Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 1lq1; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- transcription-DNA
- Method
- X-ray (2.3 Å)
- Summary
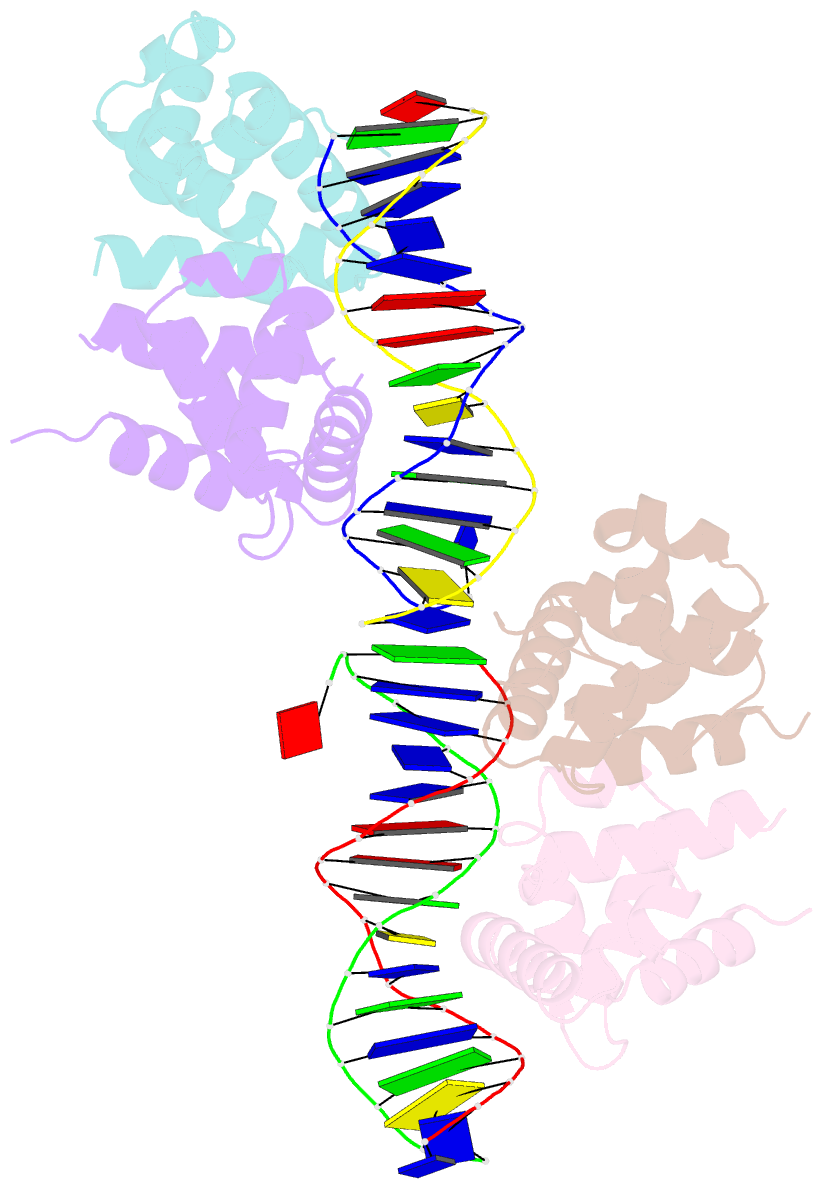
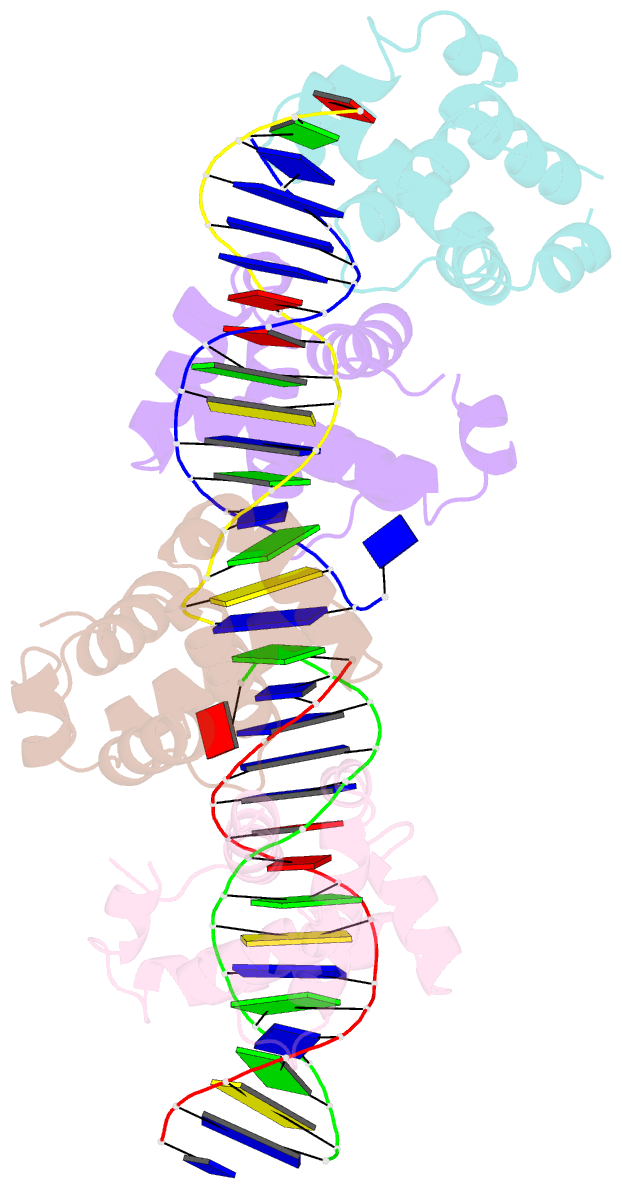
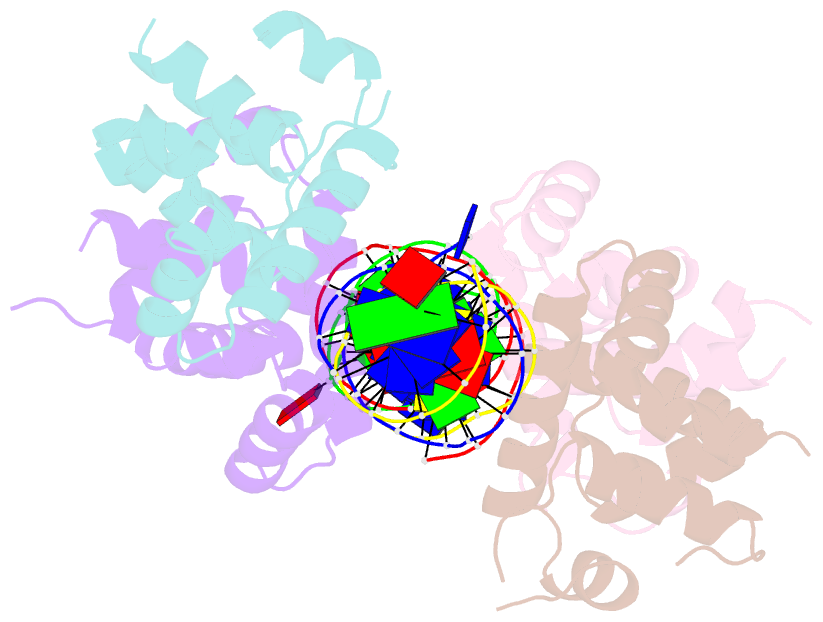
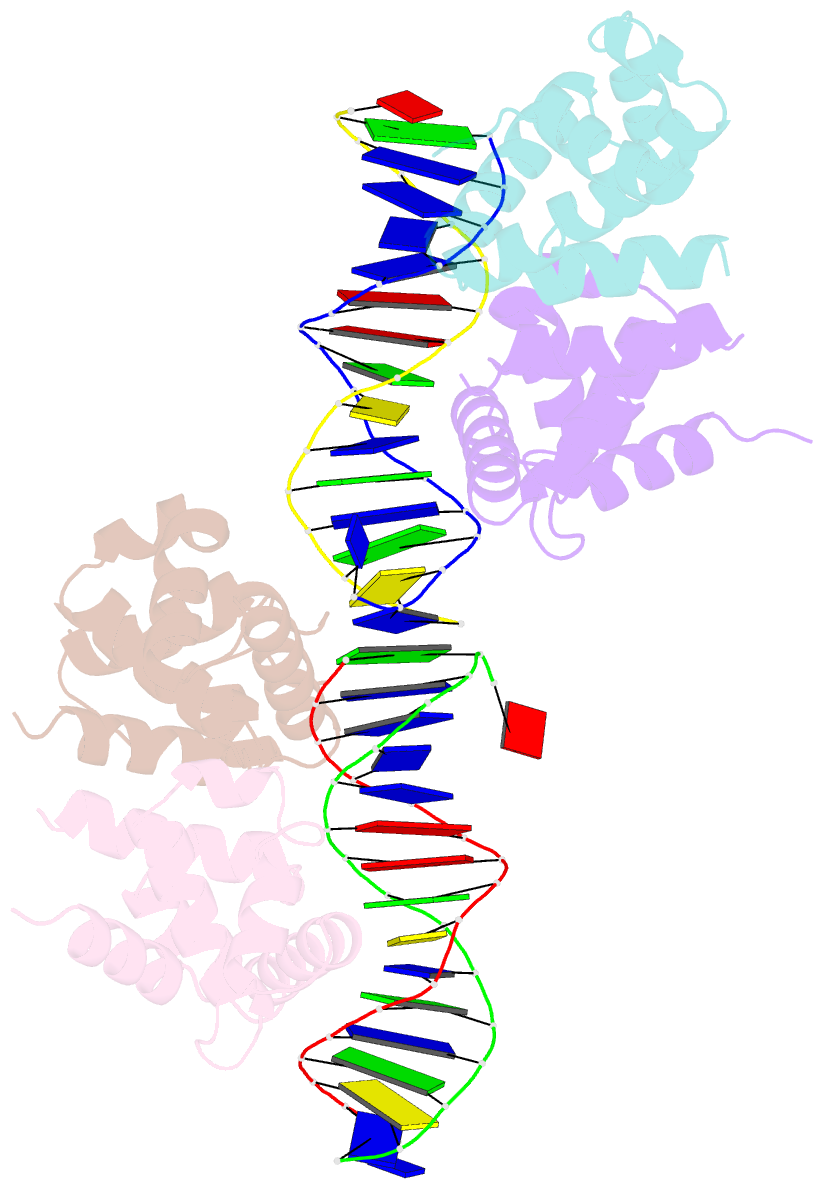
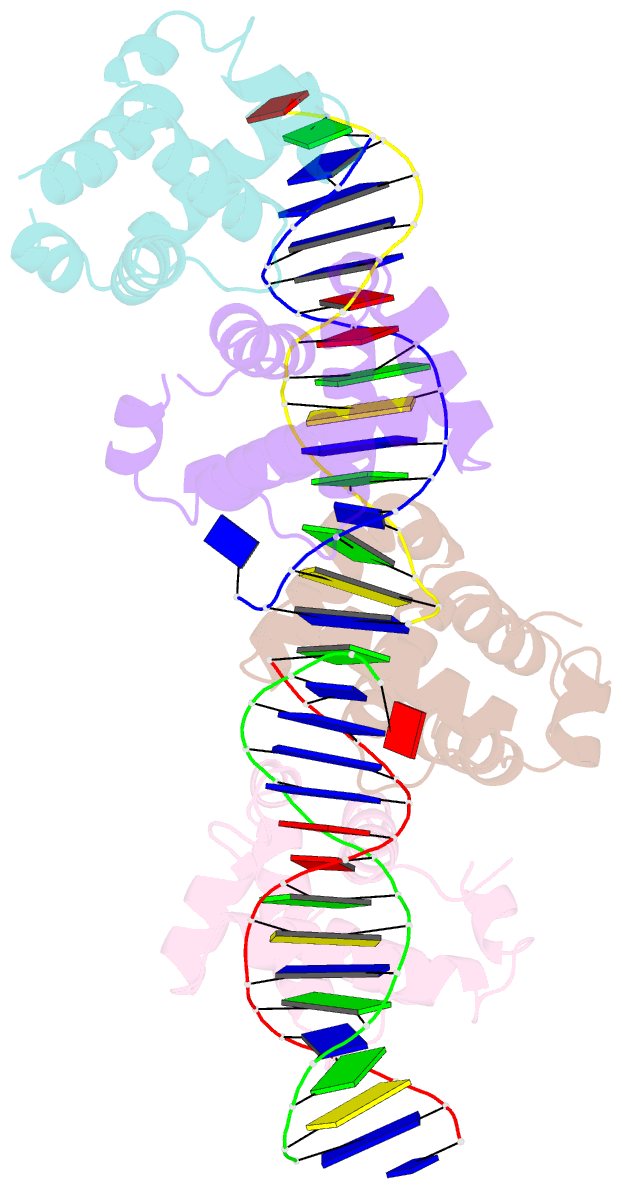
- DNA complexed structure of the key transcription factor initiating development in sporulation bacteria
- Reference
- Zhao H, Msadek T, Zapf J, Madhusudan, Hoch JA, Varughese KI (2002): "DNA complexed structure of the key transcription factor initiating development in sporulating bacteria." Structure, 10, 1041-1050. doi: 10.1016/S0969-2126(02)00803-1.
- Abstract
- Sporulation in Bacillus species, the ultimate bacterial adaptive response, requires the precisely coordinated expression of a complex genetic pathway, and is initiated through the accumulation of the phosphorylated form of Spo0A, a pleiotropic response regulator transcription factor. Spo0A controls the transcription of several hundred genes in all spore-forming Bacilli including genes for sporulation and toxin regulation in pathogens such as Bacillus anthracis. The crystal structure of the effector domain of Spo0A from Bacillus subtilis in complex with its DNA target was determined. In the crystal lattice, two molecules form a tandem dimer upon binding to adjacent sites on DNA. The protein:protein and protein:DNA interfaces revealed in the crystal provide a basis for interpreting the transcription activation process and for the design of drugs to counter infections by these bacteria.