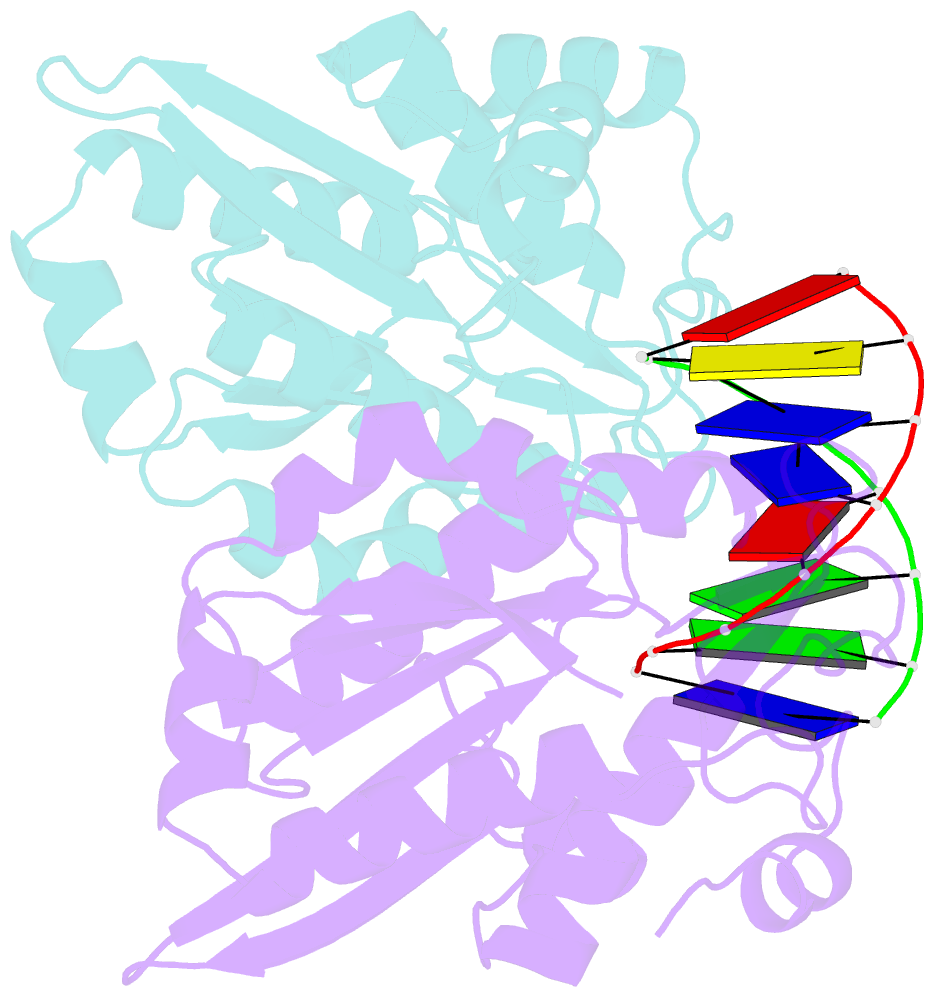
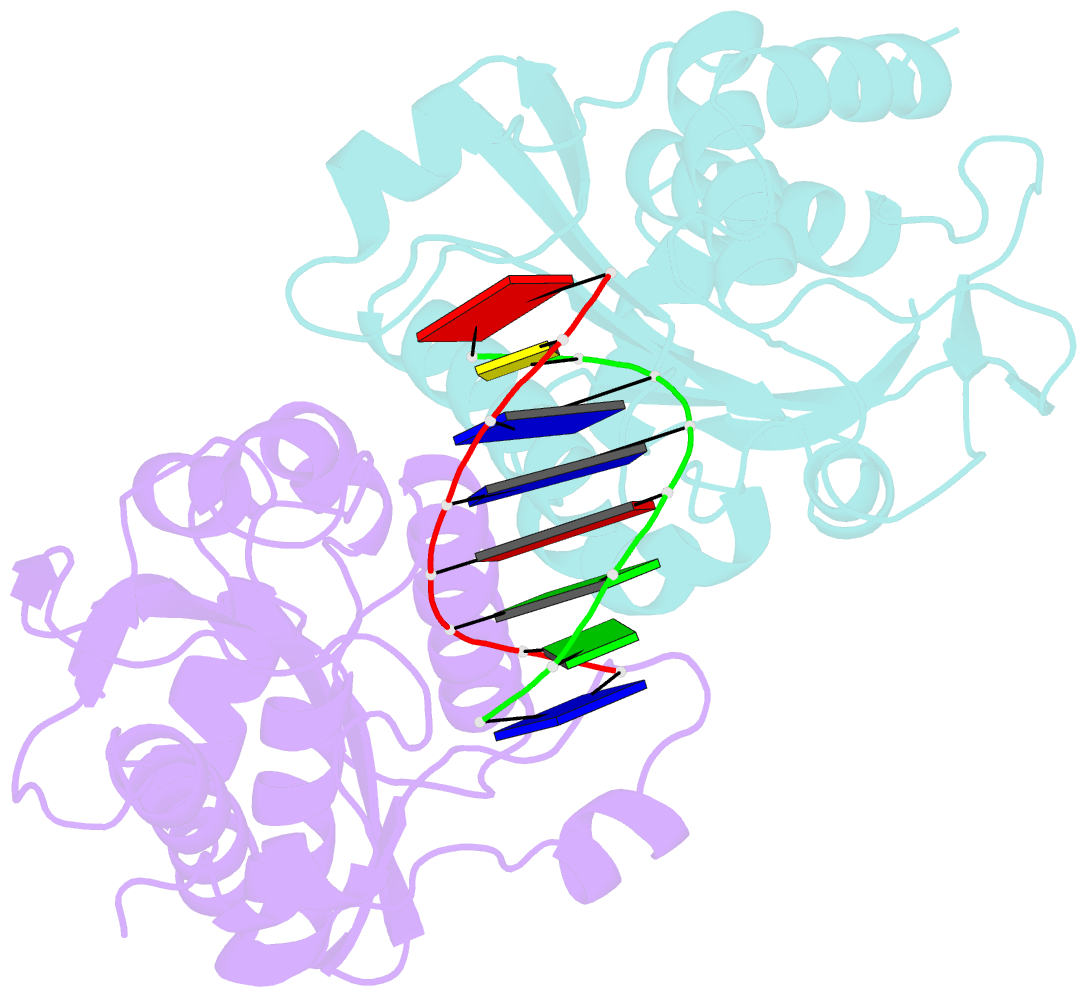
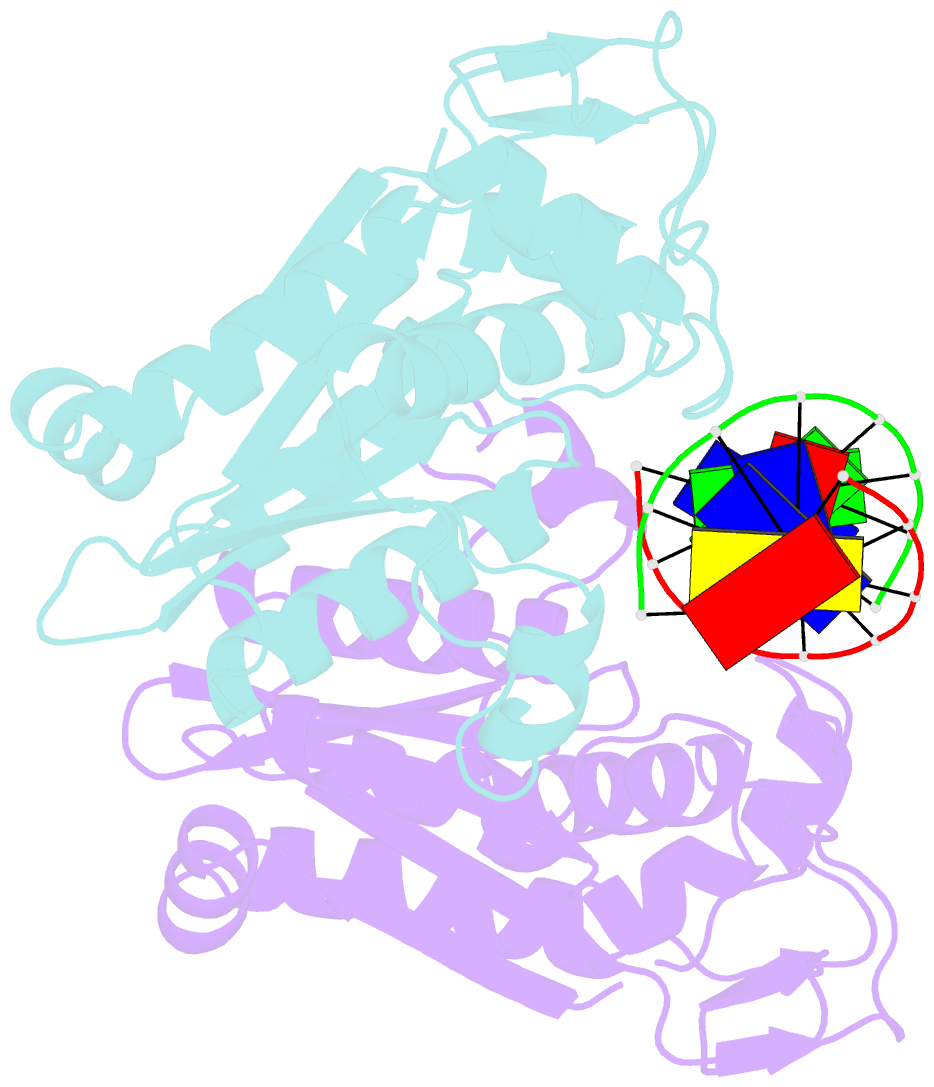
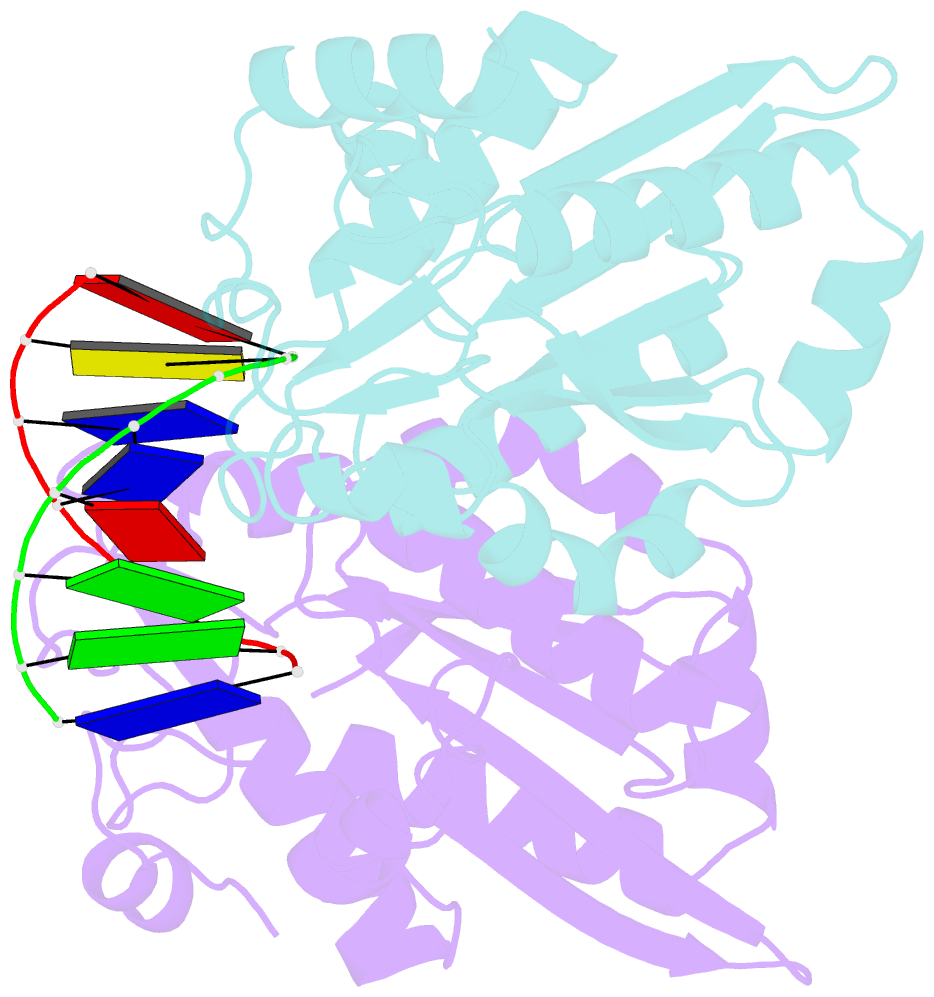
- Summary
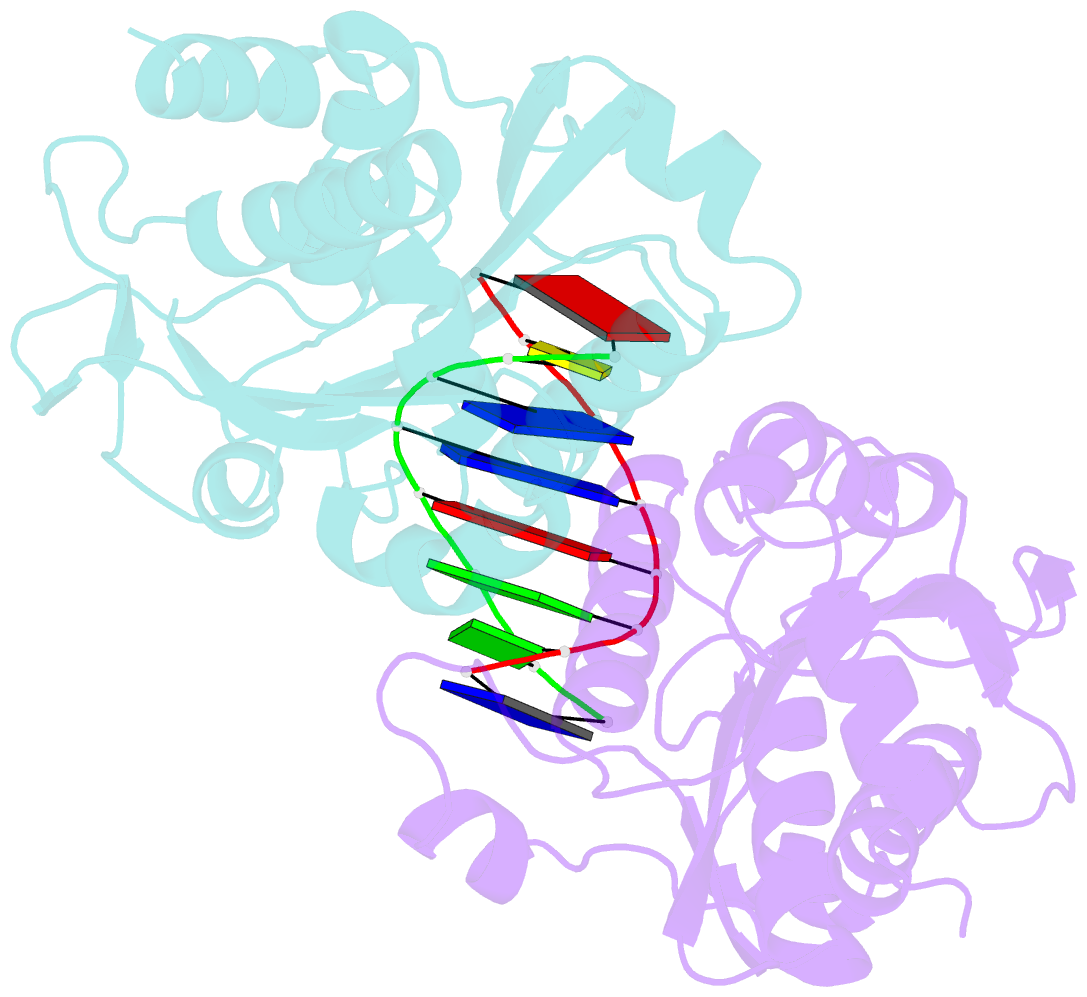
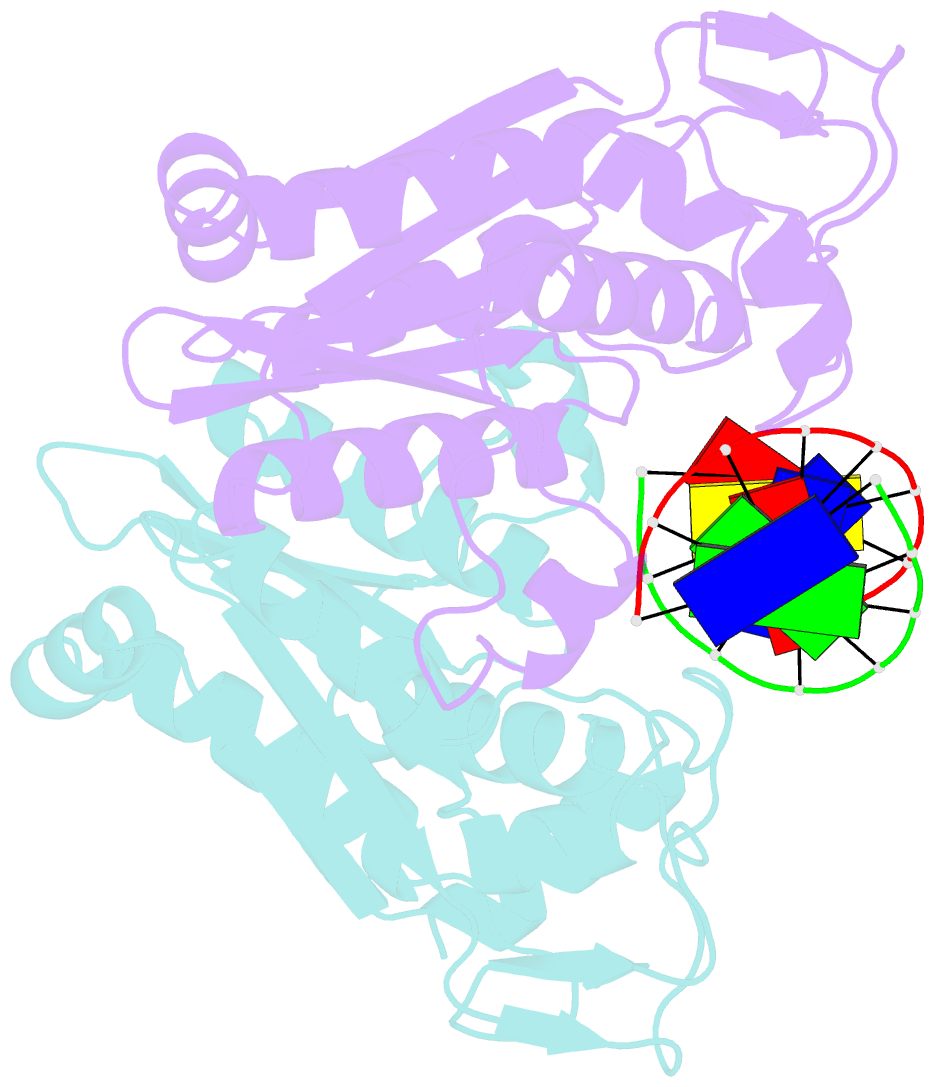
- Restriction endonuclease bamhi bound to a non-specific DNA.
- Reference
- Viadiu H, Aggarwal AK (2000): "Structure of BamHI bound to nonspecific DNA: a model for DNA sliding." Mol.Cell, 5, 889-895. doi: 10.1016/S1097-2765(00)80329-9.
- Abstract
- The central problem faced by DNA binding proteins is how to select the correct DNA sequence from the sea of nonspecific sequences in a cell. The problem is particularly acute for bacterial restriction enzymes because cleavage at an incorrect DNA site could be lethal. To understand the basis of this selectivity, we report here the crystal structure of endonuclease BamHI bound to noncognate DNA. We show that, despite only a single base pair change in the recognition sequence, the enzyme adopts an open configuration that is on the pathway between free and specifically bound forms of the enzyme. Surprisingly, the DNA drops out of the binding cleft with a total loss of base-specific and backbone contacts. Taken together, the structure provides a remarkable snapshot of an enzyme poised for linear diffusion (rather than cleavage) along the DNA.