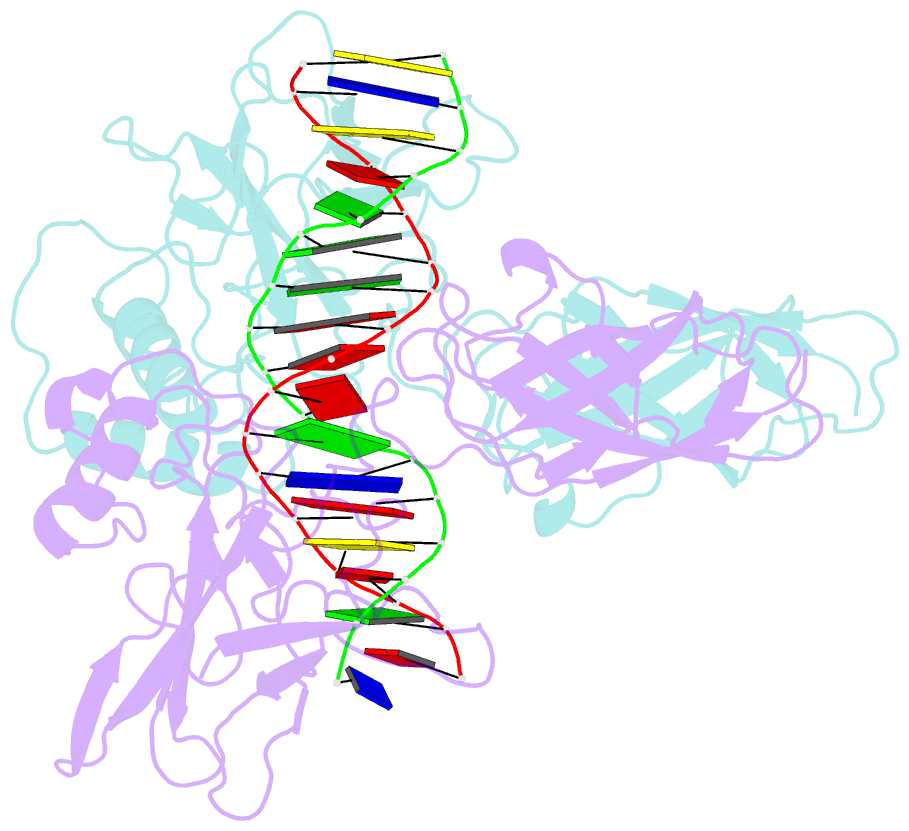
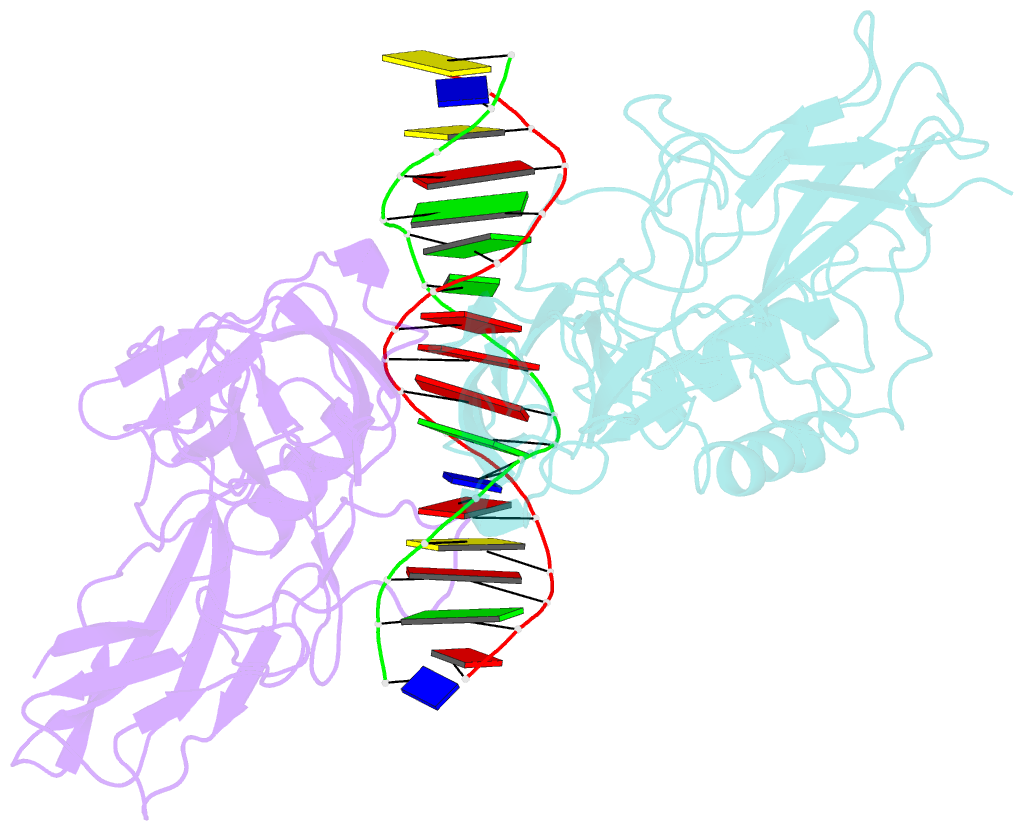
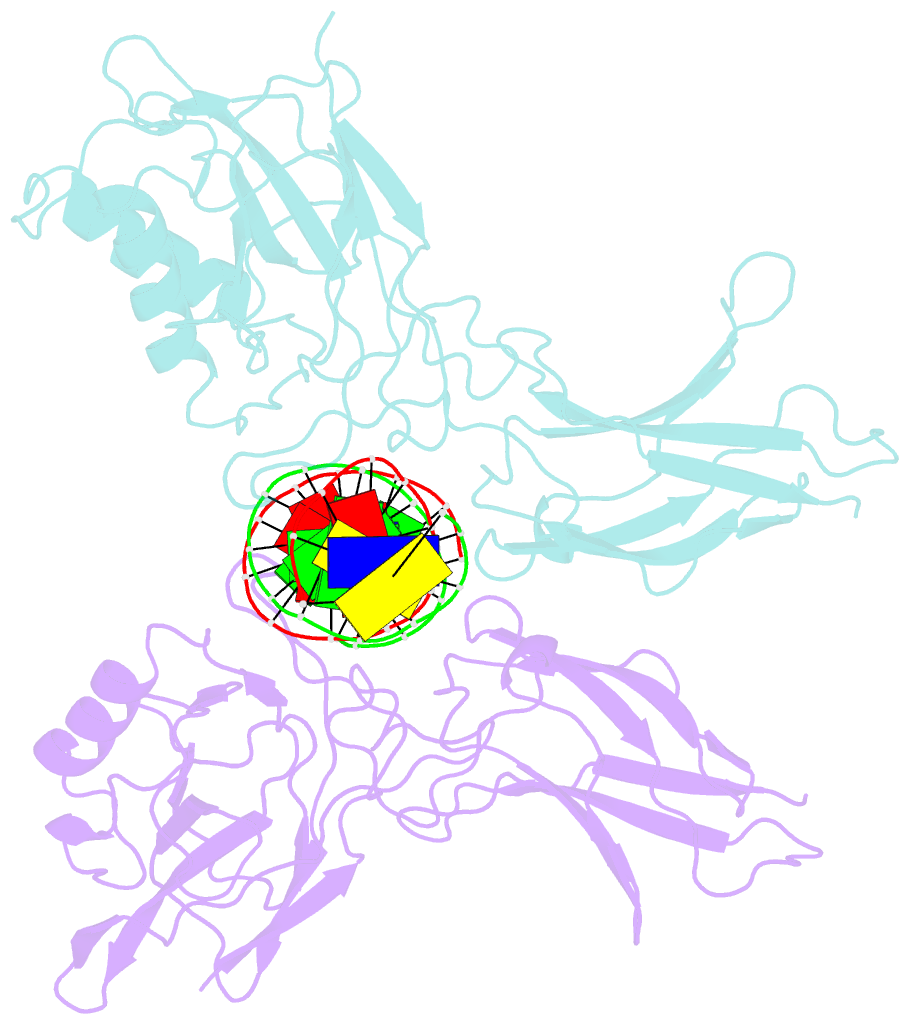
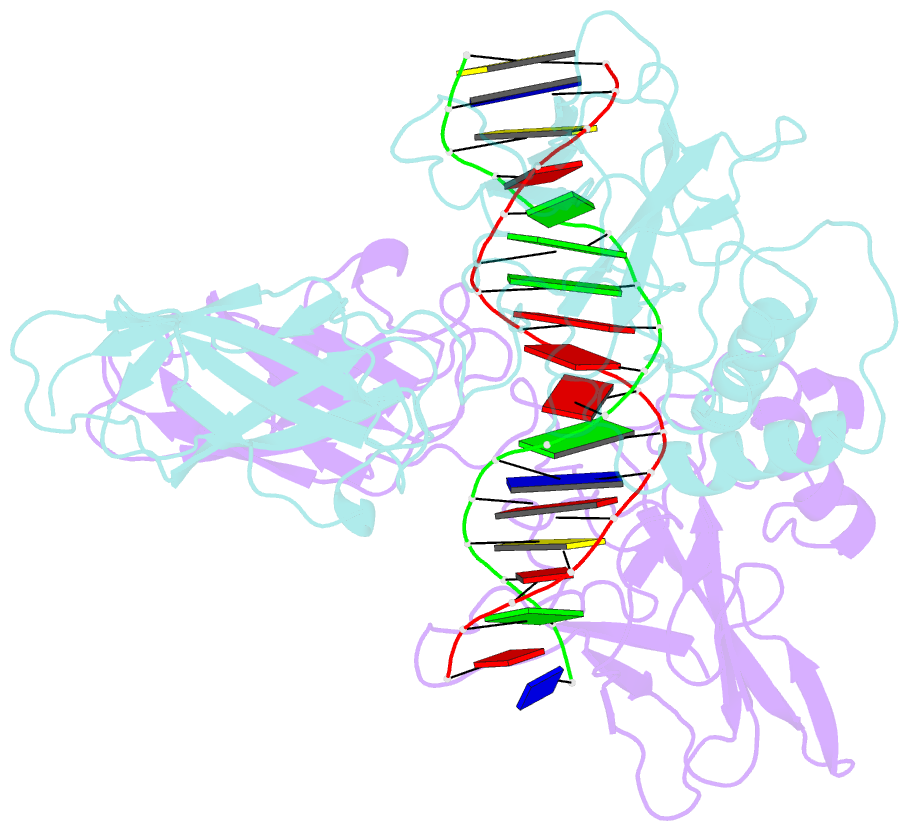
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 1lei; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- transcription-DNA
- Method
- X-ray (2.7 Å)
- Summary
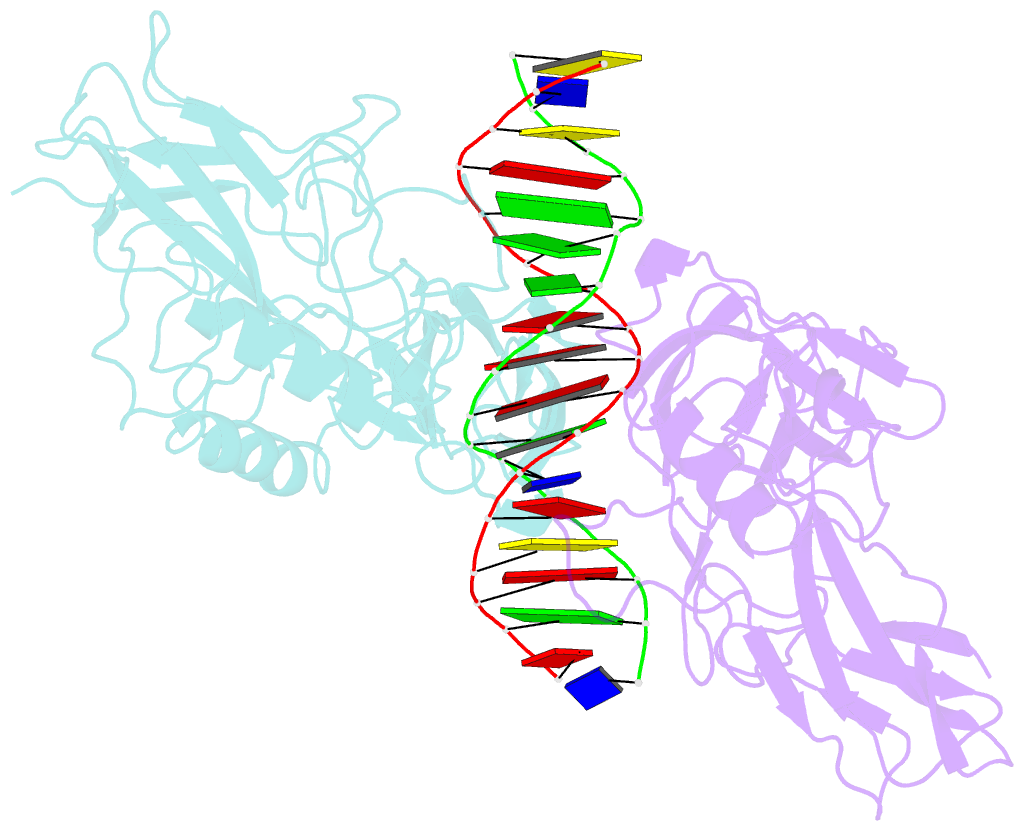
- The kb DNA sequence from the hlv-ltr functions as an allosteric regulator of hiv transcription
- Reference
- Chen-Park FE, Huang DB, Noro B, Thanos D, Ghosh G (2002): "The kB DNA sequence from the HIV Long Terminal Repeat functions as an allosteric regulator of HIV transcription." J.Biol.Chem., 277, 24701-24708. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M200007200.
- Abstract
- NF-kappaB is an inducible transcription factor involved in the immune response, inflammation, and viral transcription. To address how the two NF-kappaB and three Sp1 binding sites of the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) long terminal repeat (LTR) control multiple activator assembly and transcription, we first observed and compared unique conformations between the crystallographic structure of the NF-kappaB p50.p65 heterodimer bound to the uPA-kappaB target site to that of the p50.p65.HIV-kappaB complex. Next, cooperativity between two NF-kappaB molecules bound to tandem HIV-kappaB sequences was measured as well as that of NF-kappaB and transcription factor Sp1 when bound to adjacent sites. The cooperativity of hybrid HIV-LTR enhancers was measured with the 3' kappaB site converted to uPA-kappaB or to interferon beta gene enhancer kappaB. The hybrids were defective in transcriptional activator assembly and less active transcriptionally. These functional differences correlate with observed conformational differences and demonstrate that distinct kappaB DNA sequences function as allosteric regulators in a gene-specific manner.