Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 1j5k; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- transcription-DNA
- Method
- NMR
- Summary
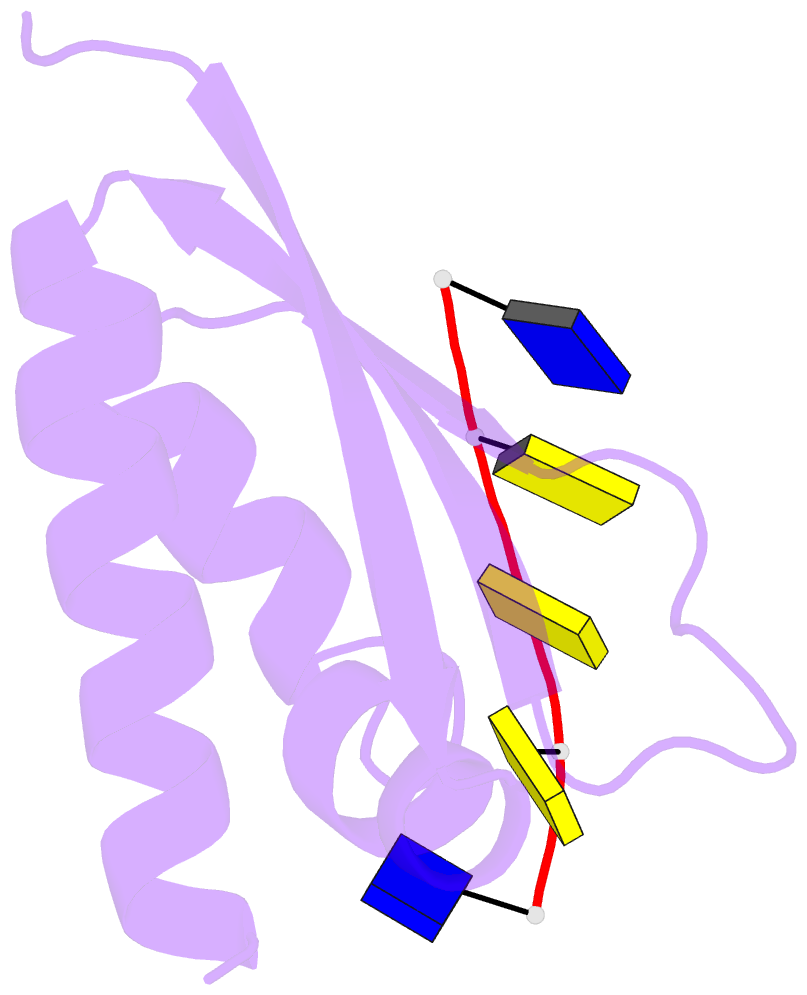
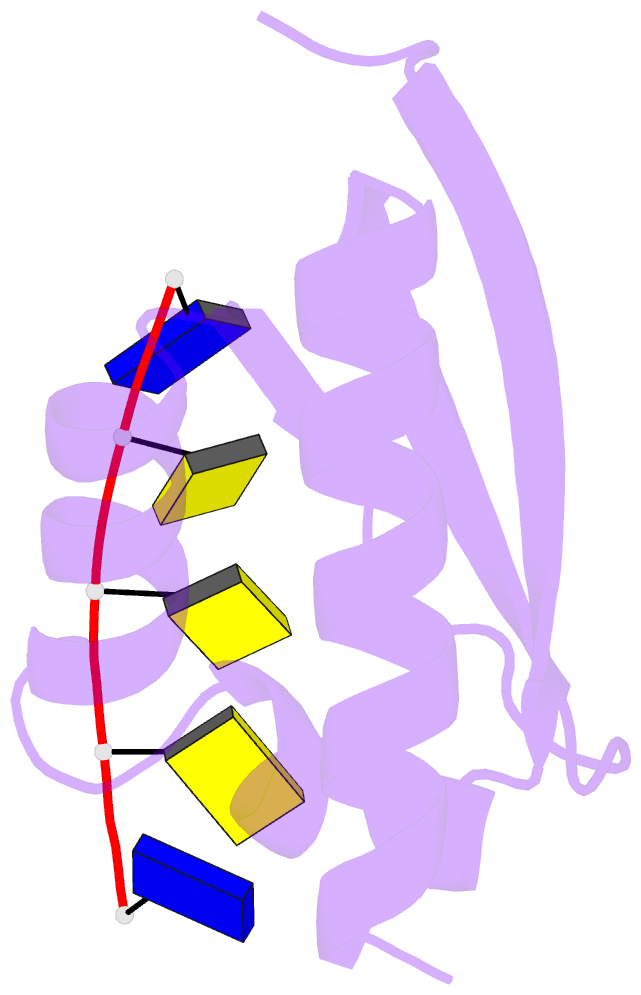
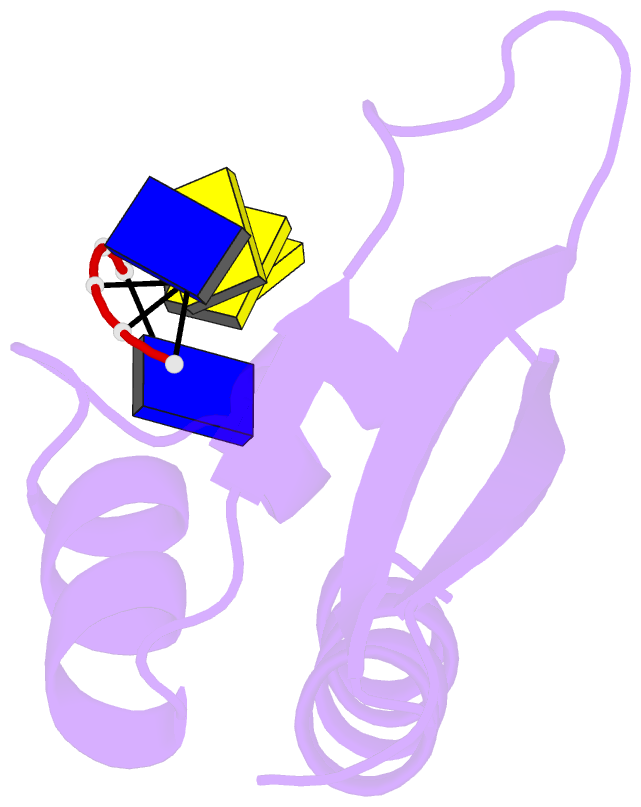
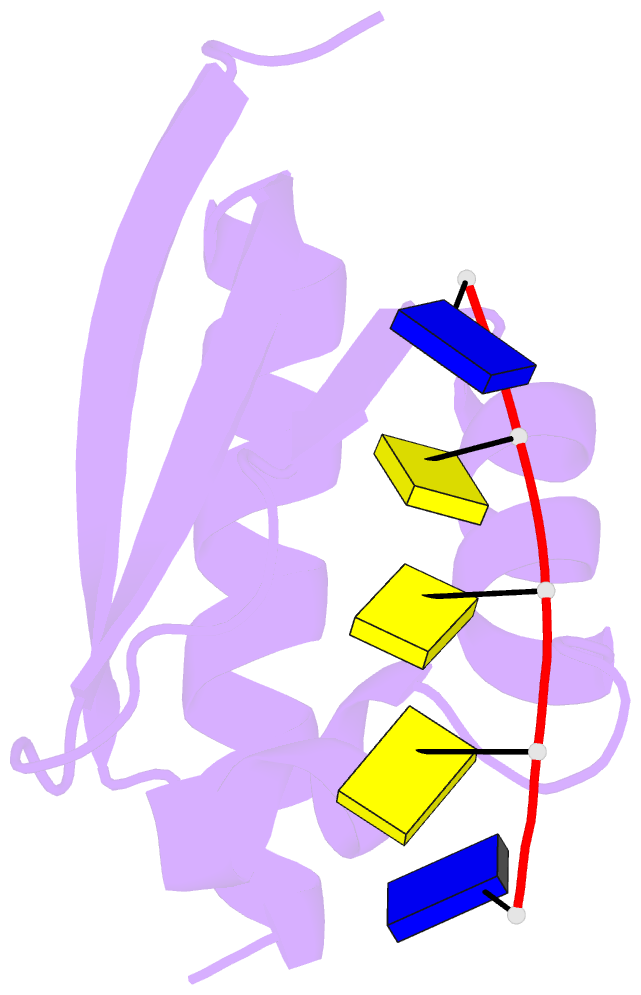
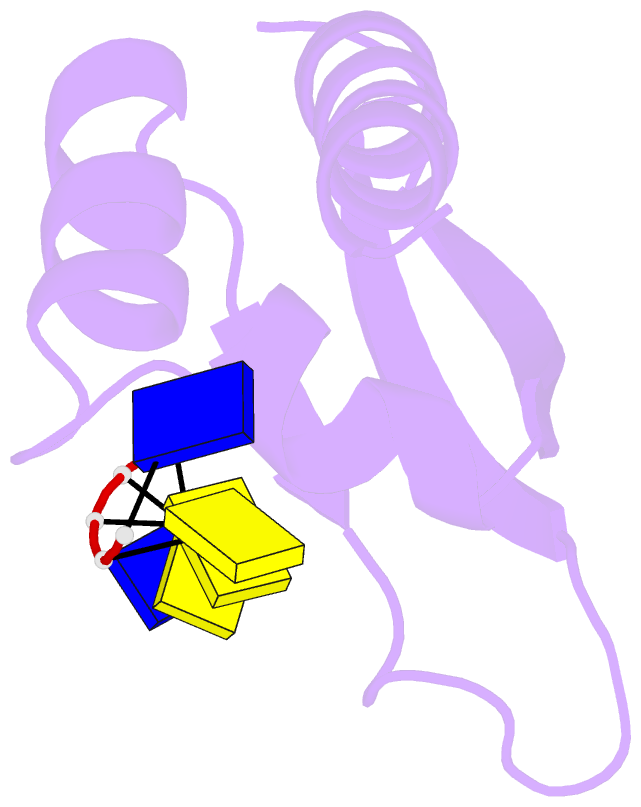
- Complex of the kh3 domain of hnrnp k with a single_stranded 10mer DNA oligonucleotide
- Reference
- Braddock DT, Baber JL, Levens D, Clore GM (2002): "Molecular basis of sequence-specific single-stranded DNA recognition by KH domains: solution structure of a complex between hnRNP K KH3 and single-stranded DNA." EMBO J., 21, 3476-3485. doi: 10.1093/emboj/cdf352.
- Abstract
- To elucidate the basis of sequence-specific single-stranded (ss) DNA recognition by K homology (KH) domains, we have solved the solution structure of a complex between the KH3 domain of the transcriptional regulator heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein K (hnRNP K) and a 10mer ssDNA. We show that hnRNP K KH3 specifically recognizes a tetrad of sequence 5'd-TCCC. The complex is stabilized by a dense network of methyl-oxygen hydrogen bonds involving the methyl groups of three isoleucine residues and the O2 and N3 atoms of the two central cytosine bases. Comparison with the recently solved structure of a specific protein-ssDNA complex involving the KH3 and KH4 domains of the far upstream element (FUSE) binding protein FBP suggests that the amino acid located five residues N-terminal of the invariant GXXG motif, which is characteristic of all KH domains, plays a crucial role in discrimination of the first two bases of the tetrad.