Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 1l1c; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- transcription-RNA
- Method
- NMR
- Summary
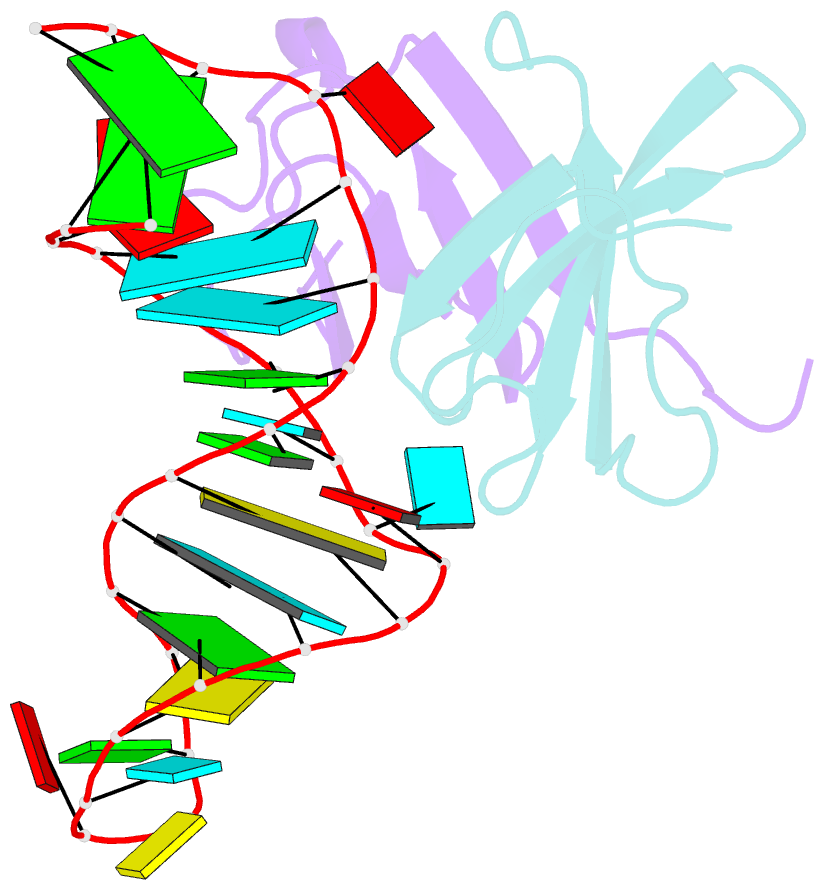
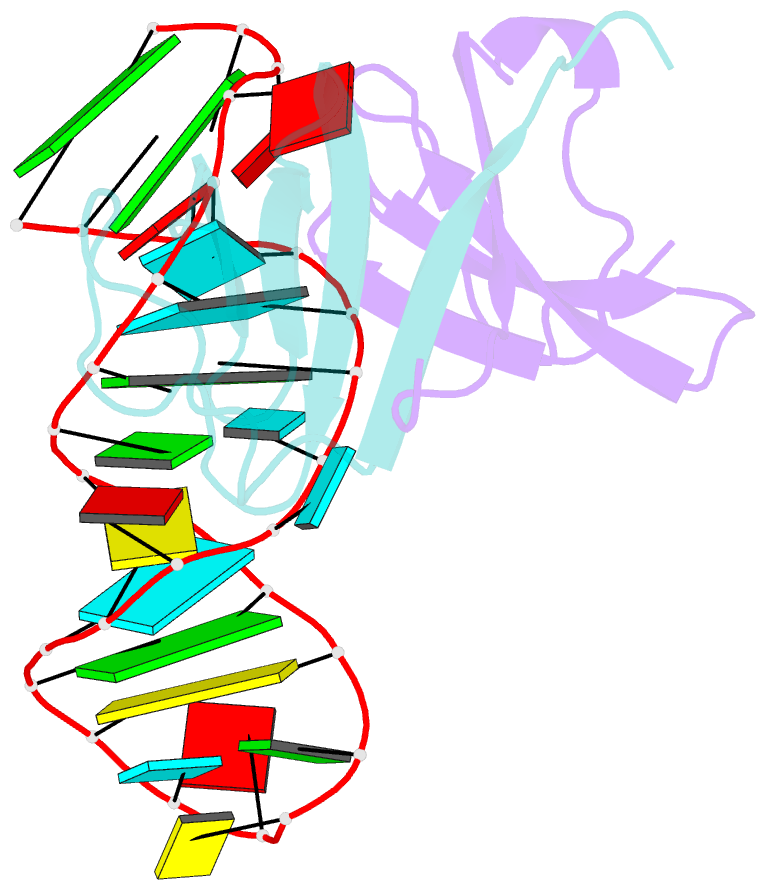
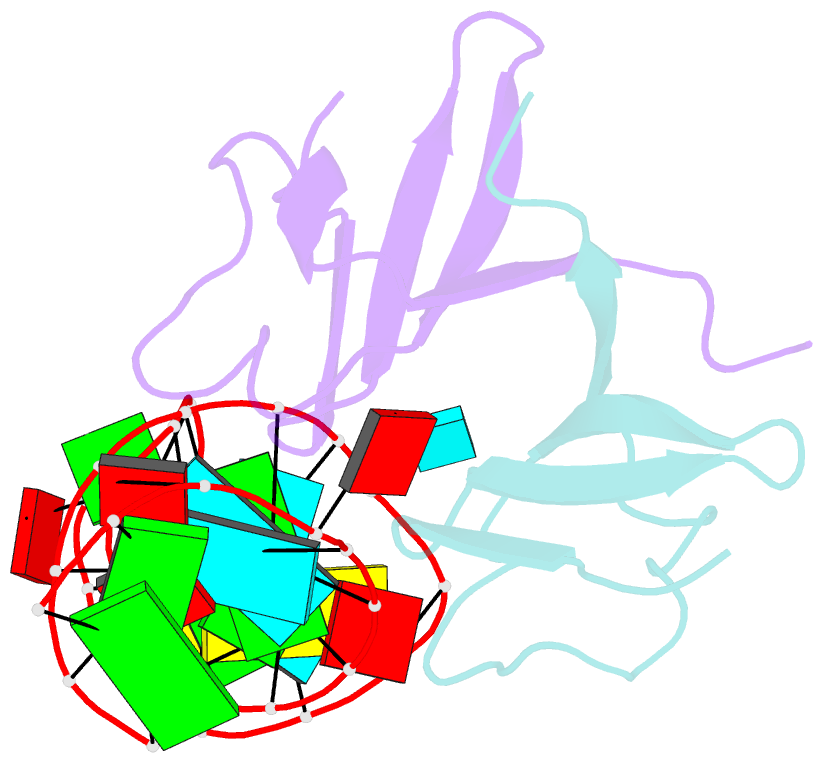
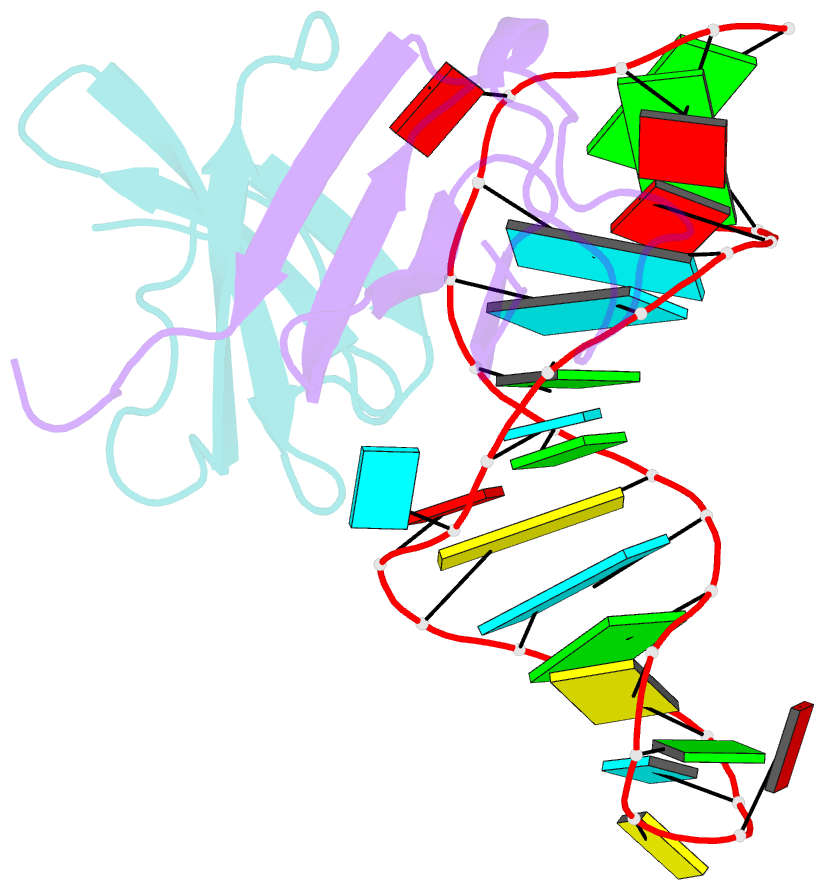
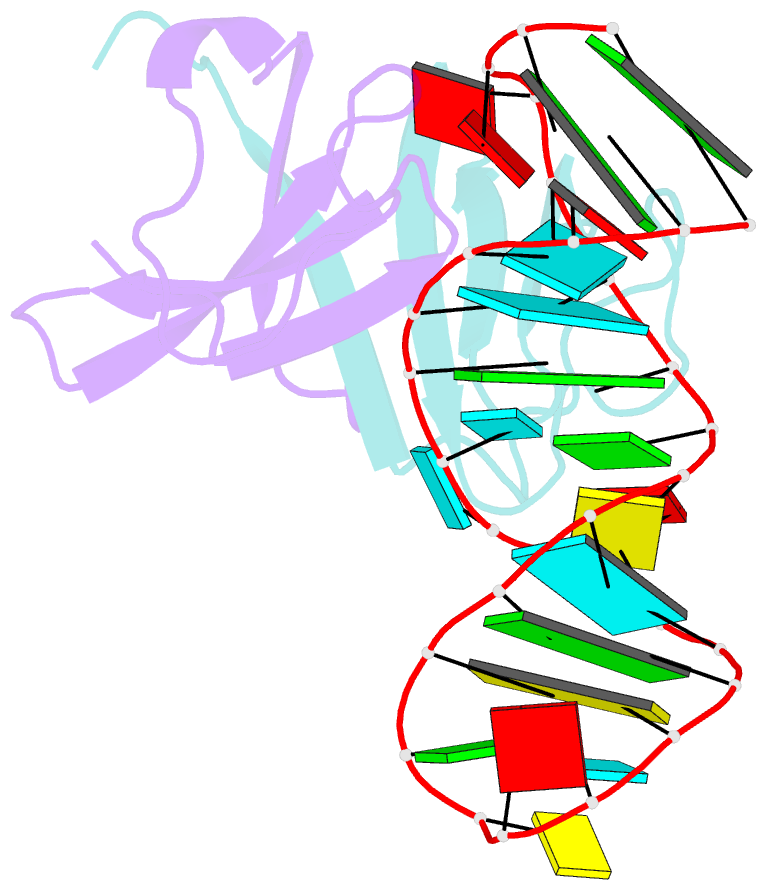
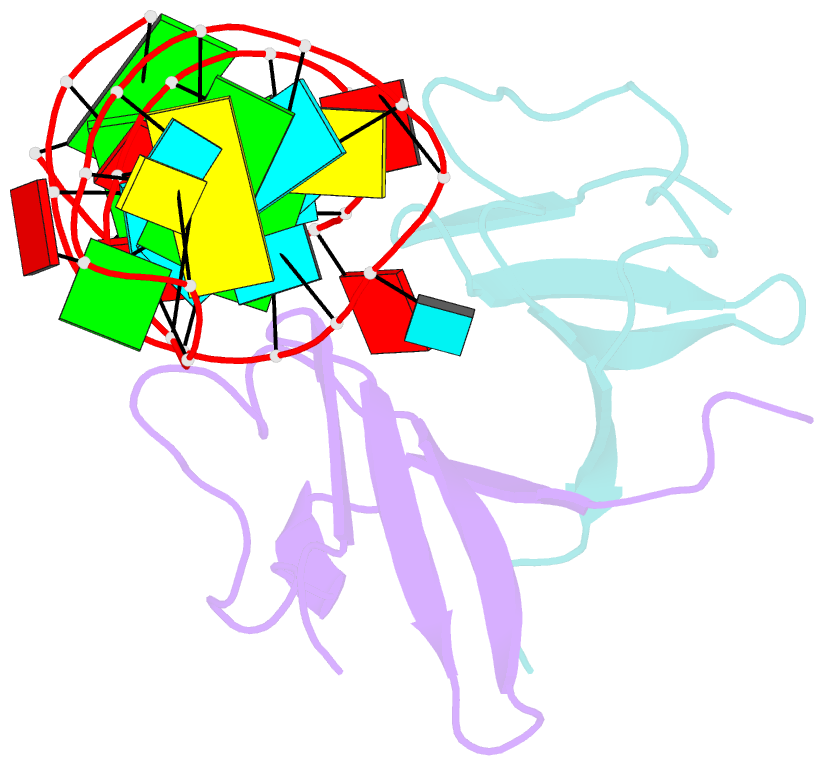
- Structure of the lict bacterial antiterminator protein in complex with its RNA target
- Reference
- Yang Y, Declerck N, Manival X, Aymerich S, Kochoyan M (2002): "Solution structure of the LicT-RNA antitermination complex: CAT clamping RAT." EMBO J., 21, 1987-1997. doi: 10.1093/emboj/21.8.1987.
- Abstract
- LicT is a bacterial regulatory protein able to prevent the premature arrest of transcription. When activated, LicT binds to a 29 base RNA hairpin overlapping a terminator located in the 5' mRNA leader region of the target genes. We have determined the solution structure of the LicT RNA-binding domain (CAT) in complex with its ribonucleic antiterminator (RAT) target by NMR spectroscopy (PDB 1L1C). CAT is a beta-stranded homodimer that undergoes no important conformational changes upon complex formation. It interacts, through mostly hydrophobic and stacking interactions, with the distorted minor groove of the hairpin stem that is interrupted by two asymmetric internal loops. Although different in sequence, these loops share sufficient structural analogy to be recognized similarly by symmetry-related elements of the protein dimer, leading to a quasi- symmetric structure reminiscent of that observed with dimeric transcription regulators bound to palindromic DNA. Sequence analysis suggests that this RNA- binding mode, where the RAT strands are clamped by the CAT dimer, is conserved in homologous systems.