Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 1ewq; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- replication-DNA
- Method
- X-ray (2.2 Å)
- Summary
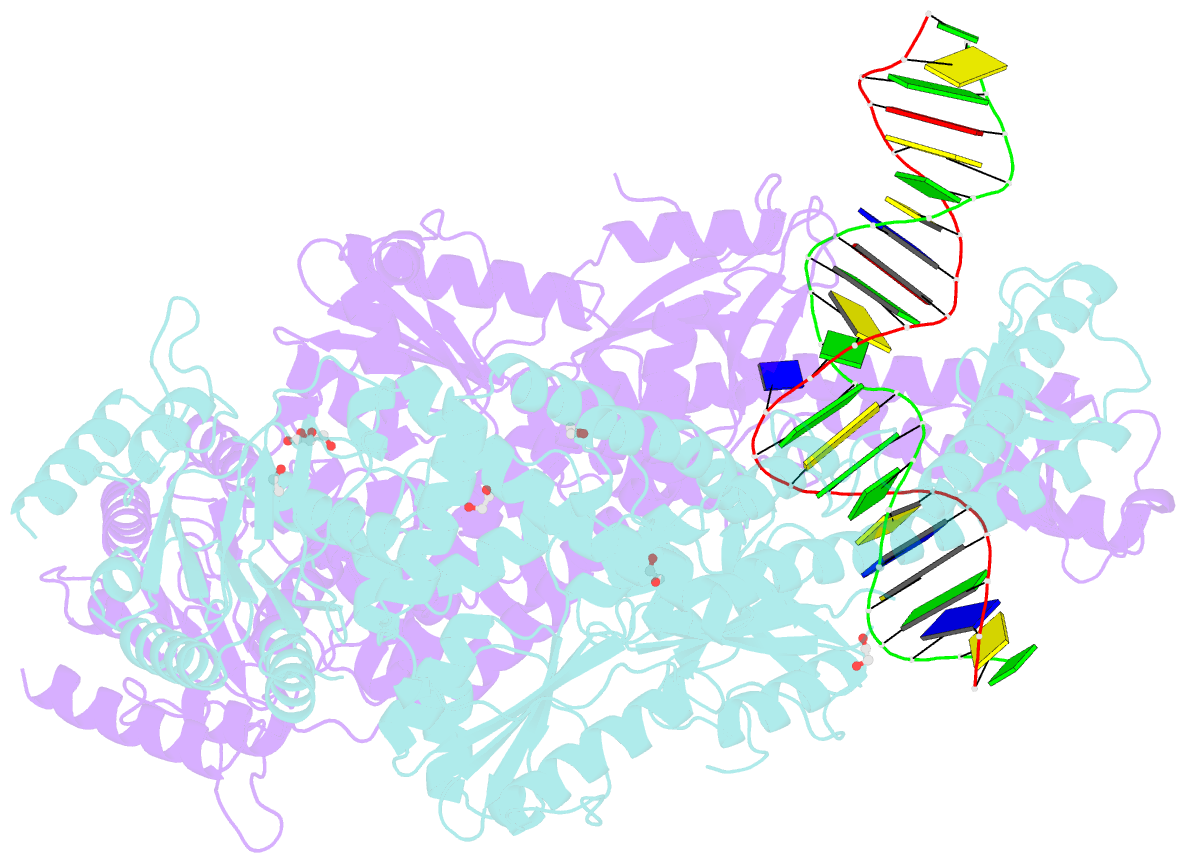
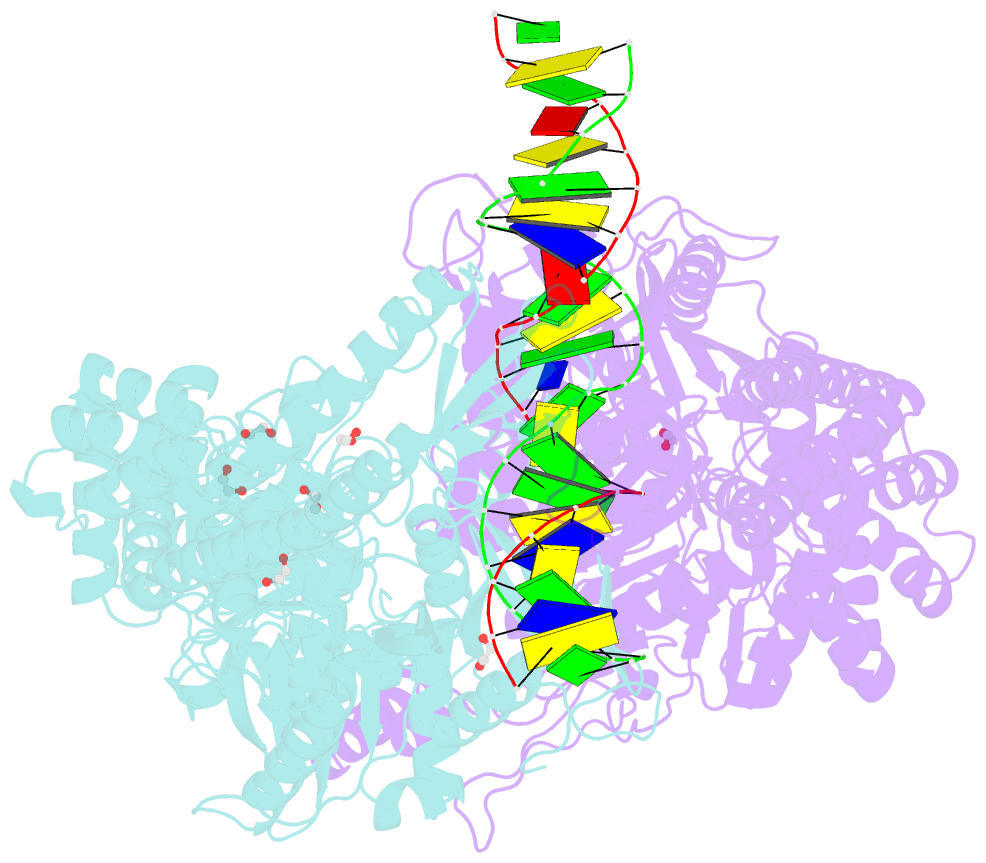
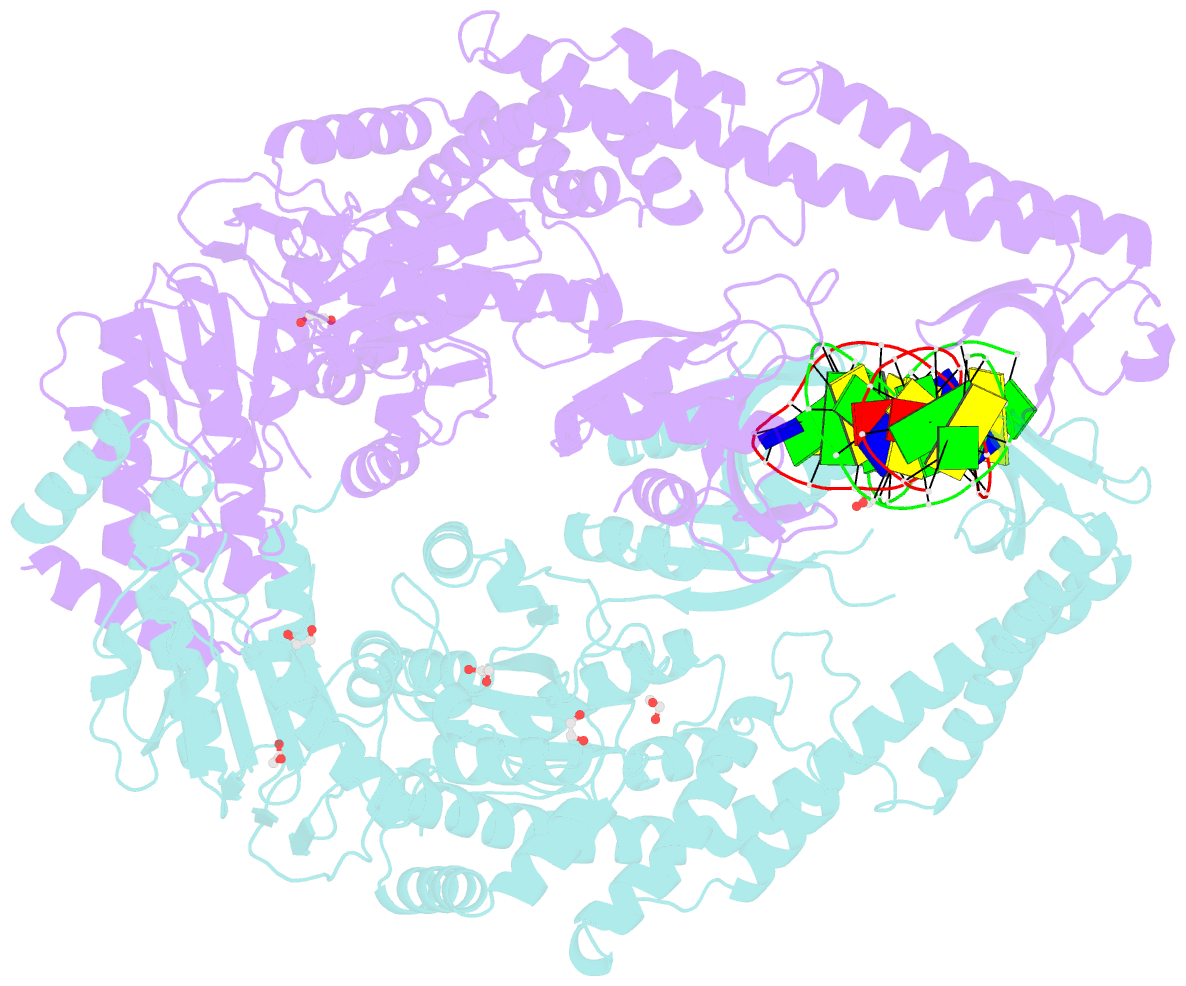
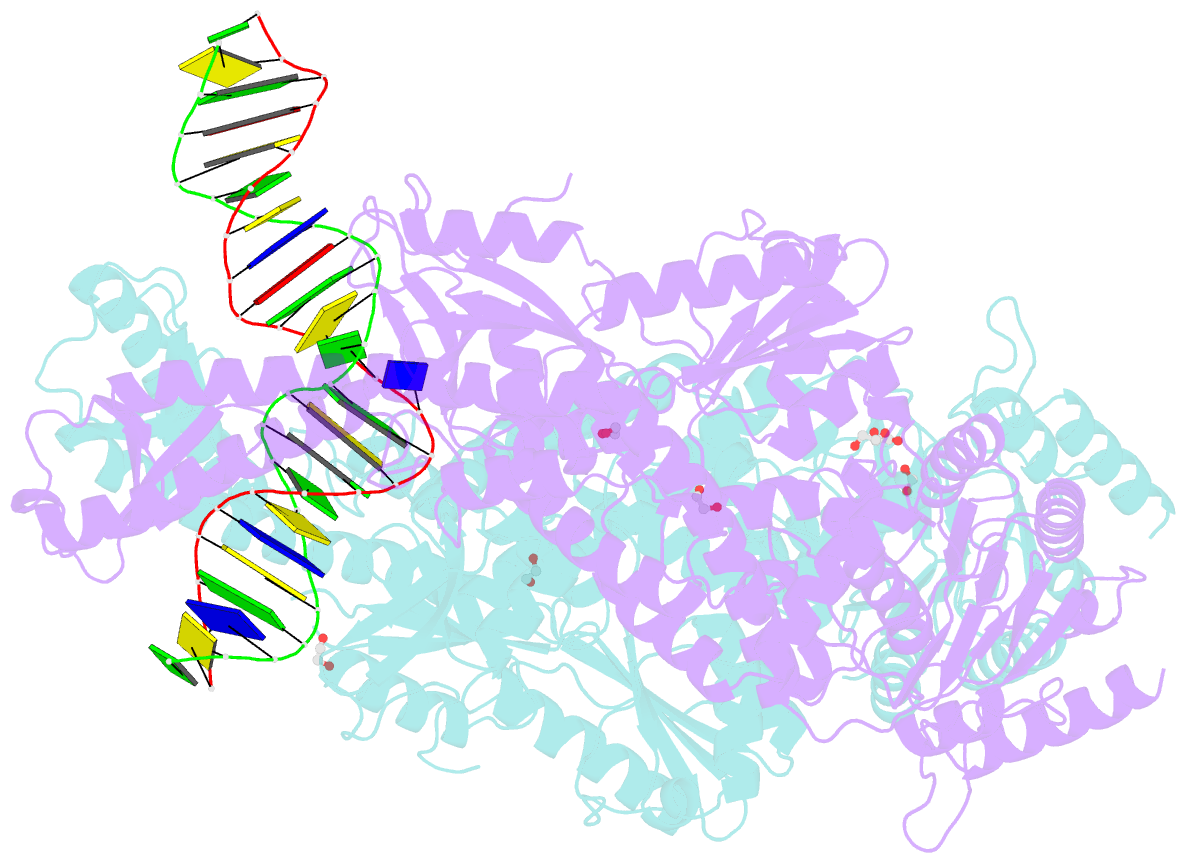
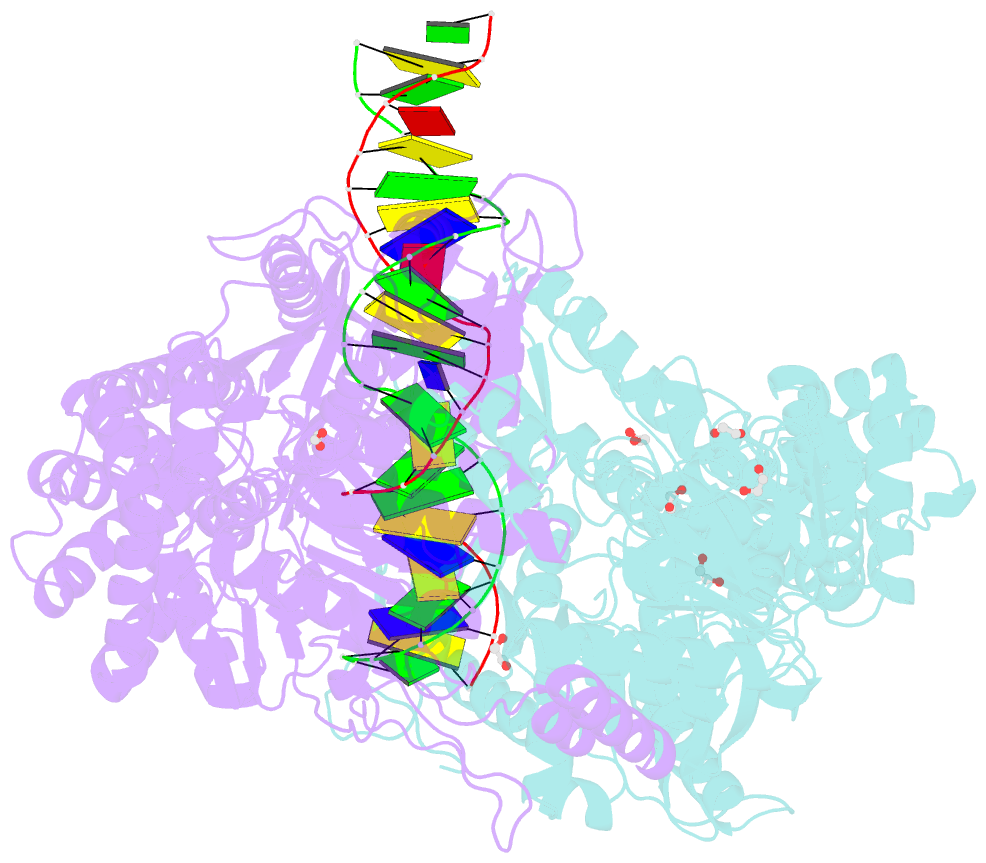
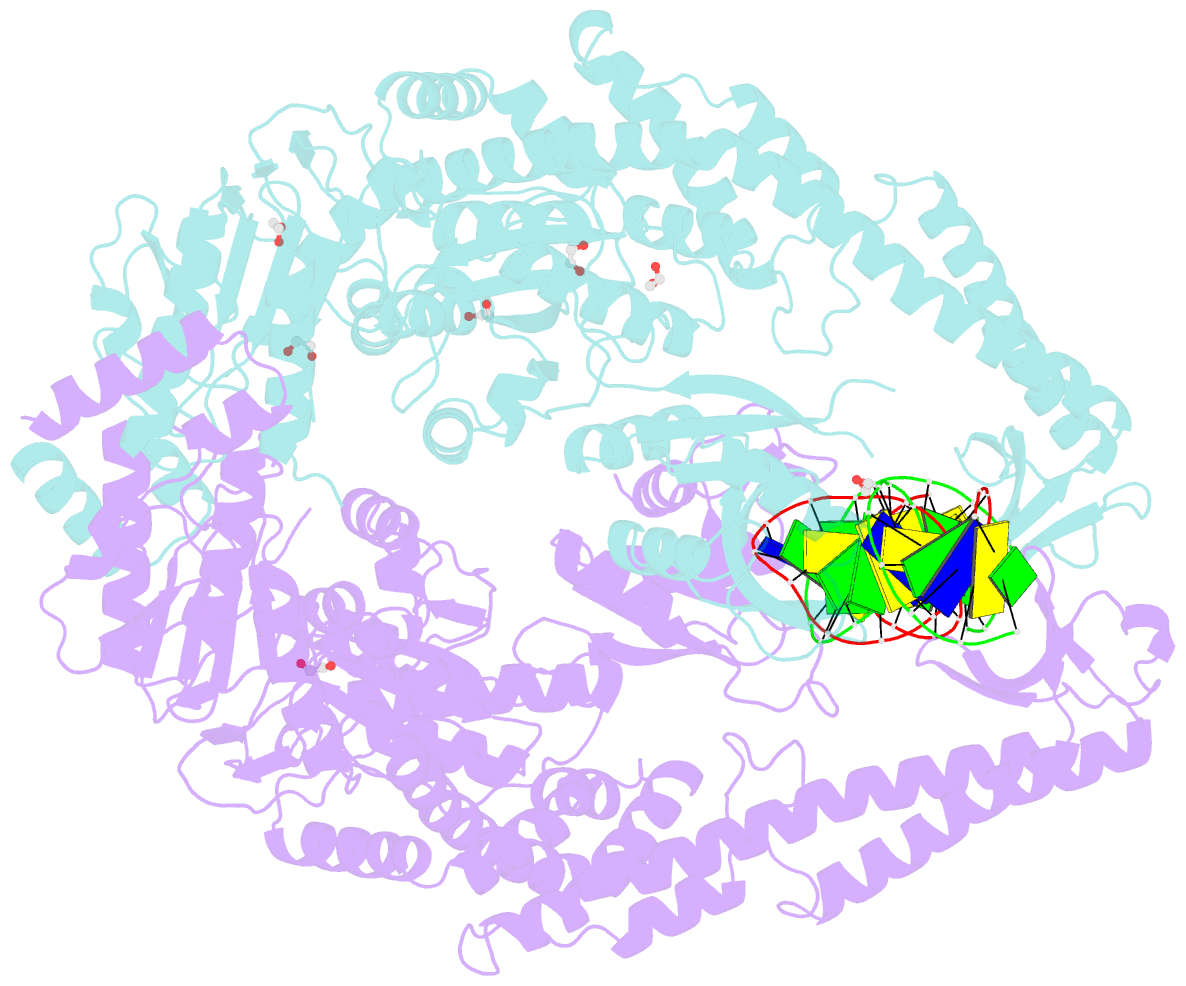
- Crystal structure taq muts complexed with a heteroduplex DNA at 2.2 Å resolution
- Reference
- Obmolova G, Ban C, Hsieh P, Yang W (2000): "Crystal structures of mismatch repair protein MutS and its complex with a substrate DNA." Nature, 407, 703-710. doi: 10.1038/35037509.
- Abstract
- DNA mismatch repair is critical for increasing replication fidelity in organisms ranging from bacteria to humans. MutS protein, a member of the ABC ATPase superfamily, recognizes mispaired and unpaired bases in duplex DNA and initiates mismatch repair. Mutations in human MutS genes cause a predisposition to hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer as well as sporadic tumours. Here we report the crystal structures of a MutS protein and a complex of MutS with a heteroduplex DNA containing an unpaired base. The structures reveal the general architecture of members of the MutS family, an induced-fit mechanism of recognition between four domains of a MutS dimer and a heteroduplex kinked at the mismatch, a composite ATPase active site composed of residues from both MutS subunits, and a transmitter region connecting the mismatch-binding and ATPase domains. The crystal structures also provide a molecular framework for understanding hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer mutations and for postulating testable roles of MutS.