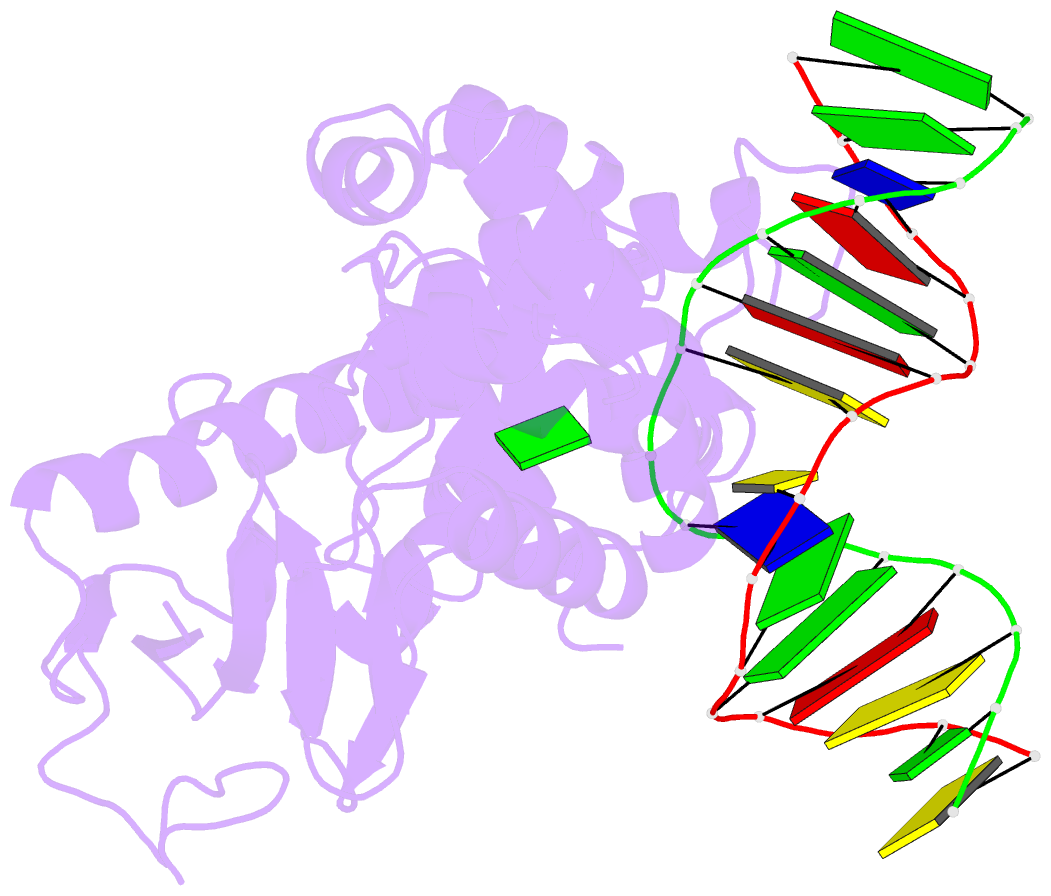
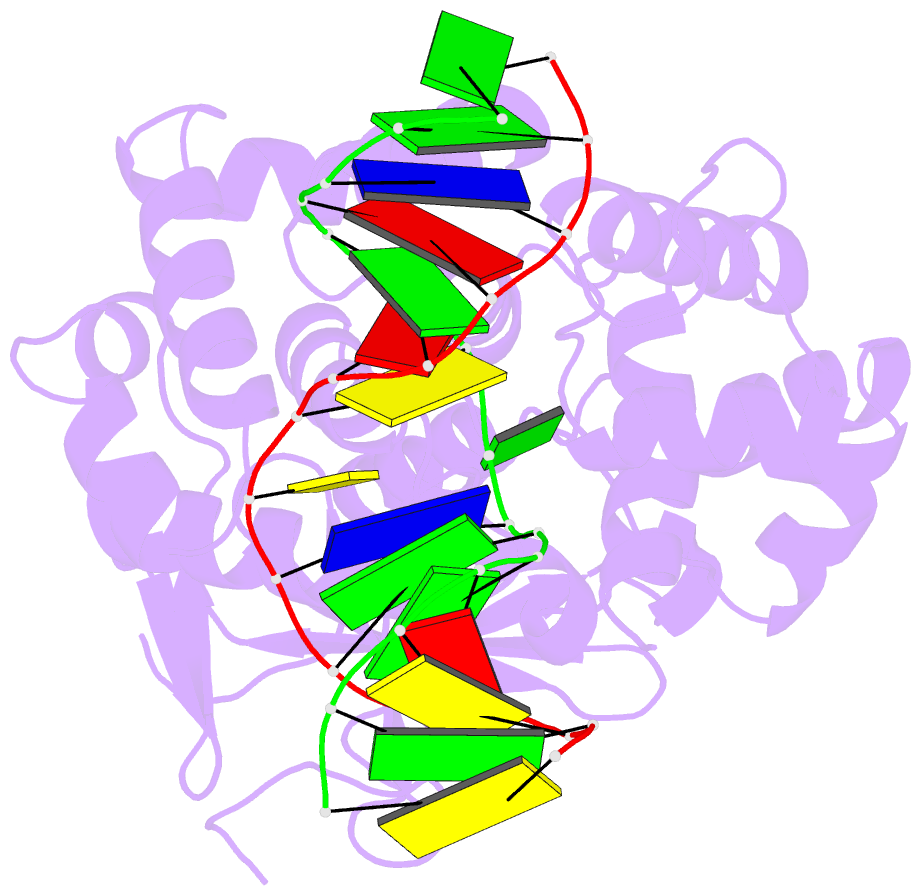
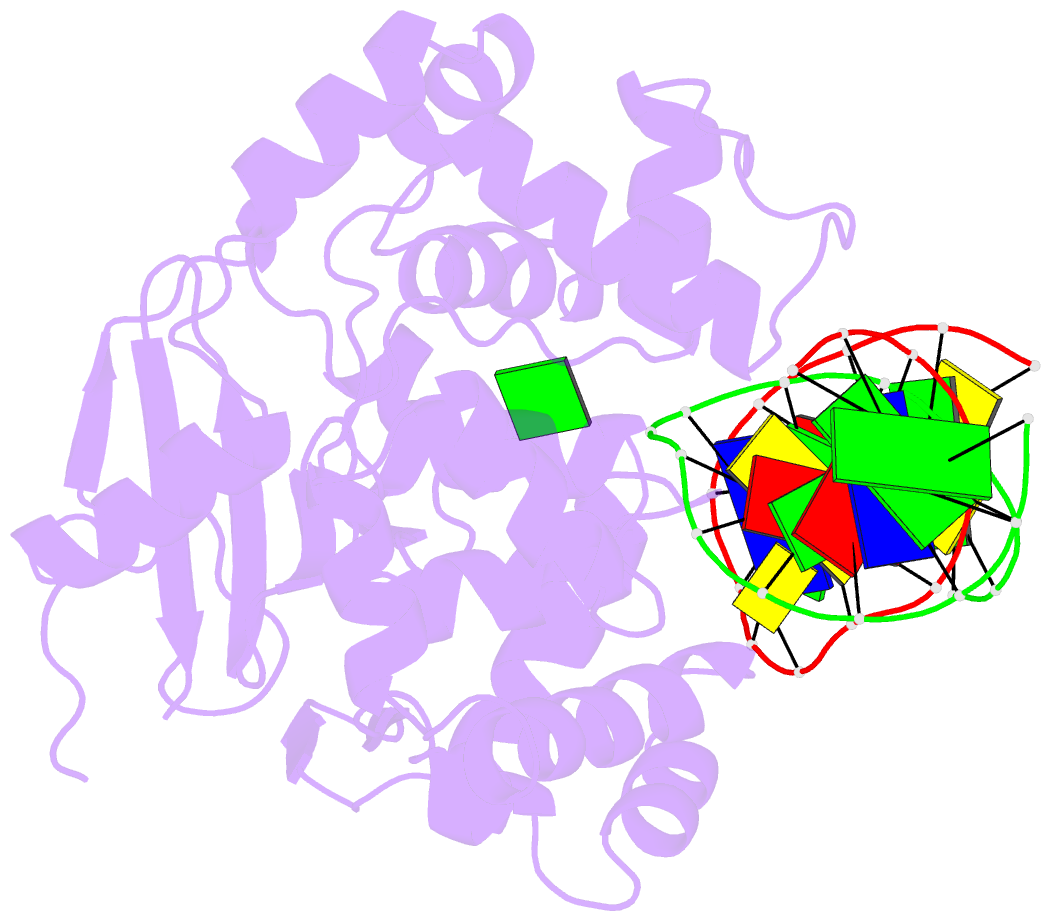
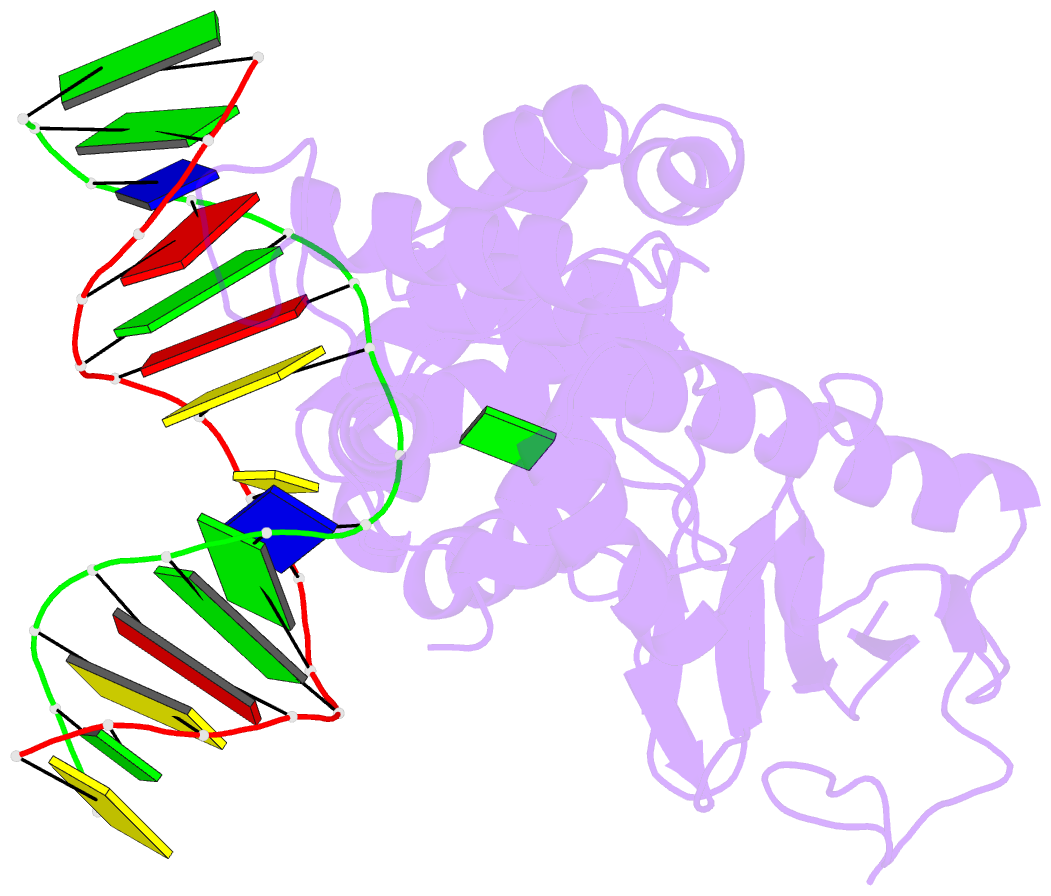
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 1lwv; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- hydrolase-DNA
- Method
- X-ray (2.3 Å)
- Summary
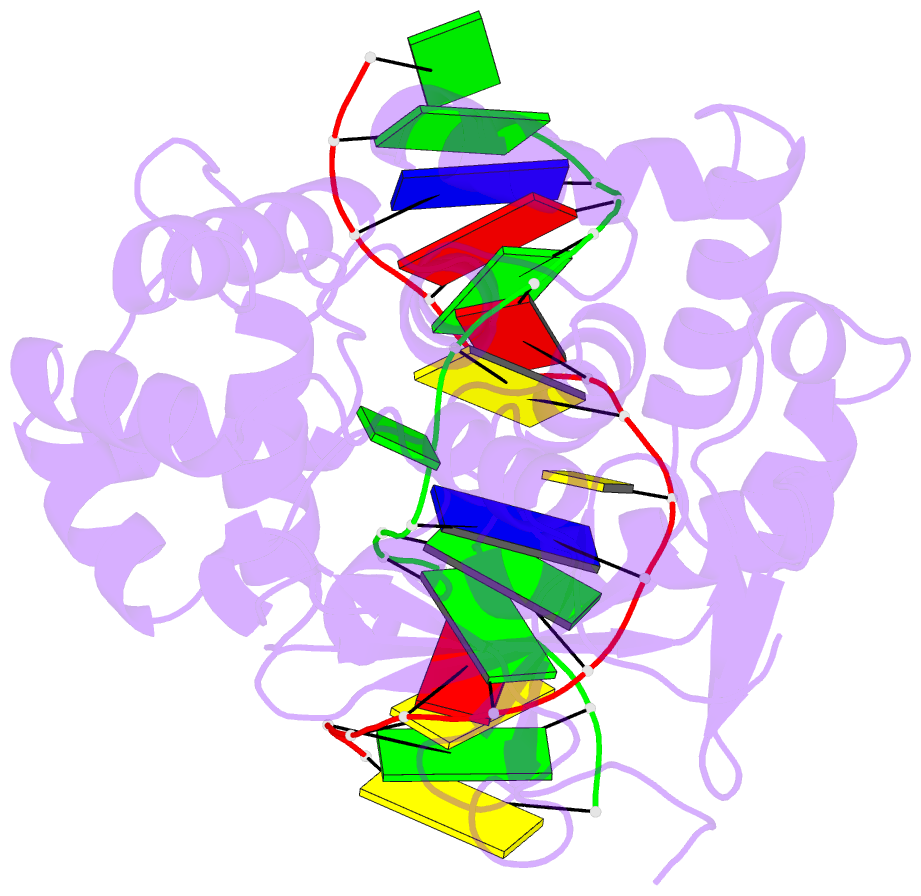
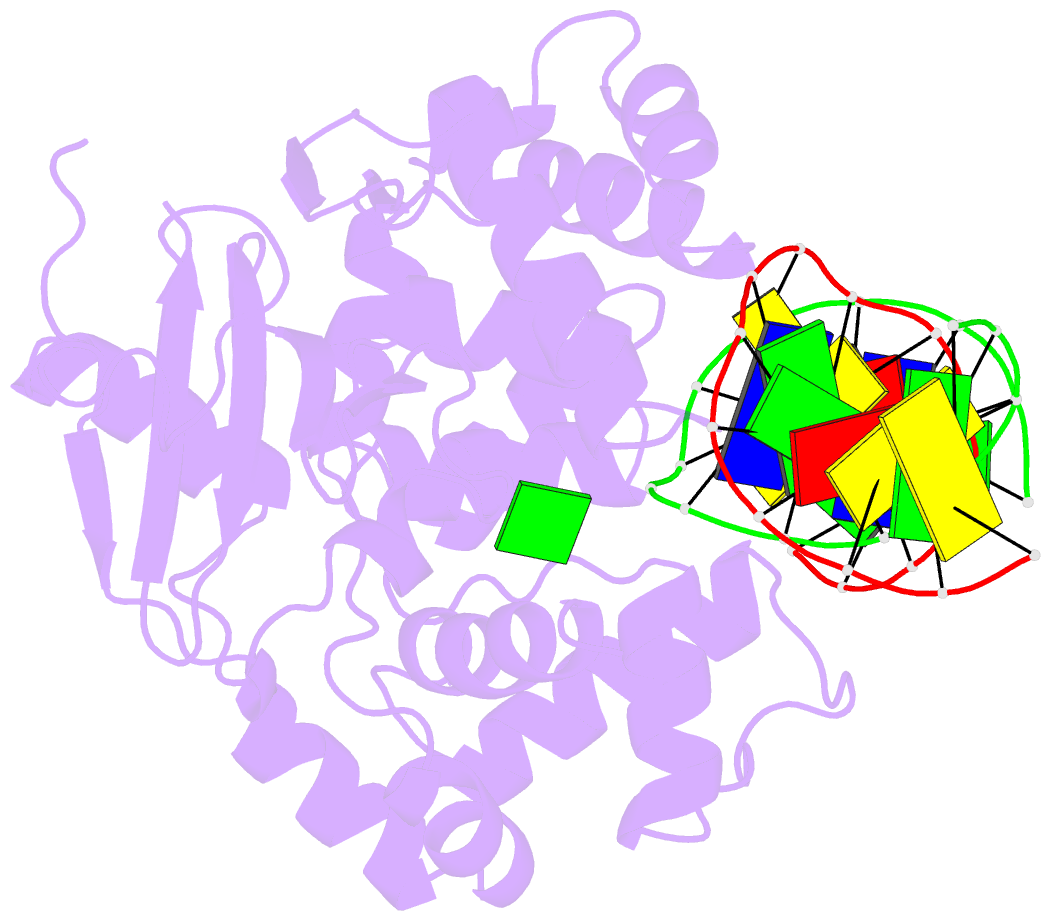
- Borohydride-trapped hogg1 intermediate structure co-crystallized with 8-aminoguanine
- Reference
- Fromme JC, Bruner SD, Yang W, Karplus M, Verdine GL (2003): "Product-Assisted Catalysis in Base Excision DNA Repair." Nat.Struct.Biol., 10, 204-211. doi: 10.1038/nsb902.
- Abstract
- Most spontaneous damage to bases in DNA is corrected through the action of the base-excision DNA repair pathway. Base excision repair is initiated by DNA glycosylases, lesion-specific enzymes that intercept aberrant bases in DNA and catalyze their excision. How such proteins accomplish the feat of catalyzing no fewer than five sequential reaction steps using a single active site has been unknown. To help answer this, we report the structure of a trapped catalytic intermediate in DNA repair by human 8-oxoguanine DNA glycosylase. This structure and supporting biochemical results reveal that the enzyme sequesters the excised lesion base and exploits it as a cofactor to participate in catalysis. To our knowledge, the present example represents the first documented case of product-assisted catalysis in an enzyme-catalyzed reaction.