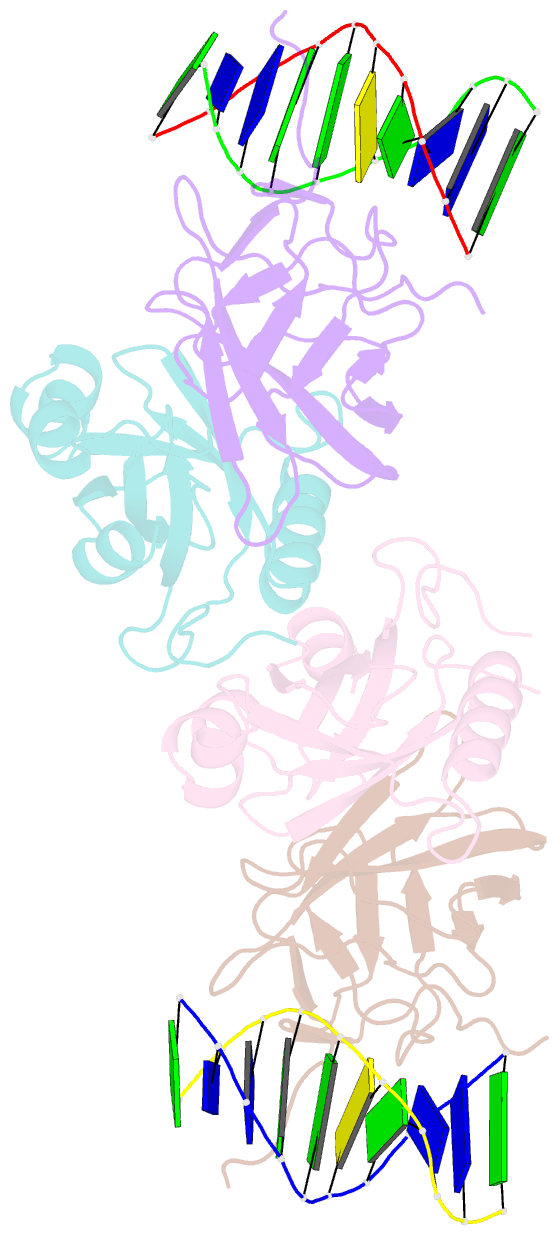
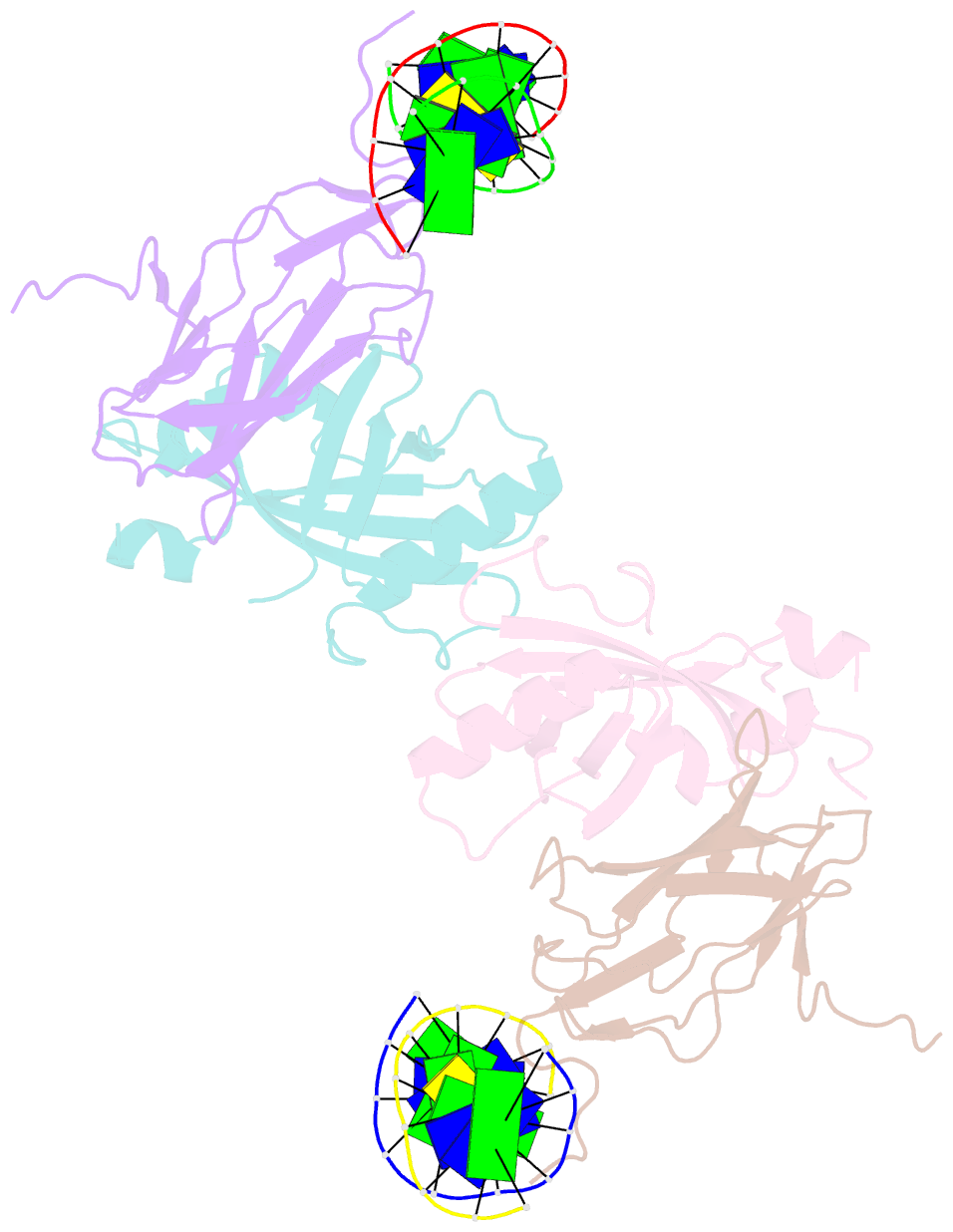
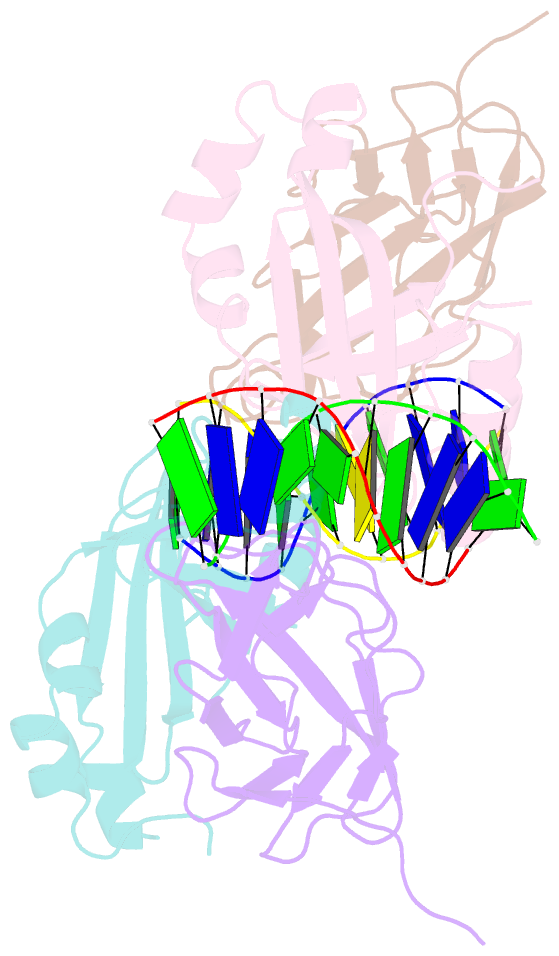
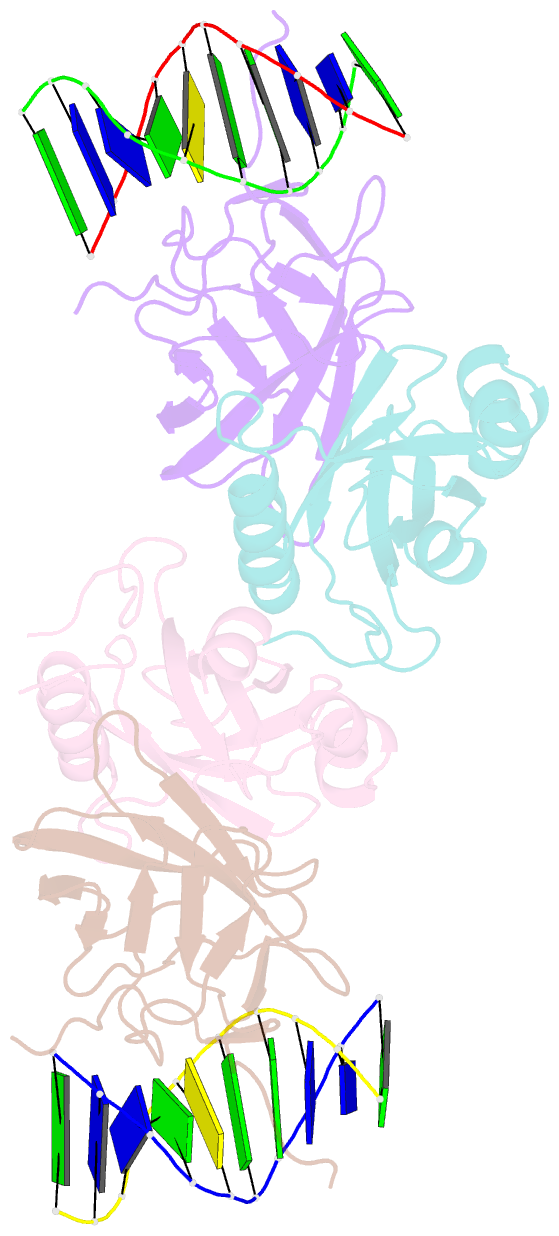
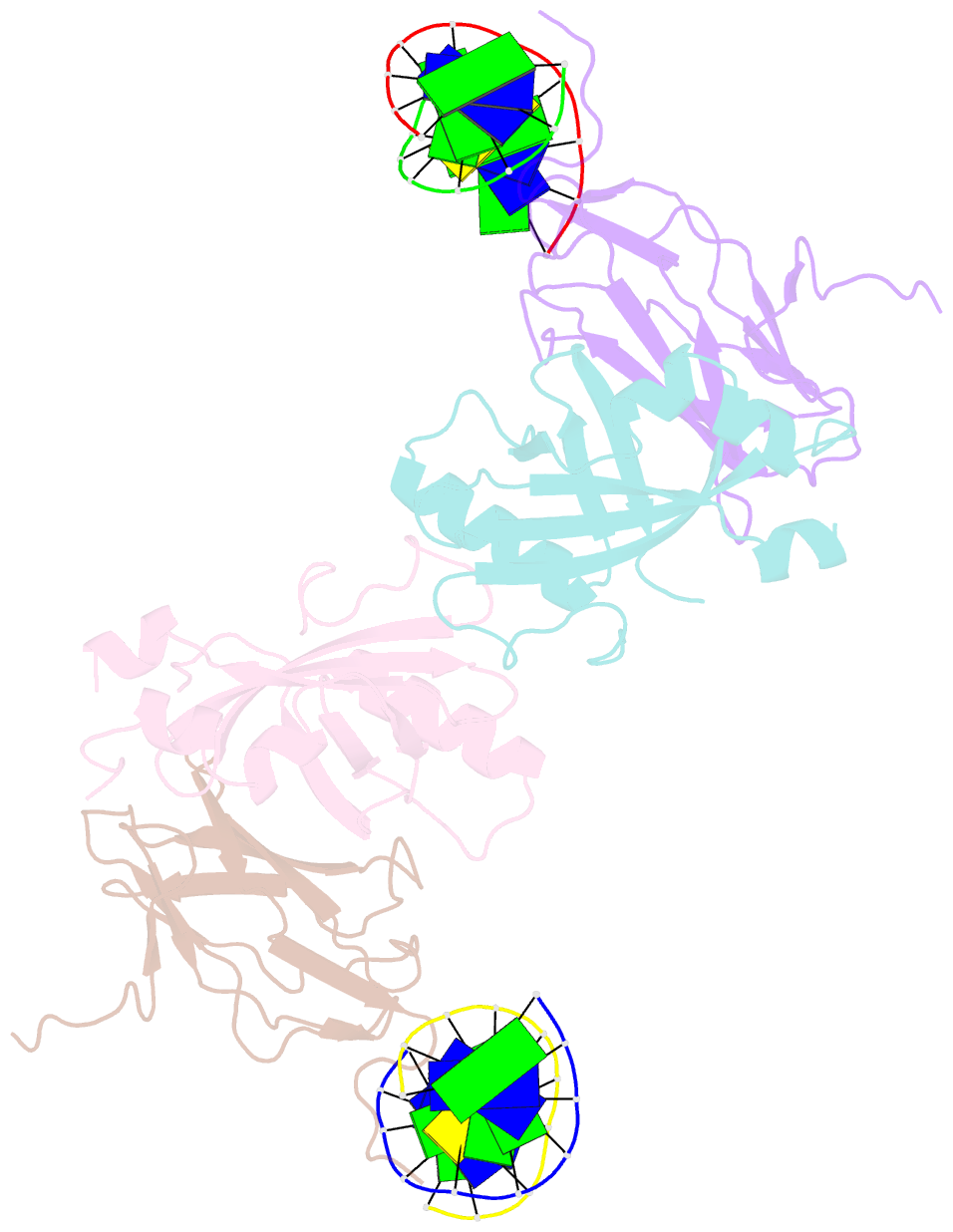
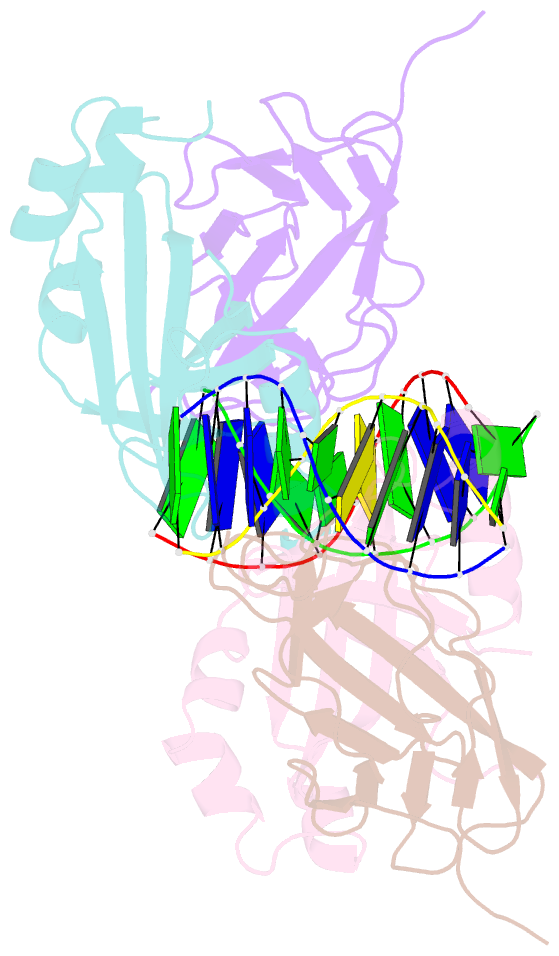
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 1h9d; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- transcription factor
- Method
- X-ray (2.6 Å)
- Summary
- Aml1-cbf-beta-DNA complex
- Reference
- Bravo J, Li Z, Speck NA, Warren AJ (2001): "The Leukemia-Associated Aml1 (Runx1)-Cbfbeta Complex Functions as a DNA-Induced Molecular Clamp." Nat.Struct.Biol., 8, 371. doi: 10.1038/86264.
- Abstract
- We have determined the structure, at 2.6 A resolution, of the AML1 (Runx1) Runt domain--CBF beta--DNA ternary complex, the most common target for mutations in human leukemia. The structure reveals that the Runt domain DNA binding mechanism is unique within the p53 family of transcription factors. The extended C-terminal 'tail' and 'wing' elements adopt a specific DNA-bound conformation that clamps the phosphate backbone between the major and minor grooves of the distorted B-form DNA recognition site. Furthermore, the extended 'tail' mediates most of the NF-kappa B/Rel-like base-specific contacts in the major groove. The structure clearly explains the molecular basis for the loss of DNA binding function of the Runt domain--CBF beta complex as a consequence of the human disease-associated mutations in leukemogenesis and cleidocranial dysplasia.