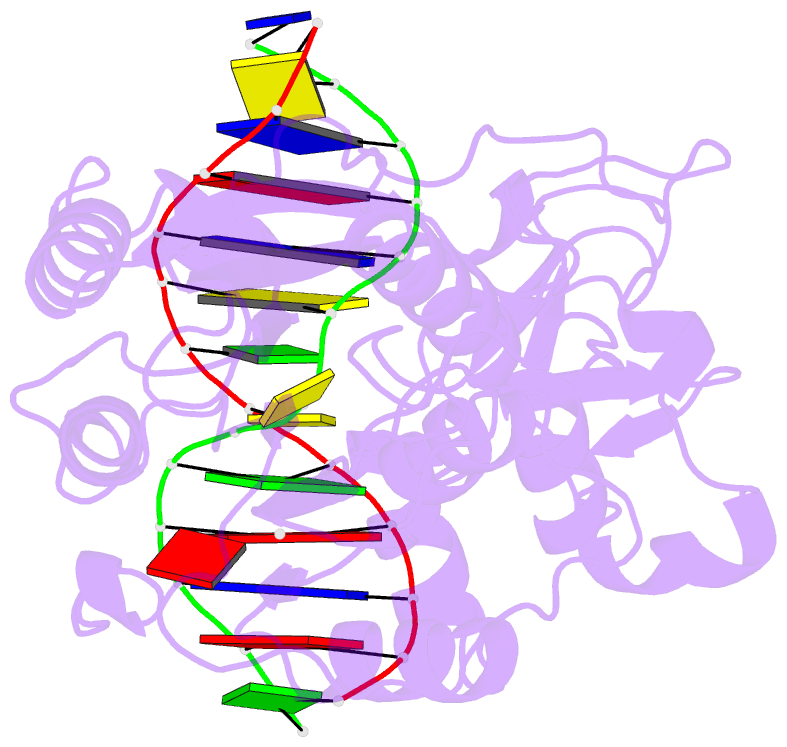
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 1mht; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- transferase-DNA
- Method
- X-ray (2.6 Å)
- Summary
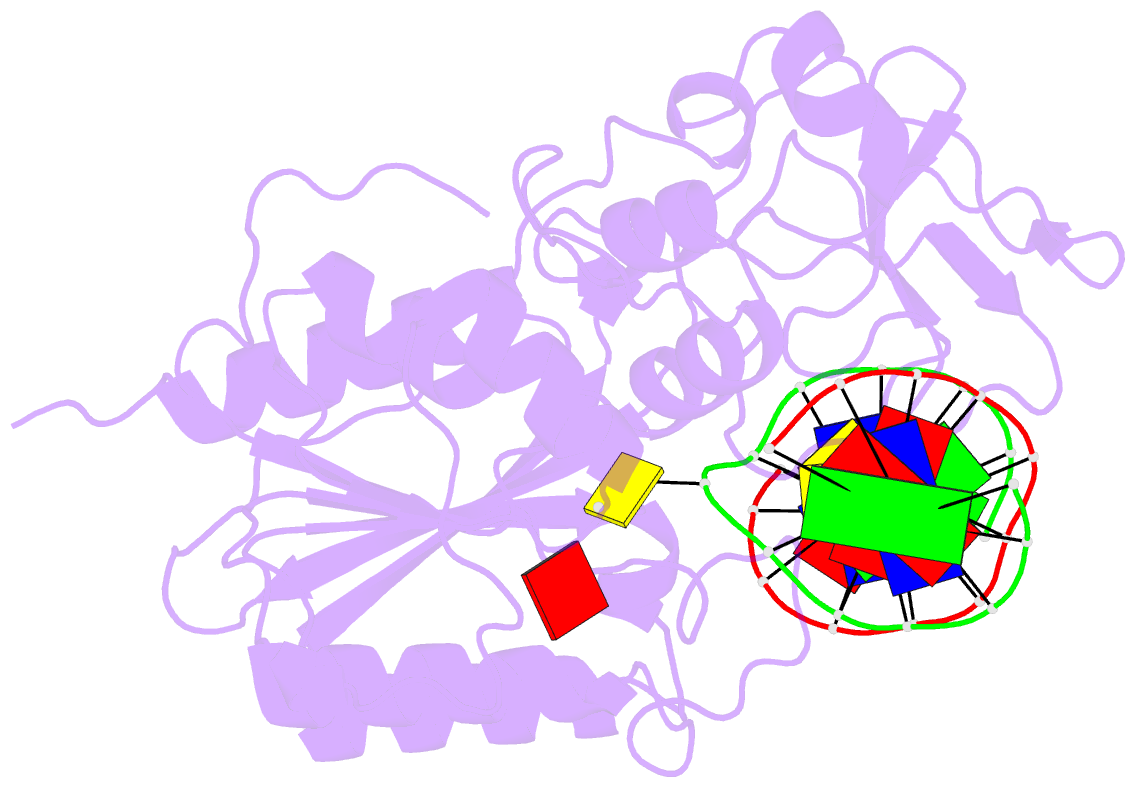
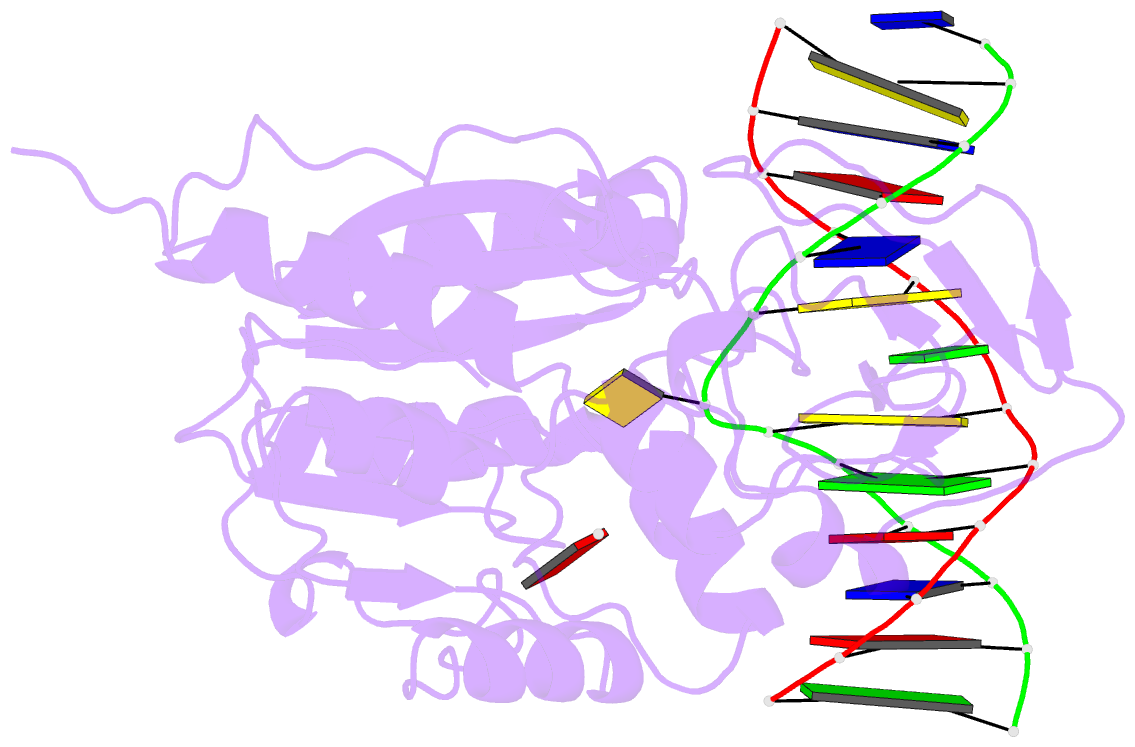
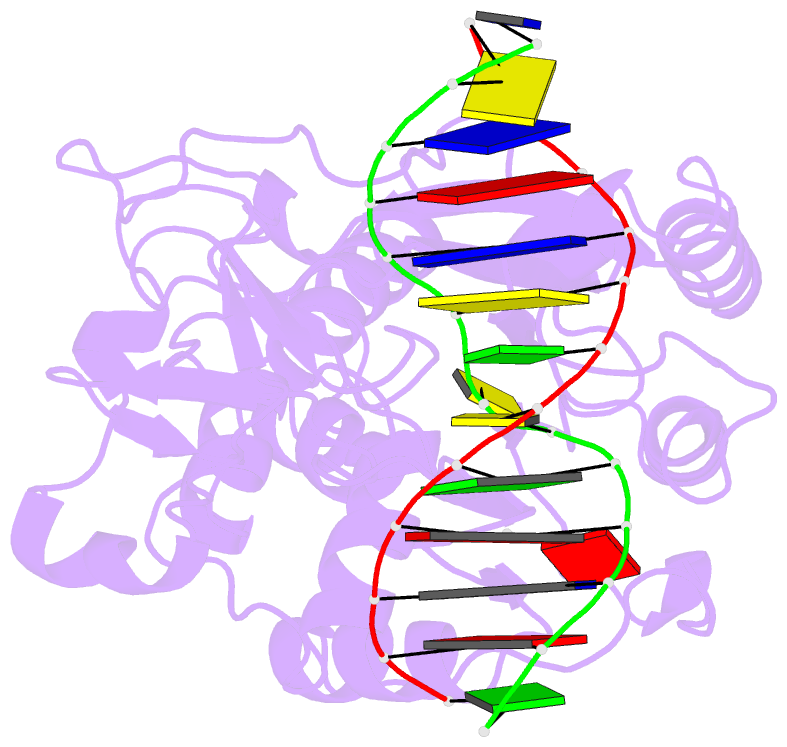
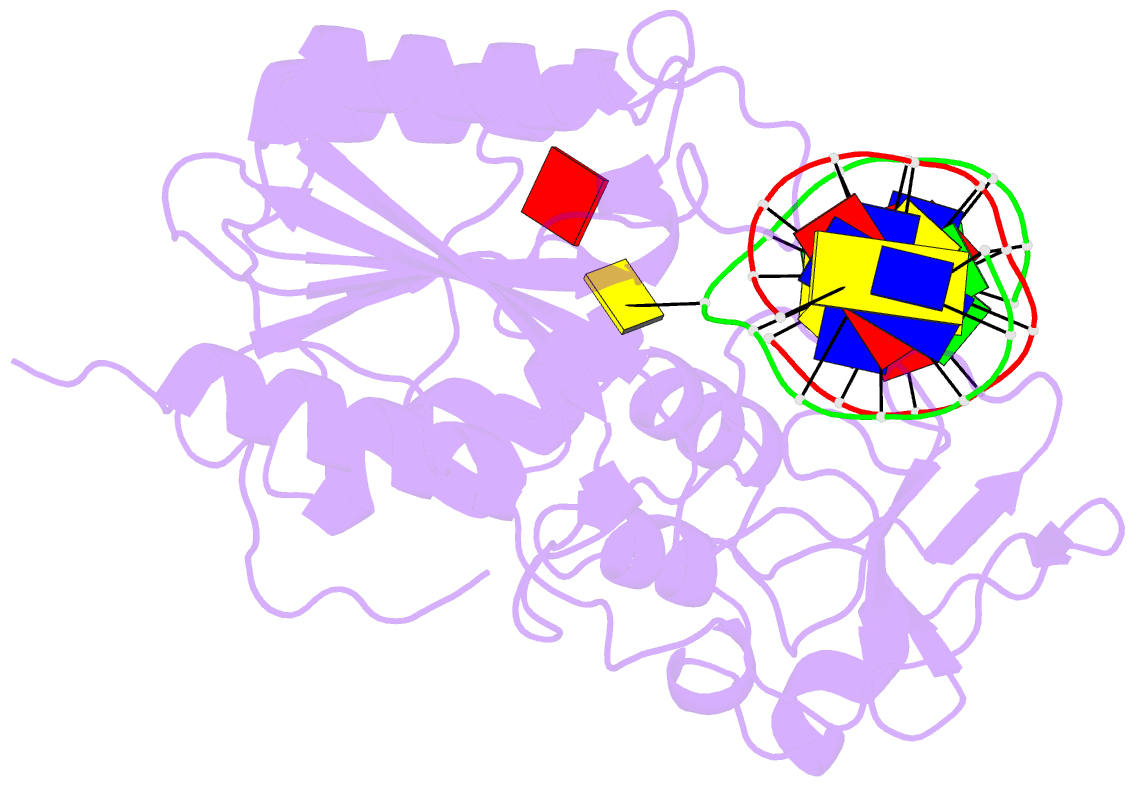
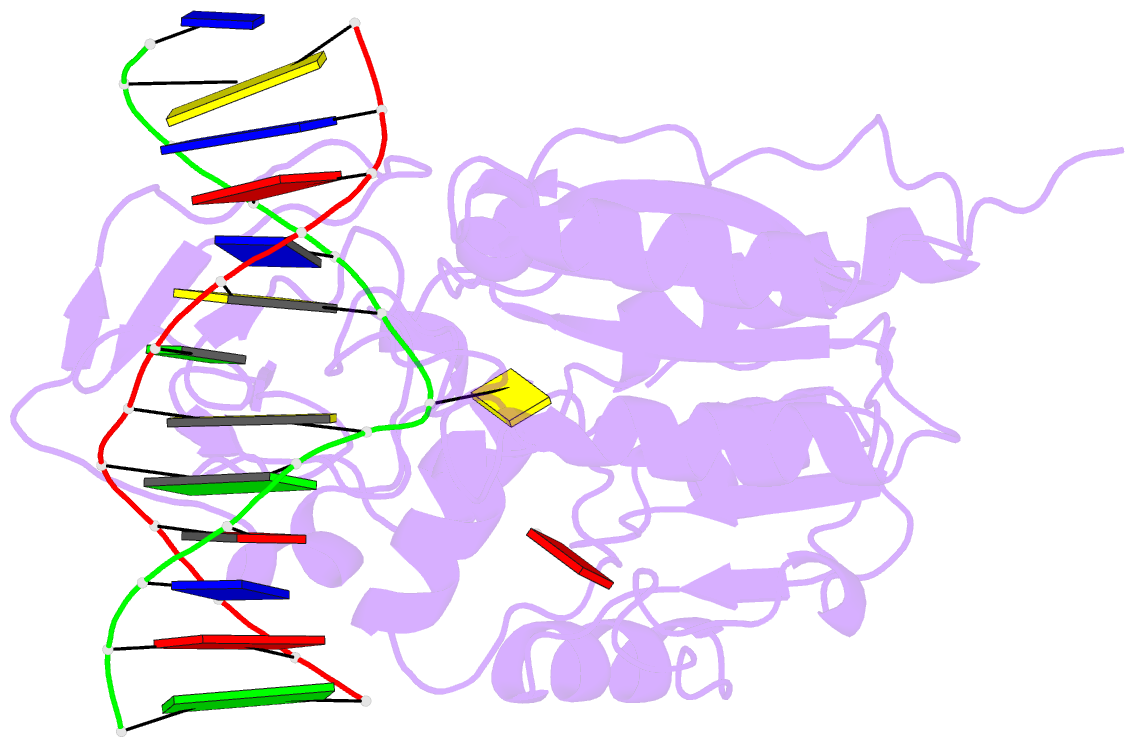
- Covalent ternary structure of hhai methyltransferase, DNA and s-adenosyl-l-homocysteine
- Reference
- Klimasauskas S, Kumar S, Roberts RJ, Cheng X (1994): "HhaI methyltransferase flips its target base out of the DNA helix." Cell(Cambridge,Mass.), 76, 357-369. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90342-5.
- Abstract
- The crystal structure has been determined at 2.8 A resolution for a chemically-trapped covalent reaction intermediate between the HhaI DNA cytosine-5-methyltransferase, S-adenosyl-L-homocysteine, and a duplex 13-mer DNA oligonucleotide containing methylated 5-fluorocytosine at its target. The DNA is located in a cleft between the two domains of the protein and has the characteristic conformation of B-form DNA, except for a disrupted G-C base pair that contains the target cytosine. The cytosine residue has swung completely out of the DNA helix and is positioned in the active site, which itself has undergone a large conformational change. The DNA is contacted from both the major and the minor grooves, but almost all base-specific interactions between the enzyme and the recognition bases occur in the major groove, through two glycine-rich loops from the small domain. The structure suggests how the active nucleophile reaches its target, directly supports the proposed mechanism for cytosine-5 DNA methylation, and illustrates a novel mode of sequence-specific DNA recognition.