Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 1j4w; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- transcription-DNA
- Method
- NMR
- Summary
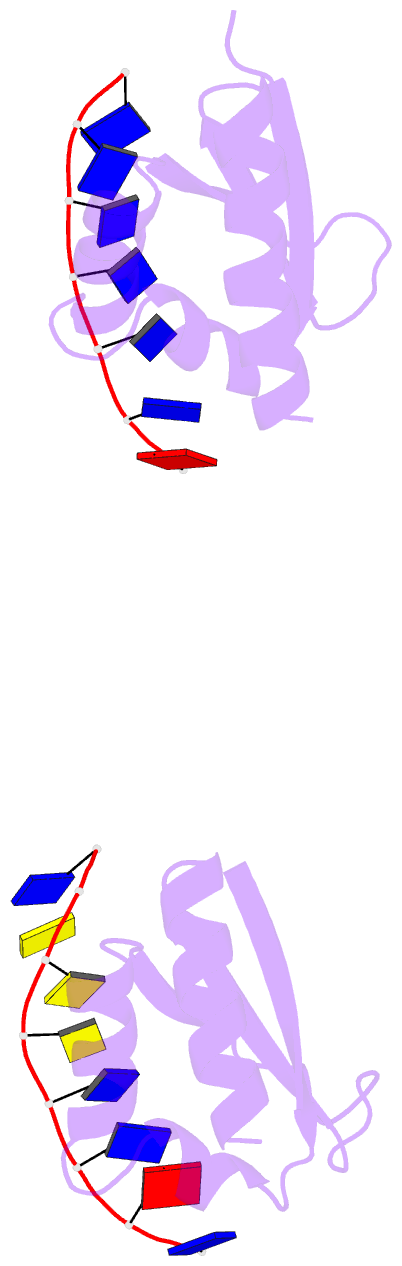
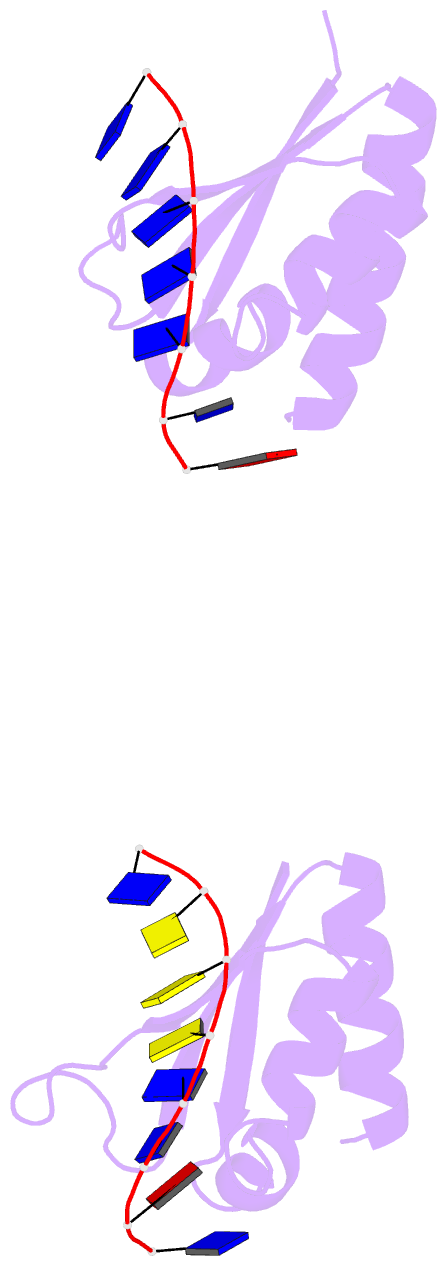
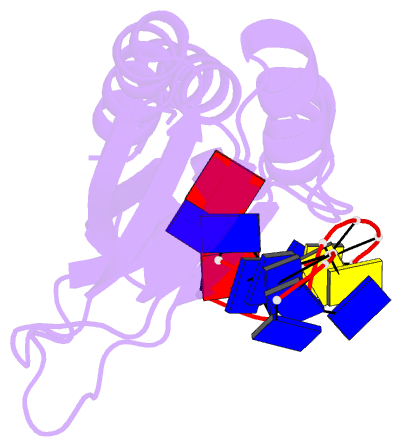
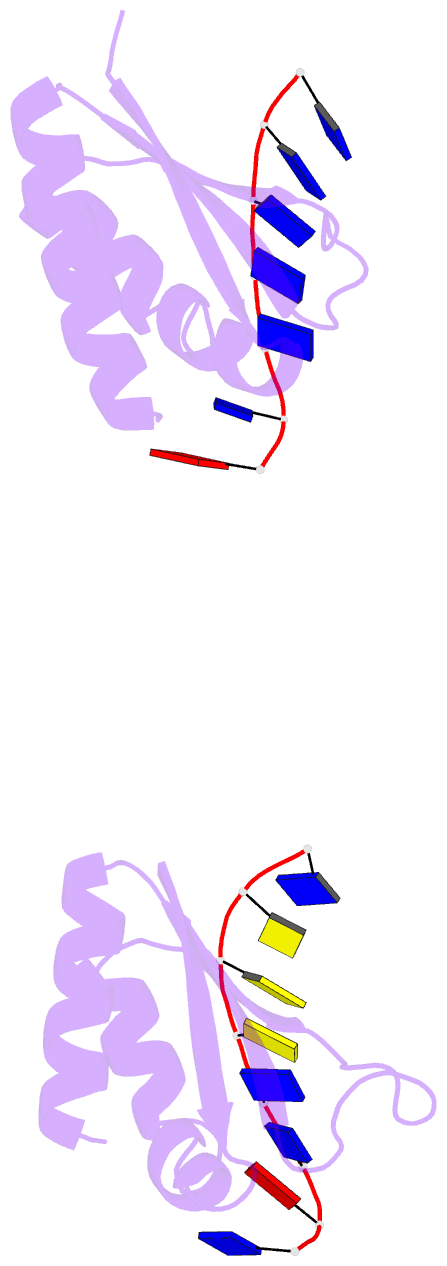
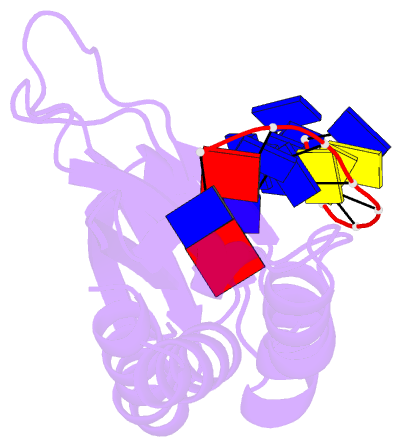
- Complex of the kh3 and kh4 domains of fbp with a single_stranded 29mer DNA oligonucleotide from the fuse element of the c-myc oncogene
- Reference
- Braddock DT, Louis JM, Baber JL, Levens D, Clore GM (2002): "Structure and dynamics of KH domains from FBP bound to single-stranded DNA." Nature, 415, 1051-1056. doi: 10.1038/4151051a.
- Abstract
- Gene regulation can be tightly controlled by recognition of DNA deformations that are induced by stress generated during transcription. The KH domains of the FUSE-binding protein (FBP), a regulator of c-myc expression, bind in vivo and in vitro to the single-stranded far-upstream element (FUSE), 1,500 base pairs upstream from the c-myc promoter. FBP bound to FUSE acts through TFIIH at the promoter. Here we report the solution structure of a complex between the KH3 and KH4 domains of FBP and a 29-base single-stranded DNA from FUSE. The KH domains recognize two sites, 9-10 bases in length, separated by 5 bases, with KH4 bound to the 5' site and KH3 to the 3' site. The central portion of each site comprises a tetrad of sequence 5'd-ATTC for KH4 and 5'd-TTTT for KH3. Dynamics measurements show that the two KH domains bind as articulated modules to single-stranded DNA, providing a flexible framework with which to recognize transient, moving targets.