Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 1gxp; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- transcriptional activator
- Method
- X-ray (2.5 Å)
- Summary
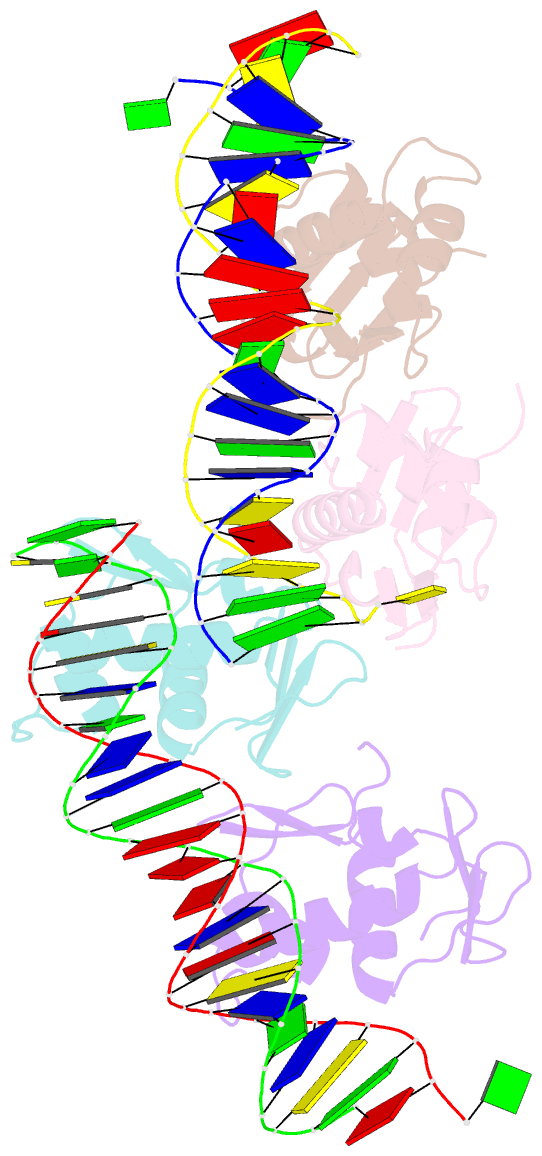
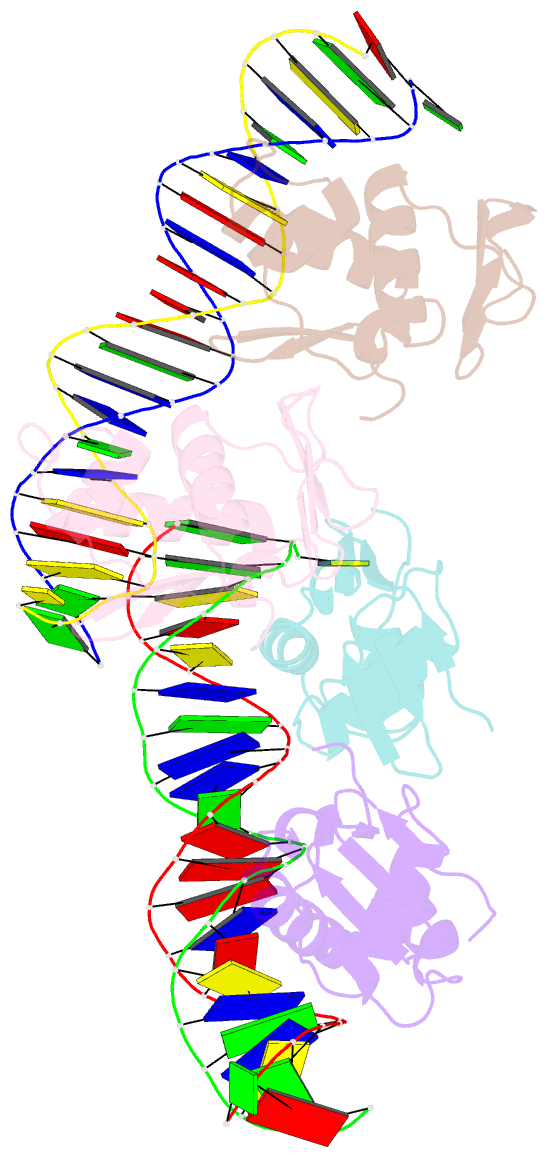
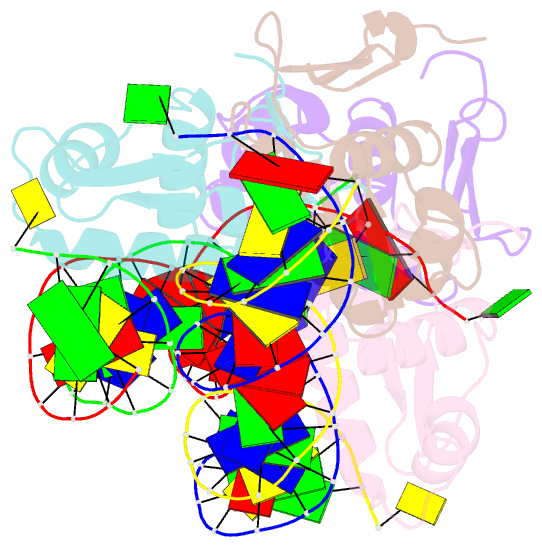
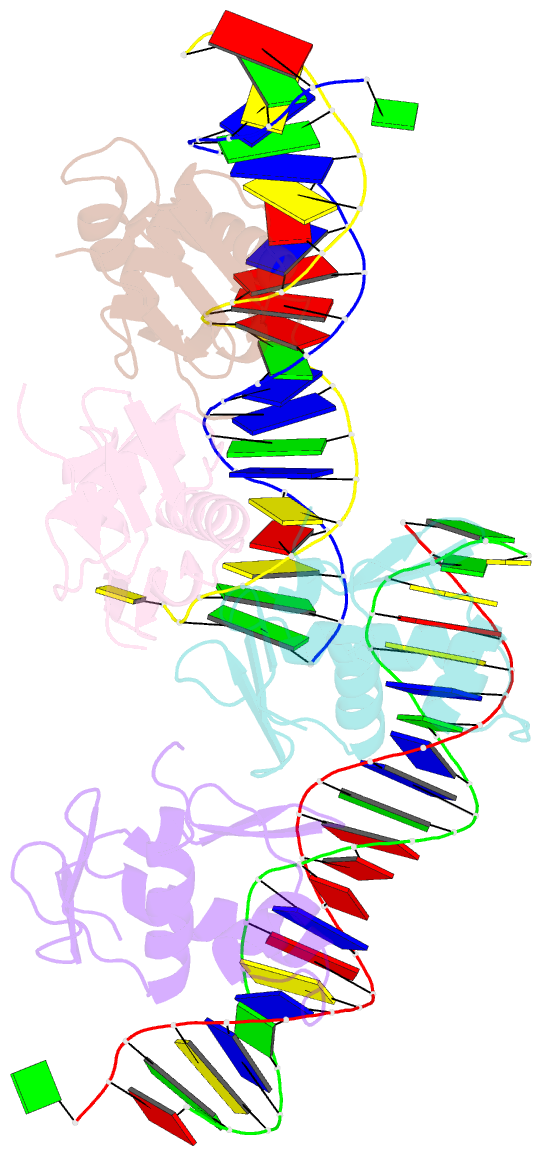
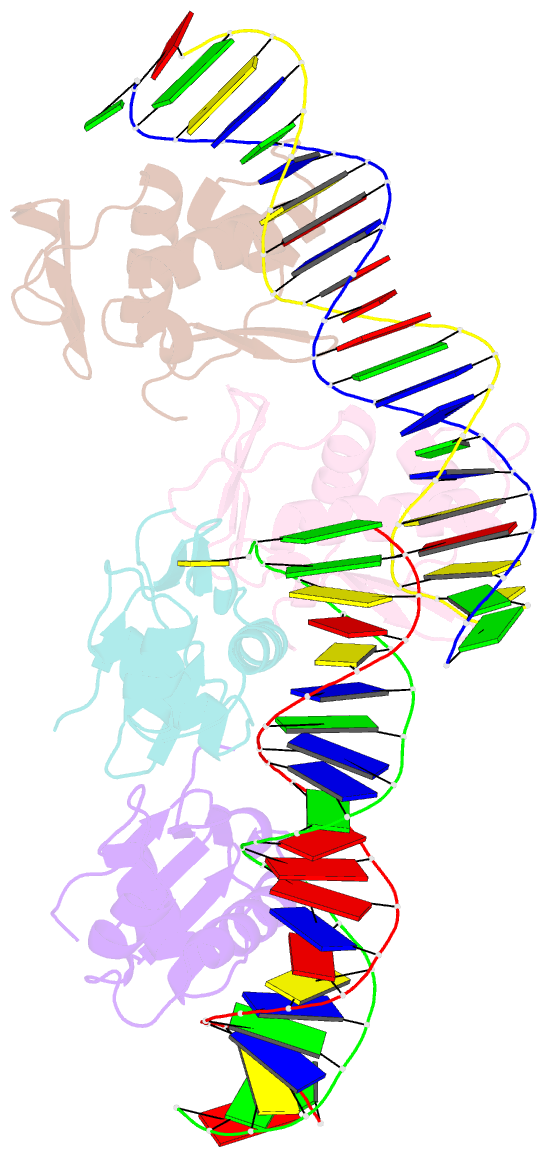
- Phob effector domain in complex with pho box DNA.
- Reference
- Blanco AG, Sola M, Gomis-Ruth FX, Coll M (2002): "Tandem DNA Recognition by Two-Component Signal Transduction Transcriptional Activator Phob." Structure, 10, 701. doi: 10.1016/S0969-2126(02)00761-X.
- Abstract
- PhoB is a signal transduction response regulator that activates nearly 40 genes in phosphate depletion conditions in E. coli and closely related bacteria. The structure of the PhoB effector domain in complex with its target DNA sequence, or pho box, reveals a novel tandem arrangement in which several monomers bind head to tail to successive 11-base pair direct-repeat sequences, coating one face of a smoothly bent double helix. The protein has a winged helix fold in which the DNA recognition elements comprise helix alpha 3, penetrating the major groove, and a beta hairpin wing interacting with a compressed minor groove via Arg219, tightly sandwiched between the DNA sugar backbones. The transactivation loops protrude laterally in an appropriate orientation to interact with the RNA polymerase sigma(70) subunit, which triggers transcription initiation.