Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 1k1g; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- gene regulation-RNA
- Method
- NMR
- Summary
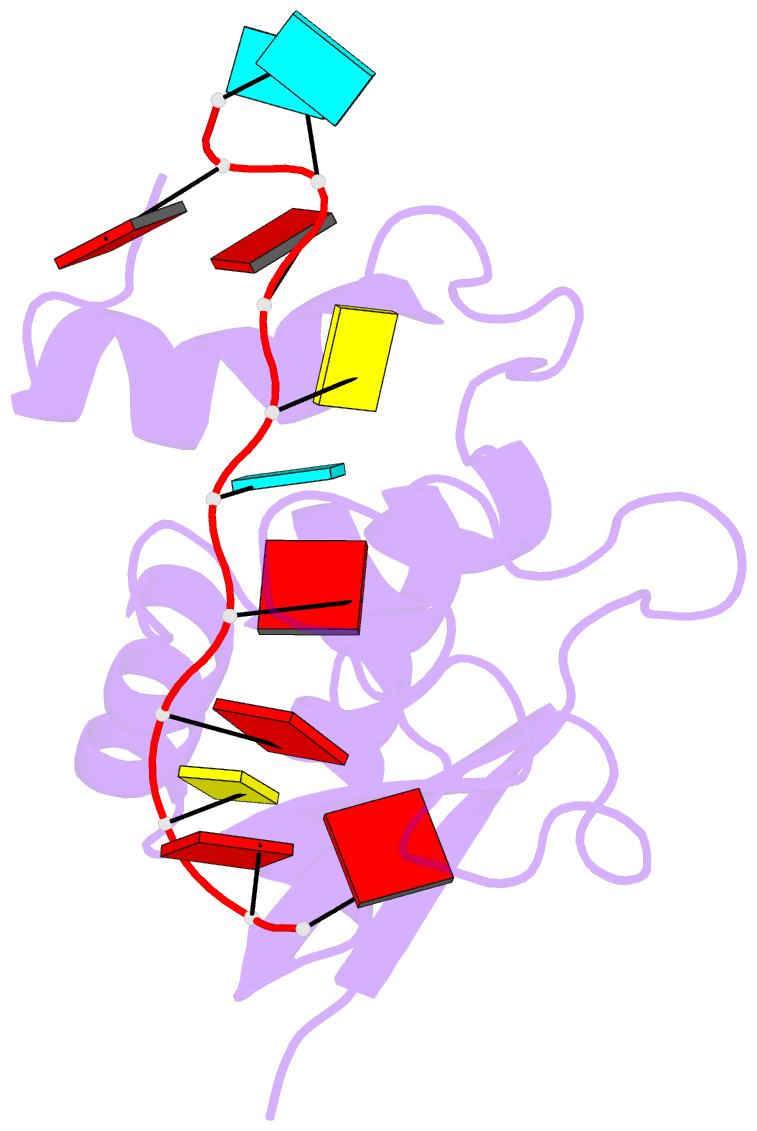
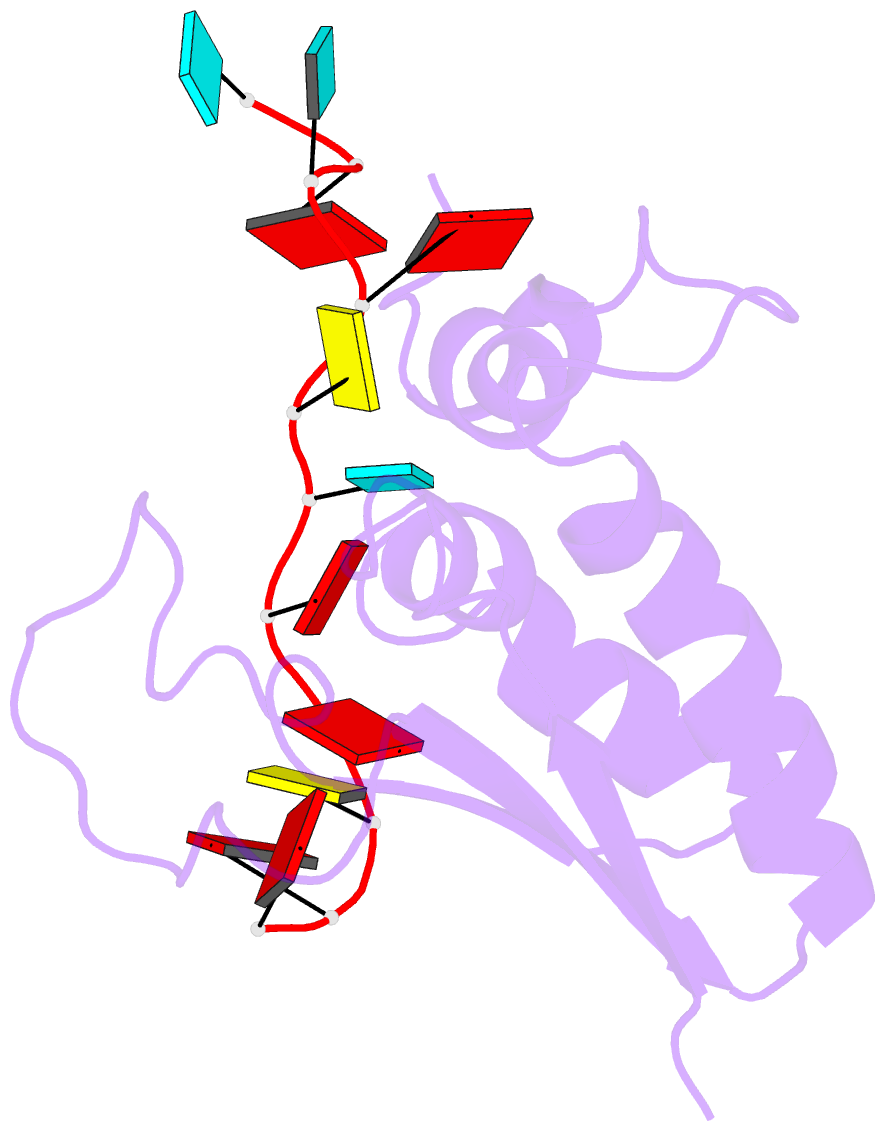
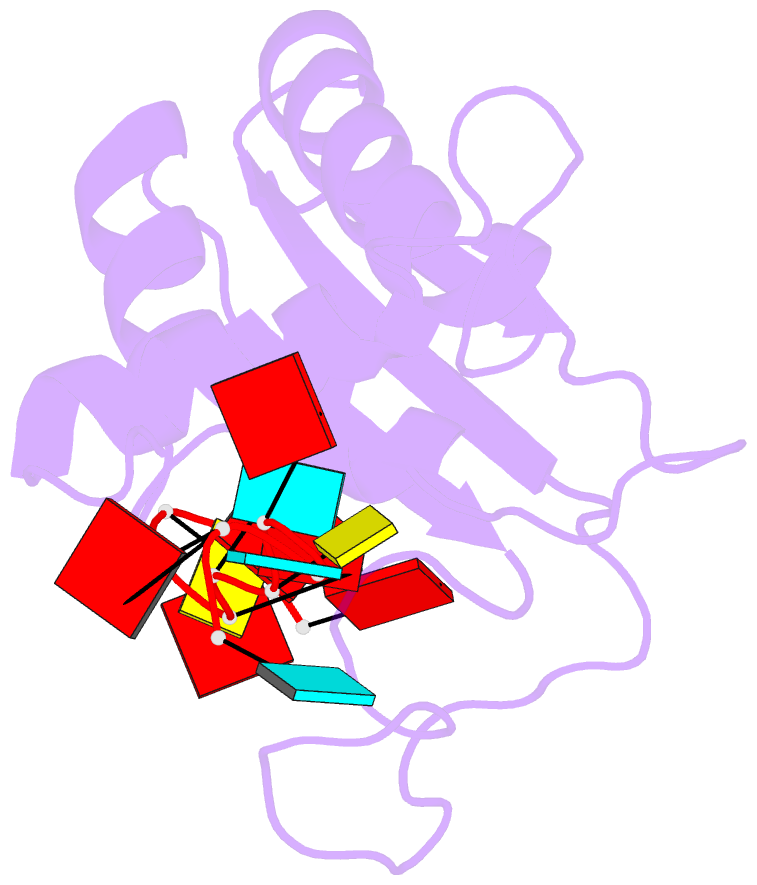
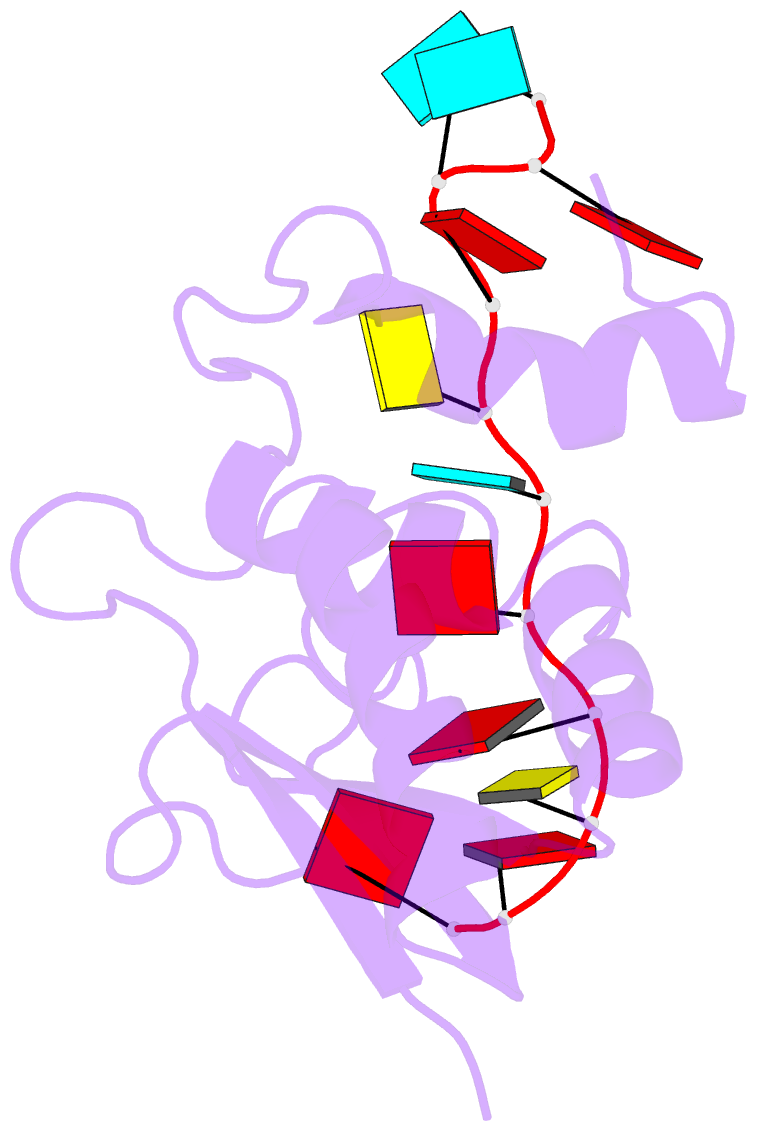
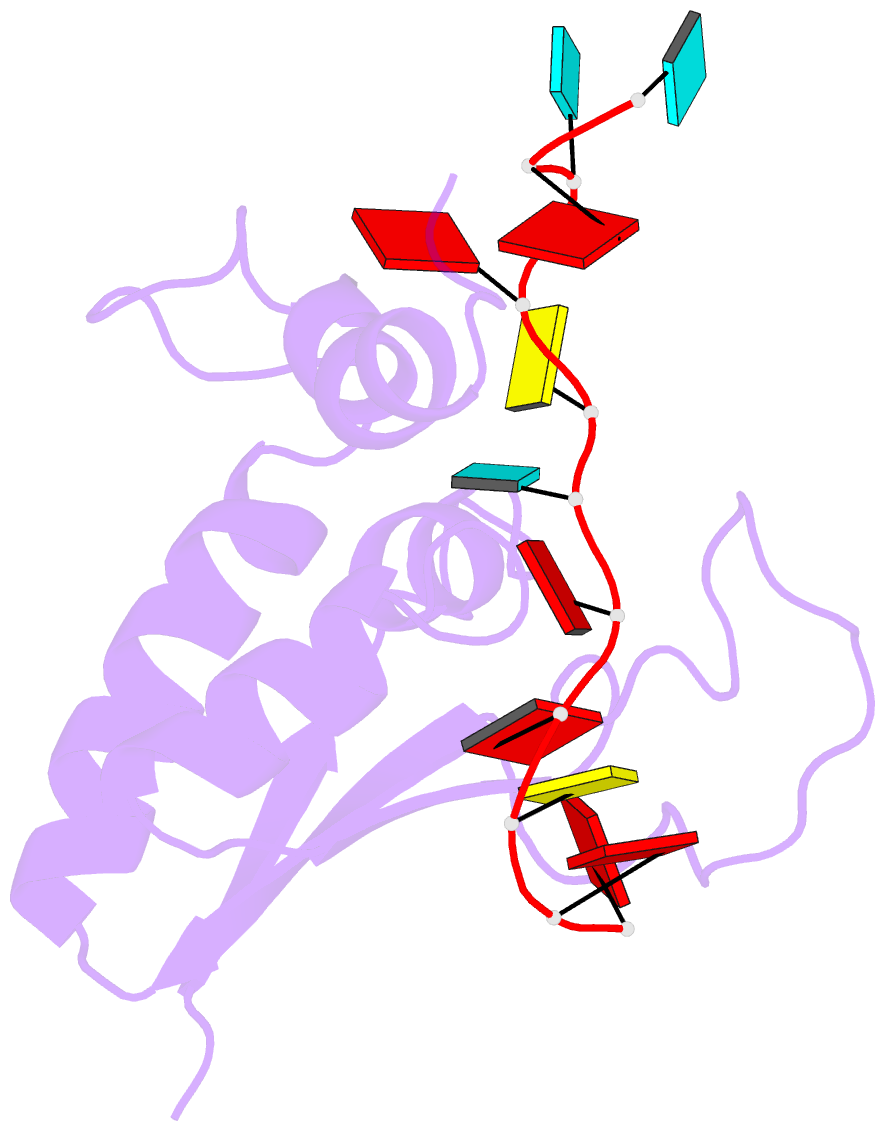
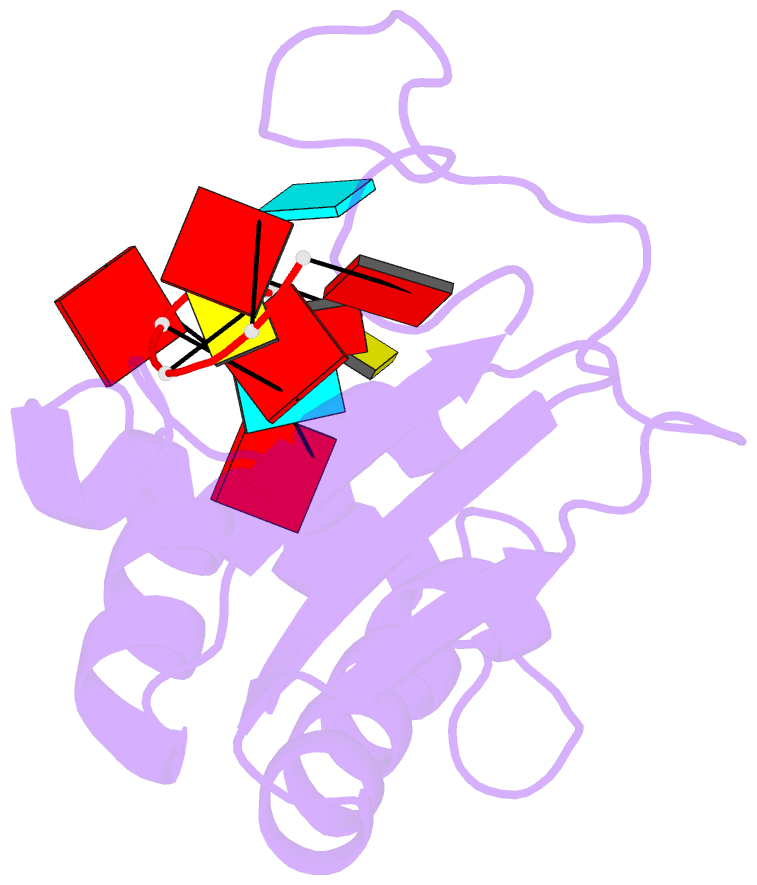
- Structural basis for recognition of the intron branch site RNA by splicing factor 1
- Reference
- Liu Z, Luyten I, Bottomley MJ, Messias AC, Houngninou-Molango S, Sprangers R, Zanier K, Kramer A, Sattler M (2001): "Structural basis for recognition of the intron branch site RNA by splicing factor 1." Science, 294, 1098-1102. doi: 10.1126/science.1064719.
- Abstract
- During spliceosome assembly, splicing factor 1 (SF1) specifically recognizes the intron branch point sequence (BPS) UACUAAC in the pre-mRNA transcripts. We show that the KH-QUA2 region of SF1 defines an enlarged KH (hn RNP K) fold which is necessary and sufficient for BPS binding. The 3' part of the BPS (UAAC), including the conserved branch point adenosine (underlined), is specifically recognized in a hydrophobic cleft formed by the Gly-Pro-Arg-Gly motif and the variable loop of the KH domain. The QUA2 region recognizes the 5' nucleotides of the BPS (ACU). The branch point adenosine acting as the nucleophile in the first biochemical step of splicing is deeply buried. BPS RNA recognition suggests how SF1 may facilitate subsequent formation of the prespliceosomal complex A.