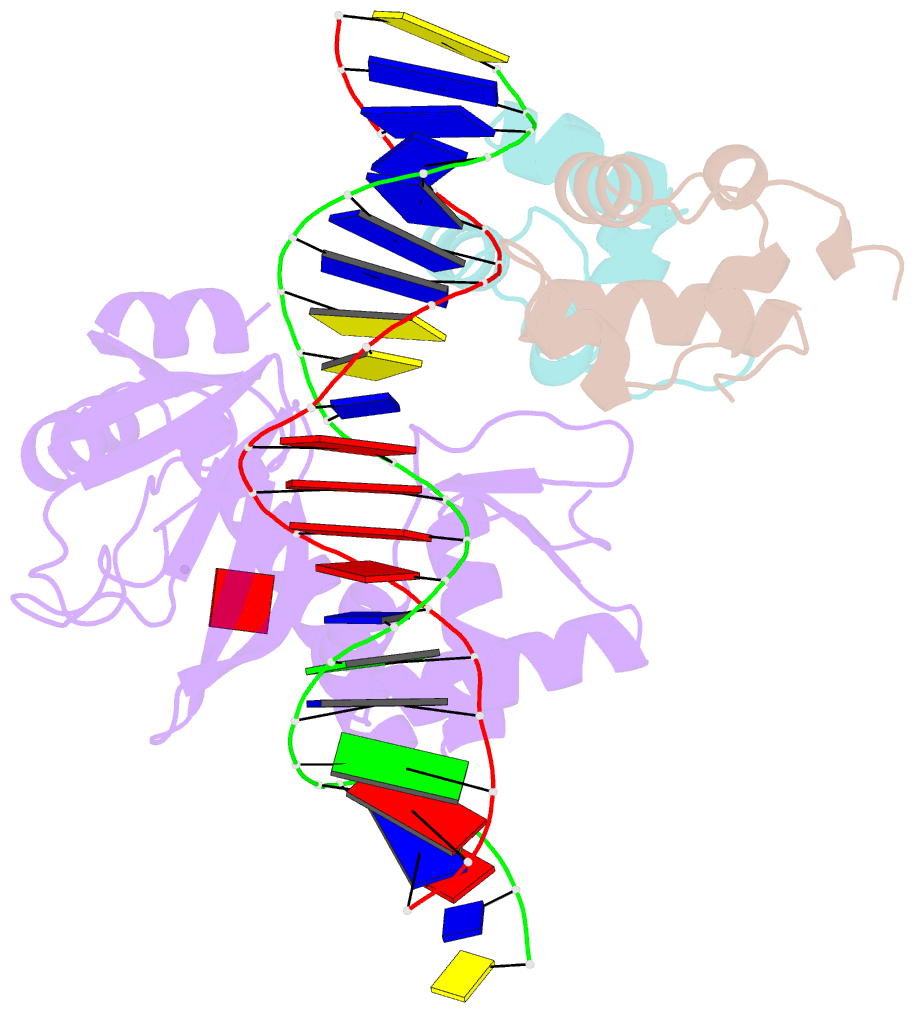
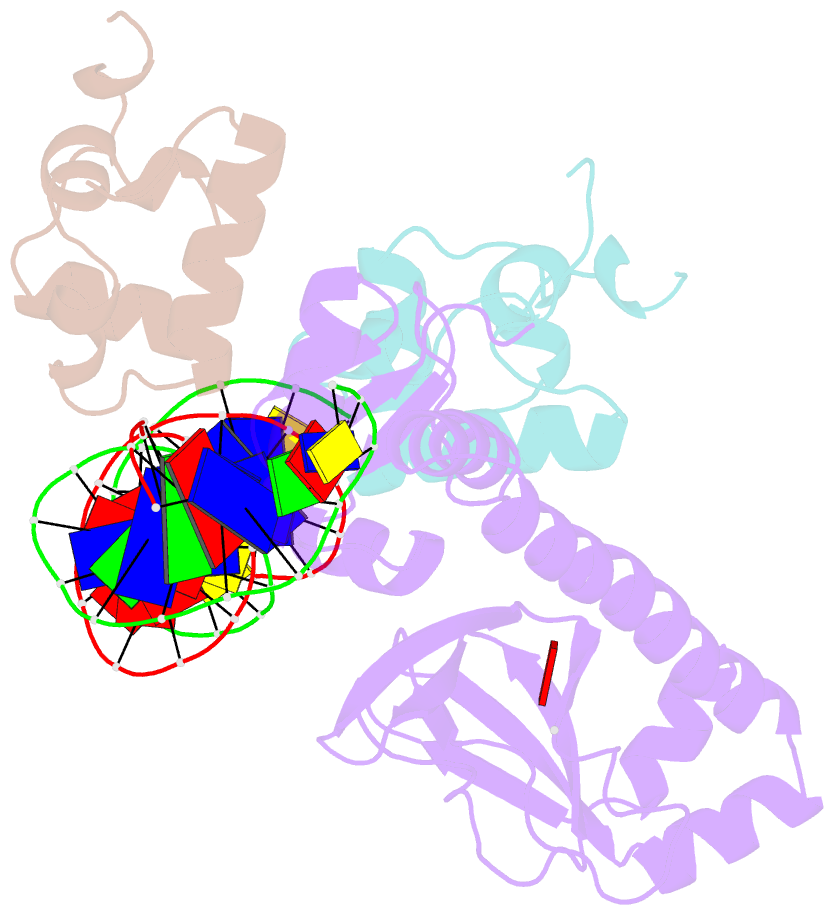
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 1lb2; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- gene regulation-DNA
- Method
- X-ray (3.1 Å)
- Summary
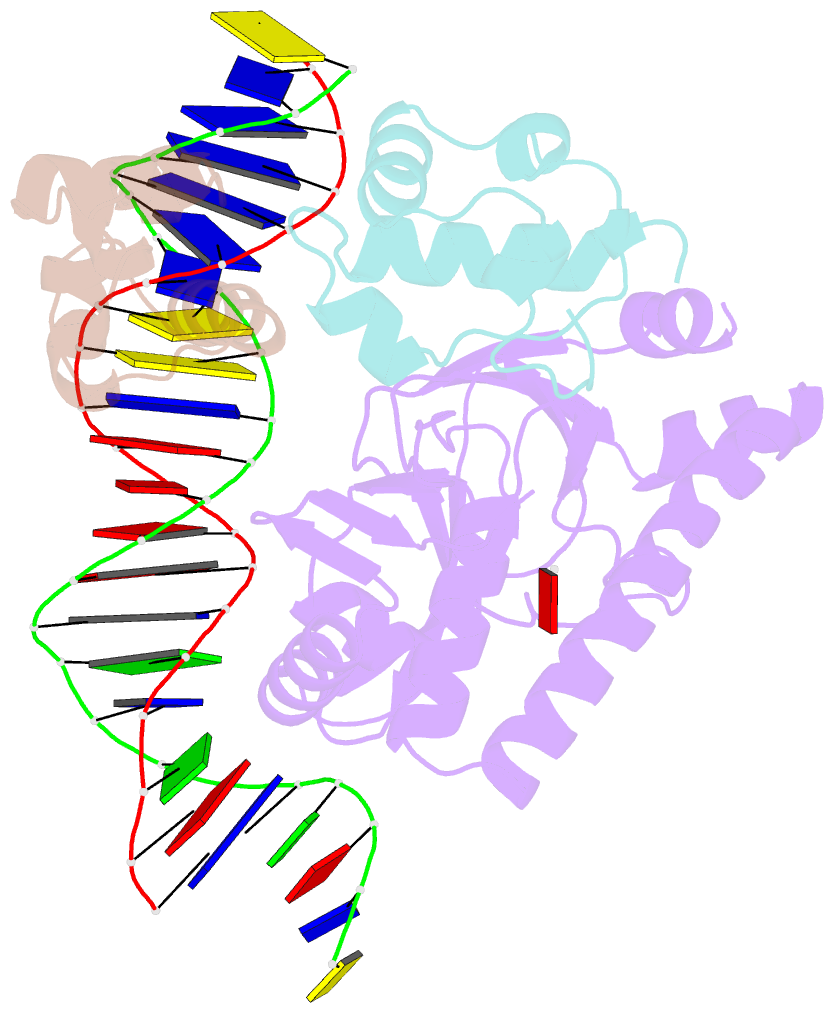
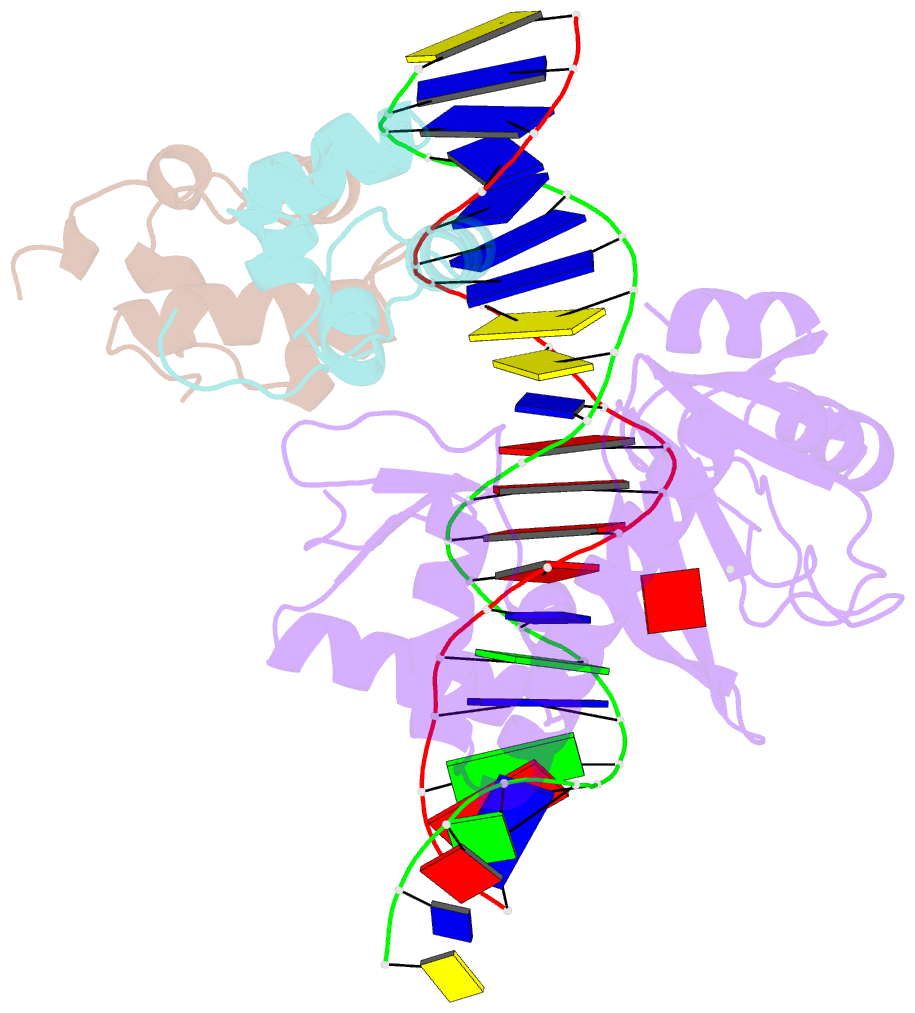
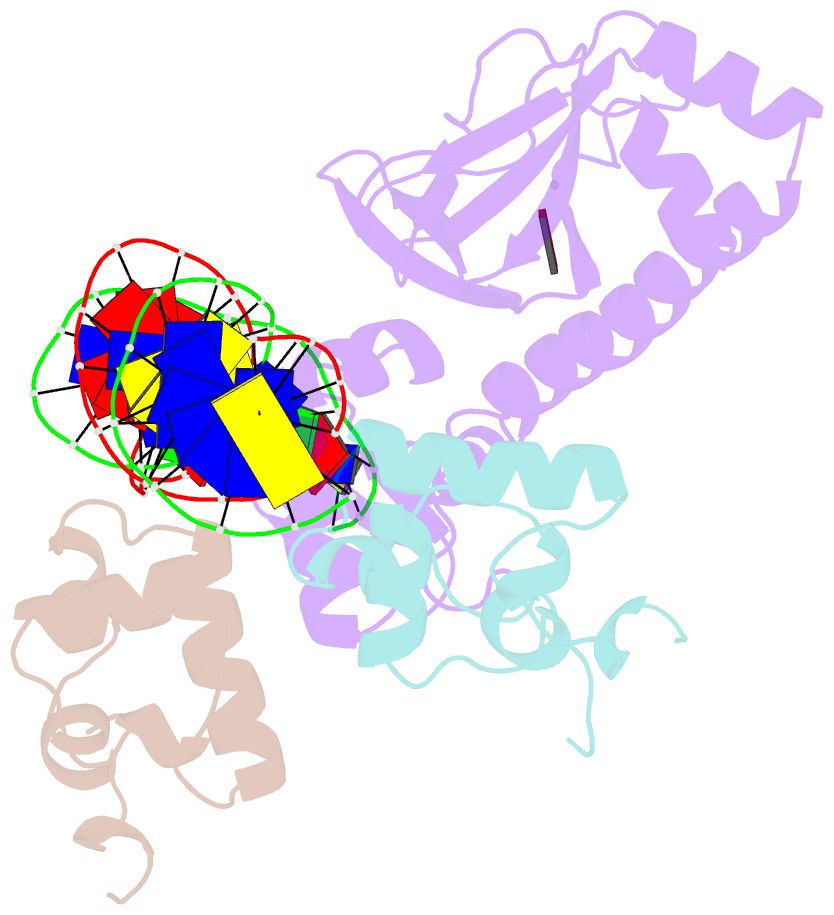
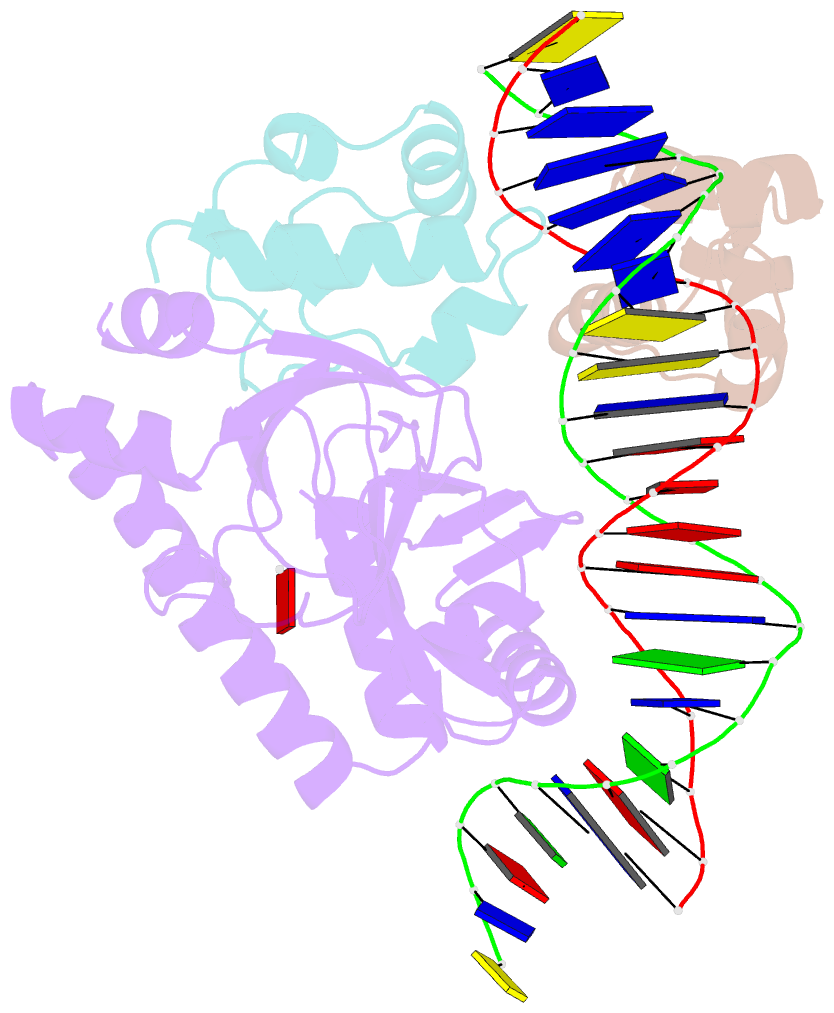
- Structure of the e. coli alpha c-terminal domain of RNA polymerase in complex with cap and DNA
- Reference
- Benoff B, Yang H, Lawson CL, Parkinson G, Liu J, Blatter E, Ebright YW, Berman HM, Ebright RH (2002): "Structural basis of transcription activation: the CAP-alpha CTD-DNA complex." Science, 297, 1562-1566. doi: 10.1126/science.1076376.
- Abstract
- The Escherichia coli catabolite activator protein (CAP) activates transcription at P(lac), P(gal), and other promoters through interactions with the RNA polymerase alpha subunit carboxyl-terminal domain (alphaCTD). We determined the crystal structure of the CAP-alphaCTD-DNA complex at a resolution of 3.1 angstroms. CAP makes direct protein-protein interactions with alphaCTD, and alphaCTD makes direct protein-DNA interactions with the DNA segment adjacent to the DNA site for CAP. There are no large-scale conformational changes in CAP and alphaCTD, and the interface between CAP and alphaCTD is small. These findings are consistent with the proposal that activation involves a simple "recruitment" mechanism.