Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 1g59; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- ligase-RNA
- Method
- X-ray (2.4 Å)
- Summary
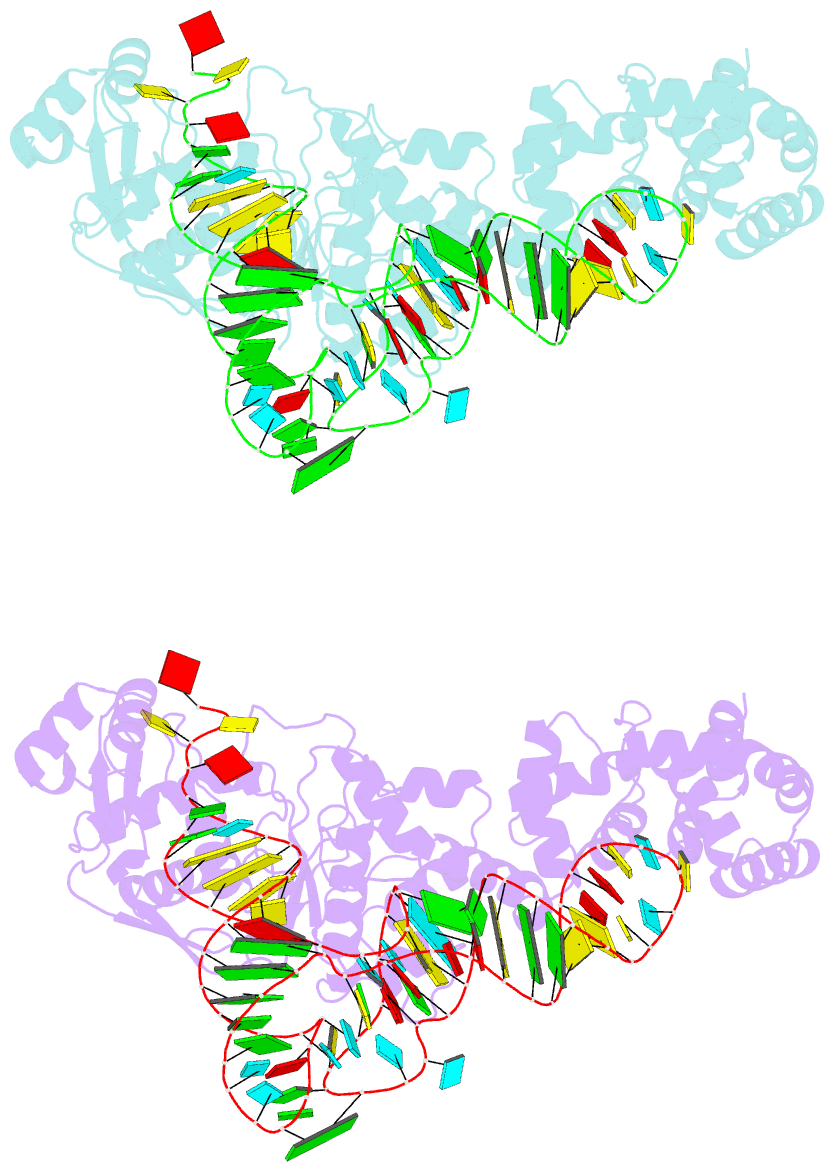
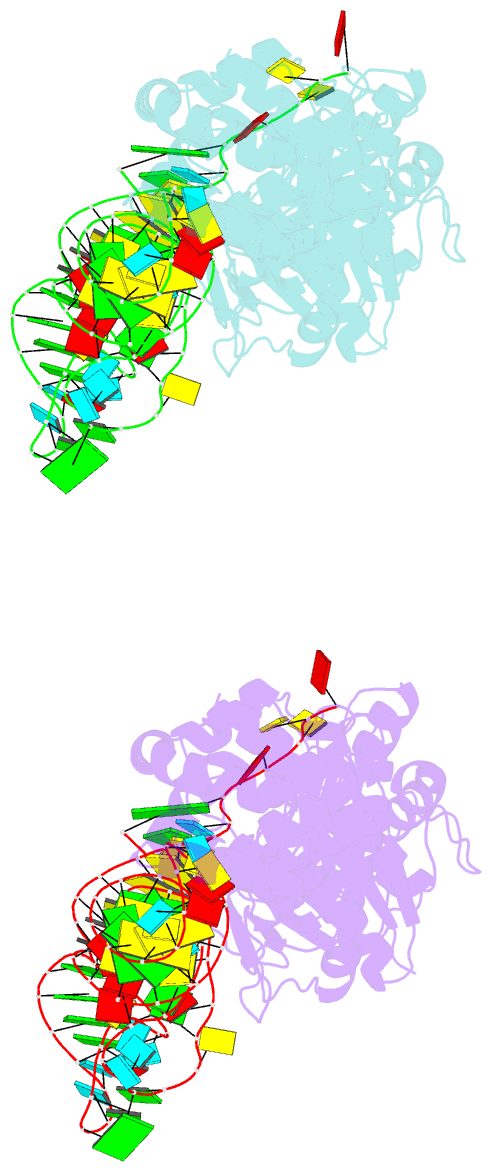
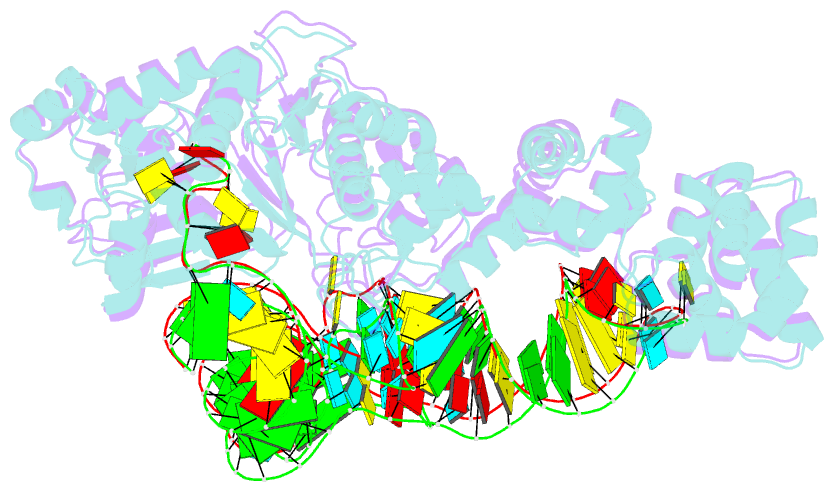
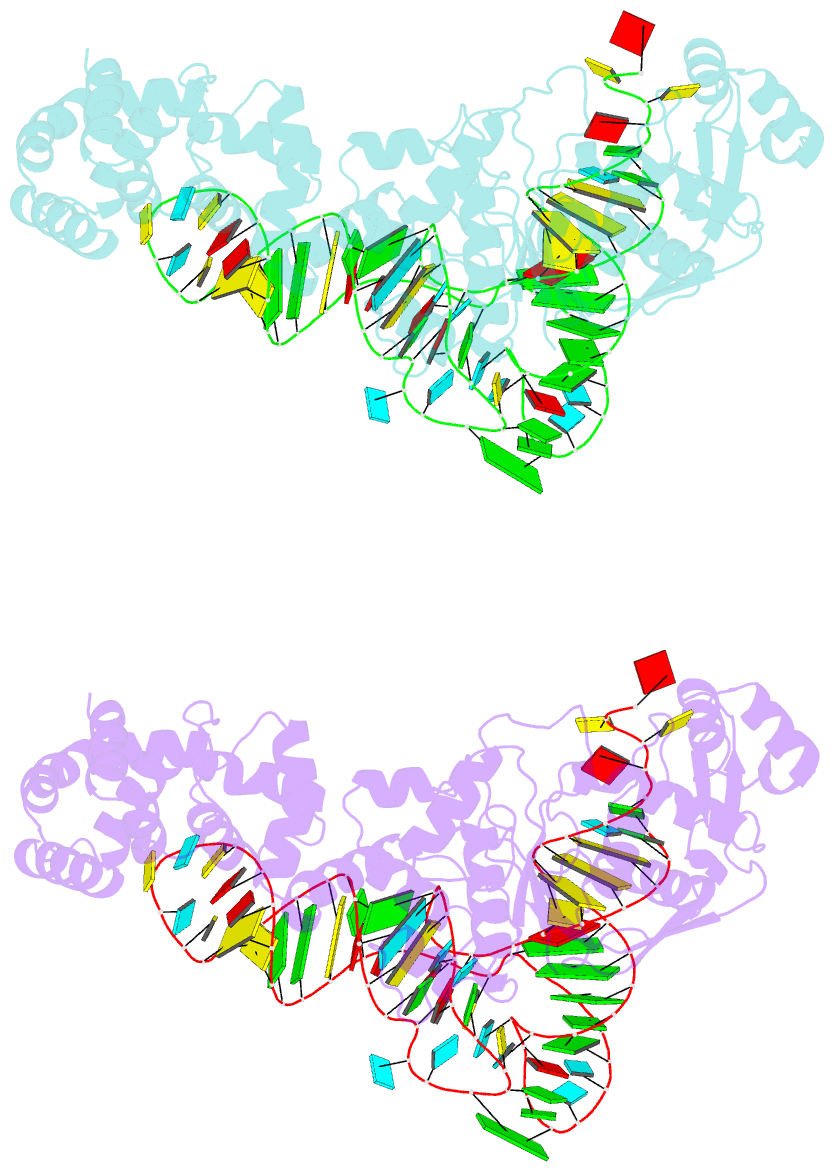
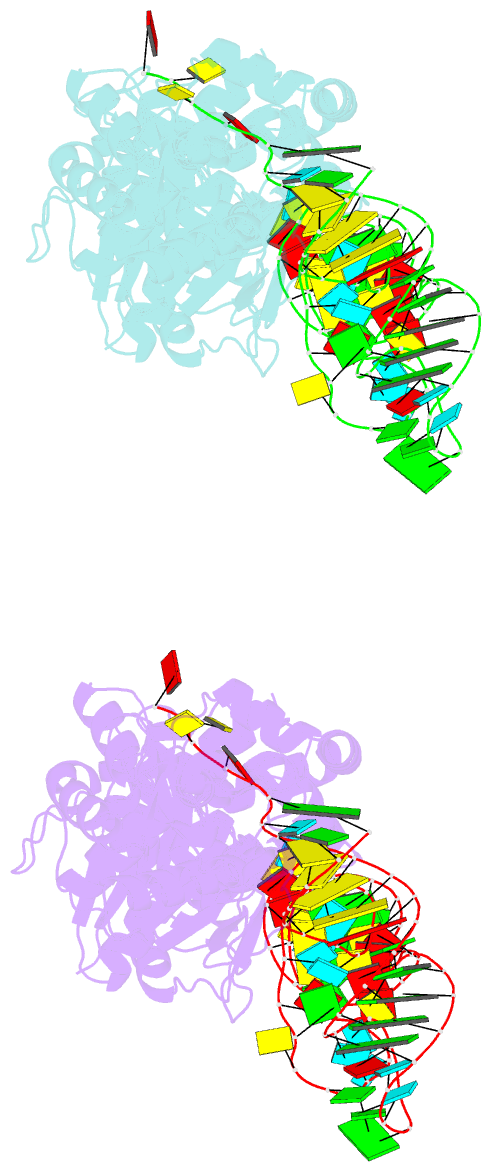
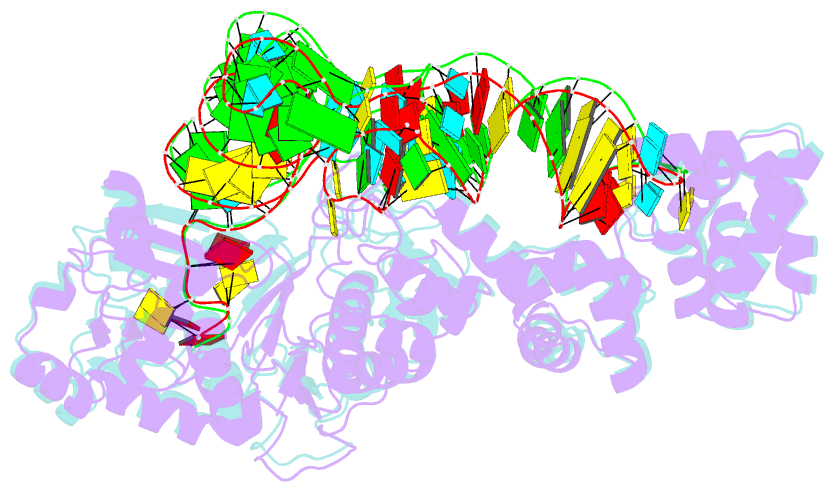
- Glutamyl-trna synthetase complexed with trna(glu).
- Reference
- Sekine S, Nureki O, Shimada A, Vassylyev DG, Yokoyama S (2001): "Structural basis for anticodon recognition by discriminating glutamyl-tRNA synthetase." Nat.Struct.Biol., 8, 203-206. doi: 10.1038/84927.
- Abstract
- Glutamyl-tRNA synthetases (GluRSs) are divided into two distinct types, with regard to the presence or absence of glutaminyl-tRNA synthetase (GlnRS) in the genetic translation systems. In the original 19-synthetase systems lacking GlnRS, the 'non-discriminating' GluRS glutamylates both tRNAGlu and tRNAGln. In contrast, in the evolved 20-synthetase systems with GlnRS, the 'discriminating' GluRS aminoacylates only tRNAGlu. Here we report the 2.4 A resolution crystal structure of a 'discriminating' GluRS.tRNAGlu complex from Thermus thermophilus. The GluRS recognizes the tRNAGlu anticodon bases via two alpha-helical domains, maintaining the base stacking. We show that the discrimination between the Glu and Gln anticodons (34YUC36 and 34YUG36, respectively) is achieved by a single arginine residue (Arg 358). The mutation of Arg 358 to Gln resulted in a GluRS that does not discriminate between the Glu and Gln anticodons. This change mimics the reverse course of GluRS evolution from anticodon 'non-dicsriminating' to 'discriminating'.