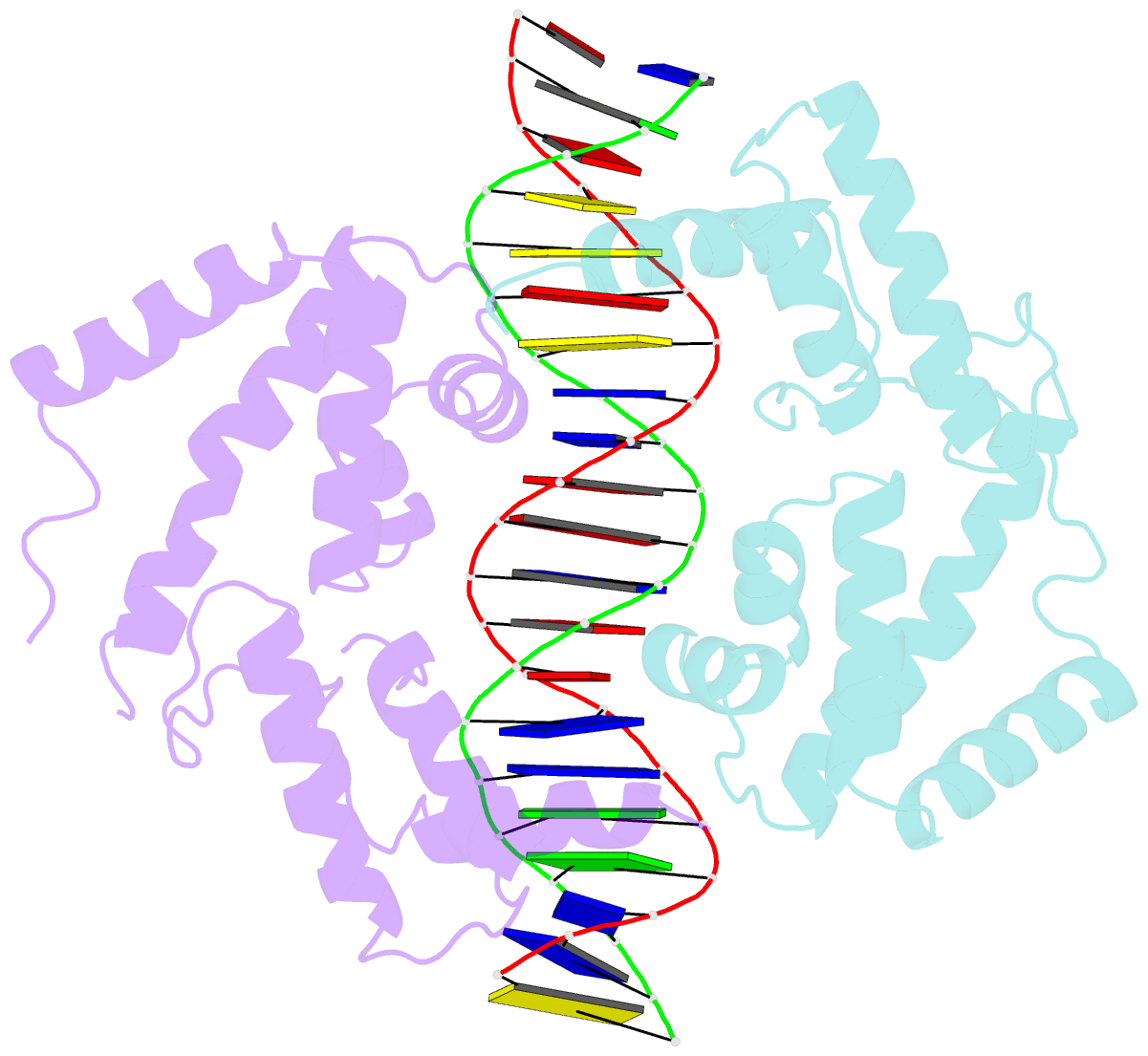
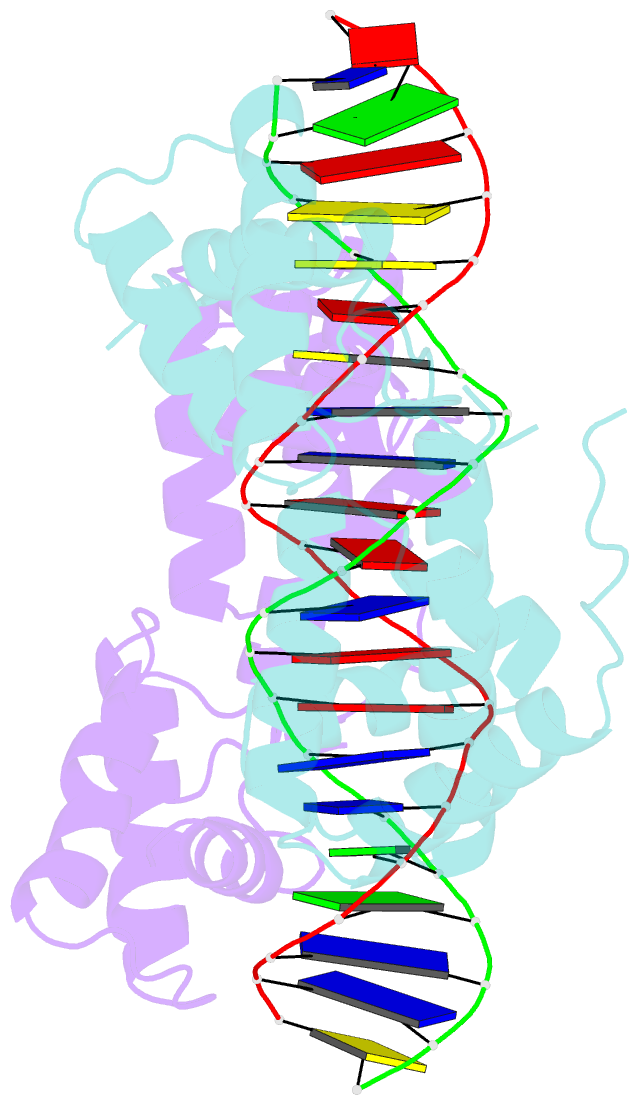
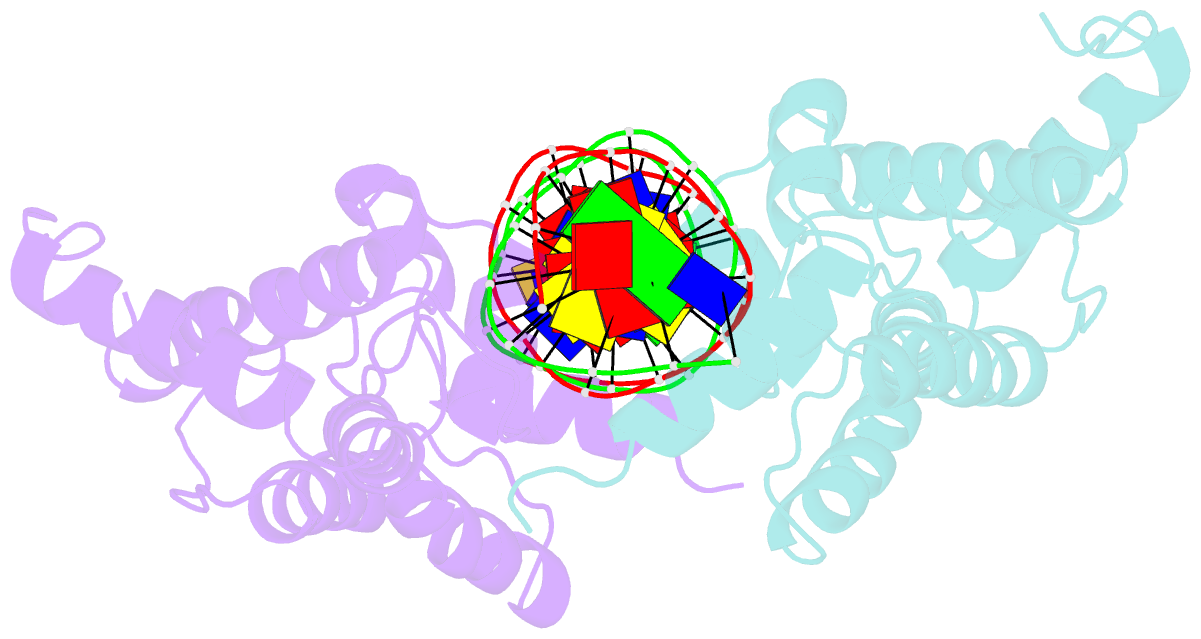
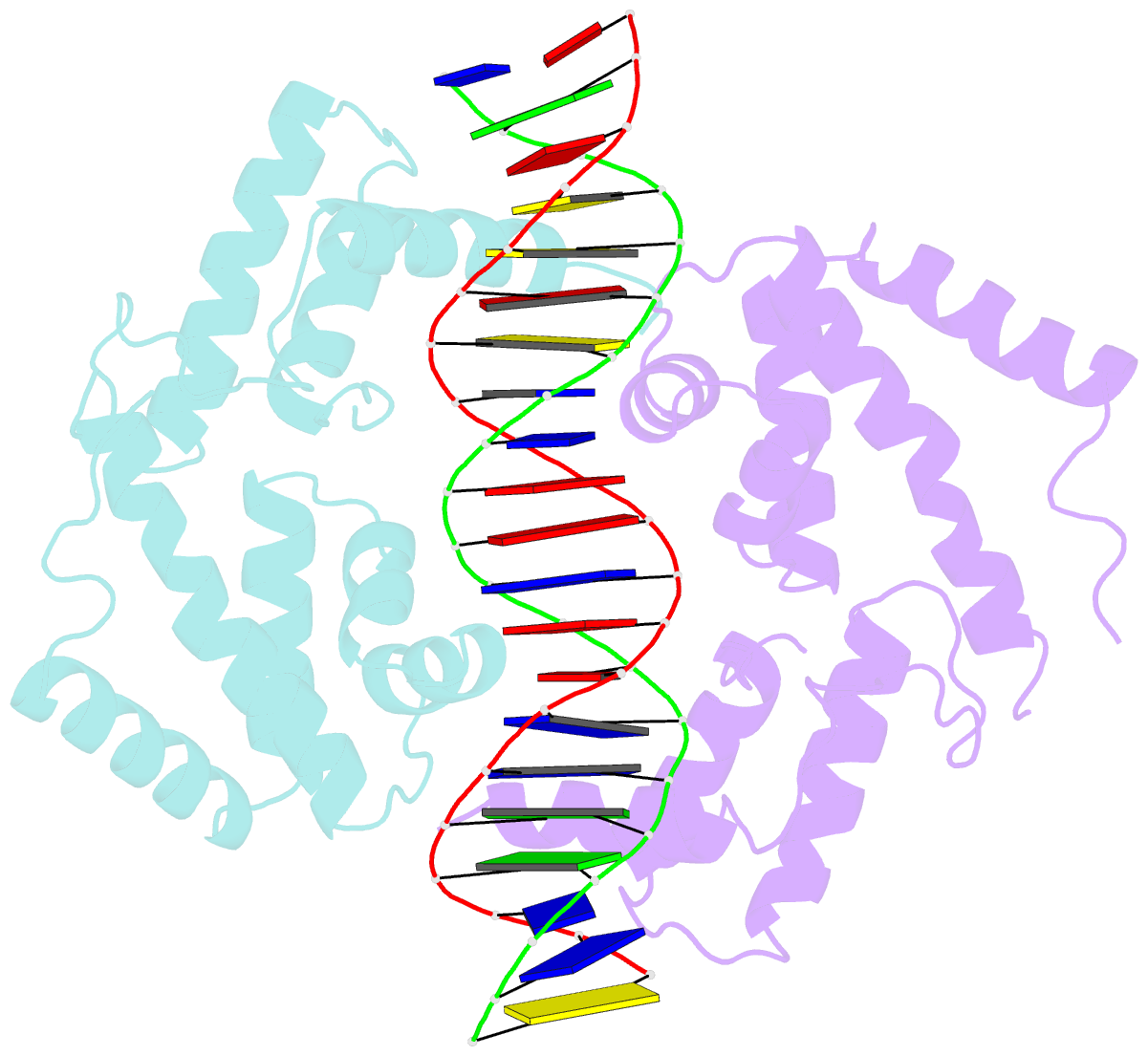
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 1ic8; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- transcription-DNA
- Method
- X-ray (2.6 Å)
- Summary
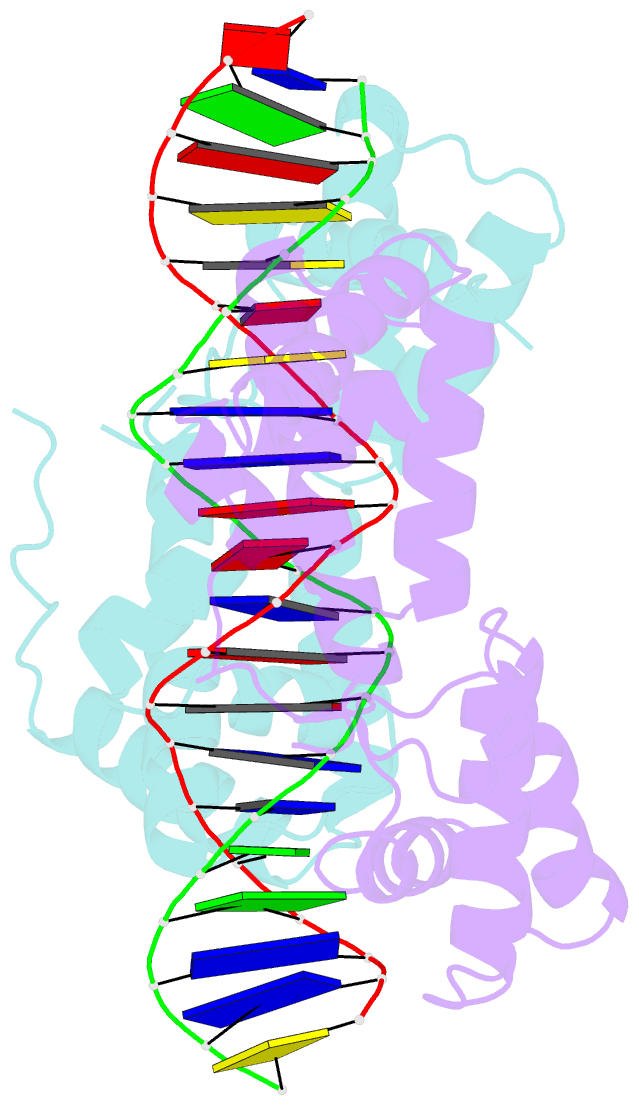
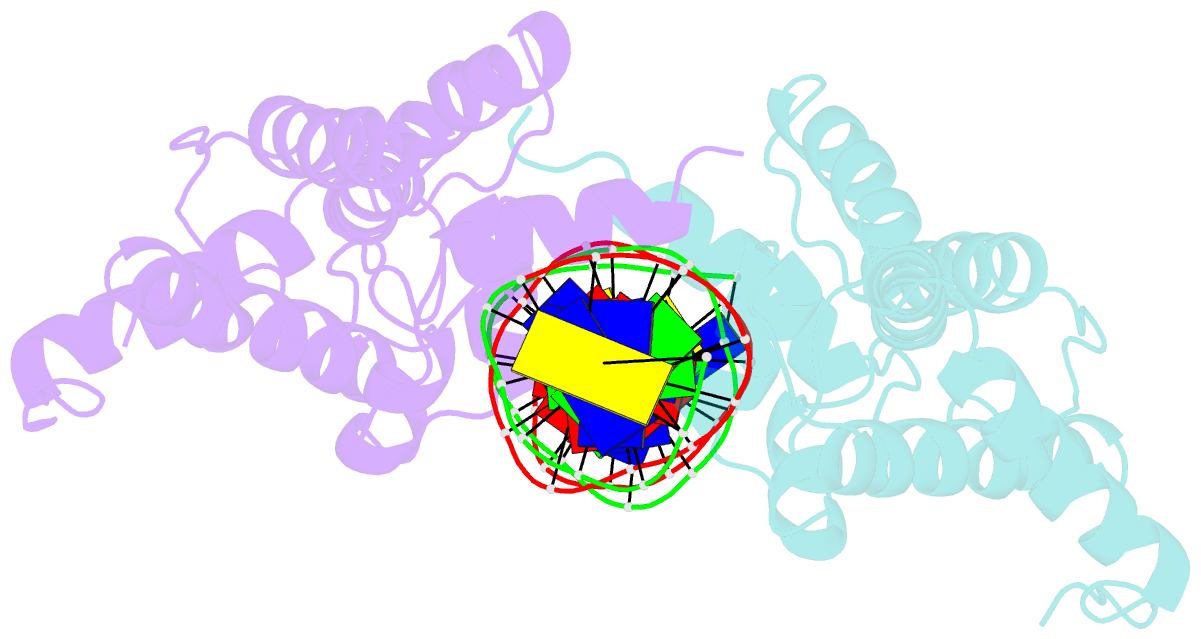
- Hepatocyte nuclear factor 1a bound to DNA : mody3 gene product
- Reference
- Chi Y-I, Frantz JD, Oh B-C, Hansen L, Dhe-Paganon S, Shoelson SE (2002): "Diabetes mutations delineate an
atypical POU domains in HNF1-Alpha." Mol.Cell, 10, 1129-1137. doi: 10.1016/S1097-2765(02)00704-9.
- Abstract
- Mutations in Hnf-1alpha are the most common Mendelian cause of diabetes mellitus. To elucidate the molecular function of a mutational hotspot, we cocrystallized human HNF-1alpha 83-279 with a high-affinity promoter and solved the structure of the complex. Two identical protein molecules are bound to the promoter. Each contains a homeodomain and a second domain structurally similar to POU-specific domains that was not predicted on the basis of amino acid sequence. Atypical elements in both domains create a stable interface that further distinguishes HNF-1alpha from other flexible POU-homeodomain proteins. The numerous diabetes-causing mutations in HNF-1alpha thus identified a previously unrecognized POU domain which was used as a search model to identify additional POU domain proteins in sequence databases.