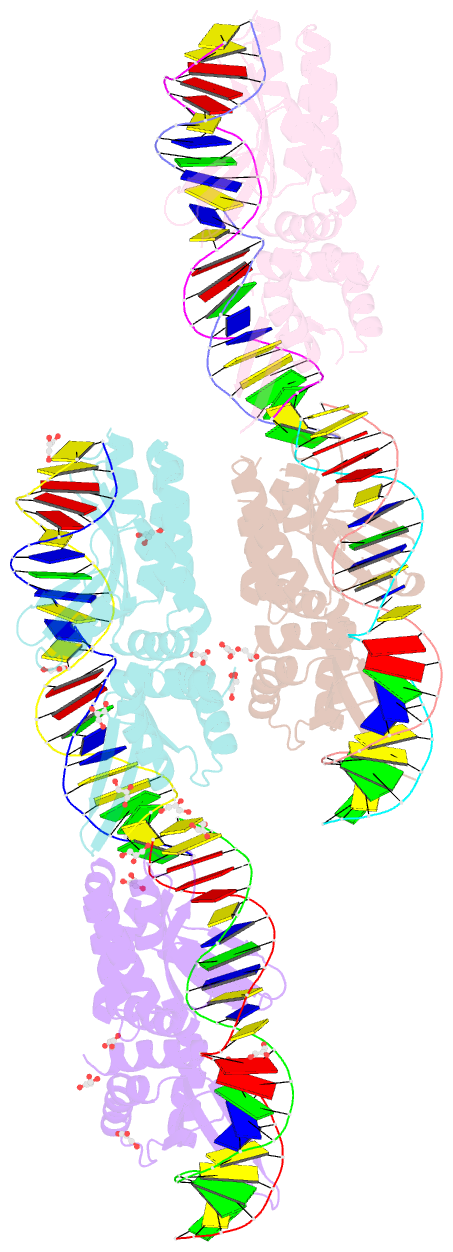
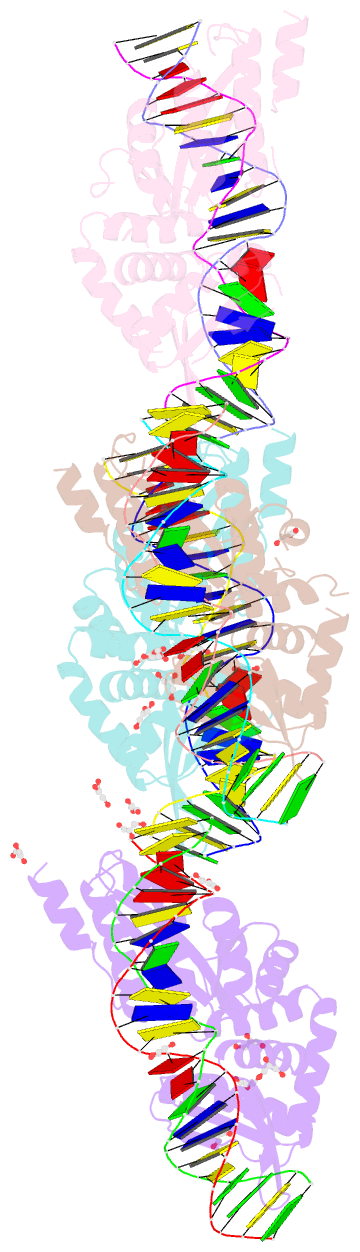
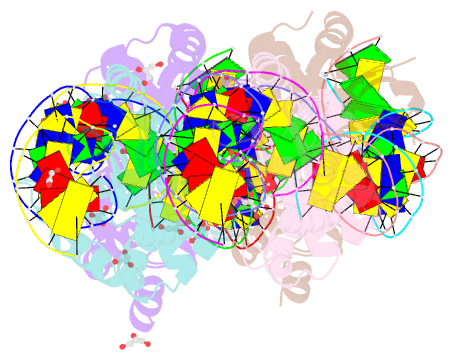
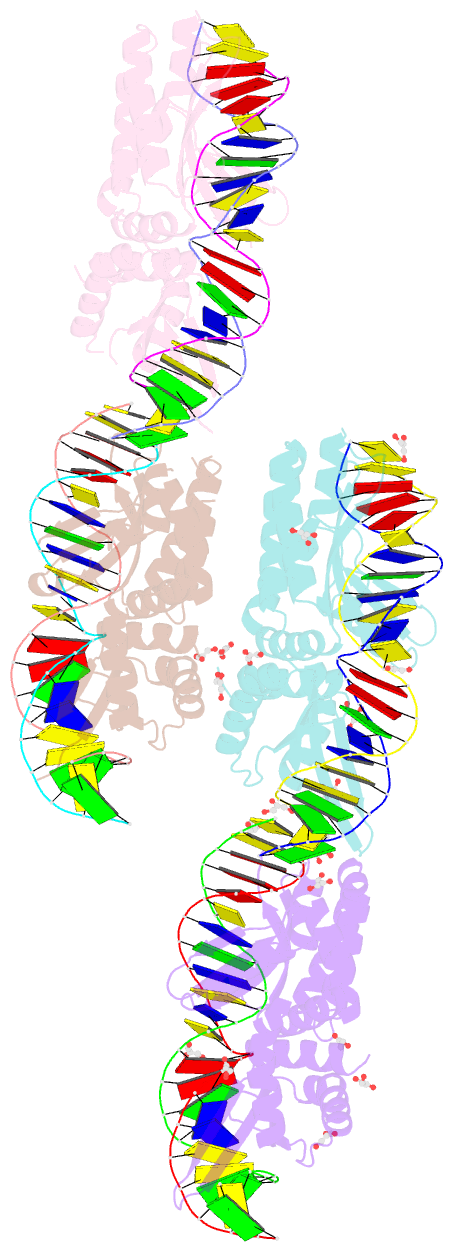
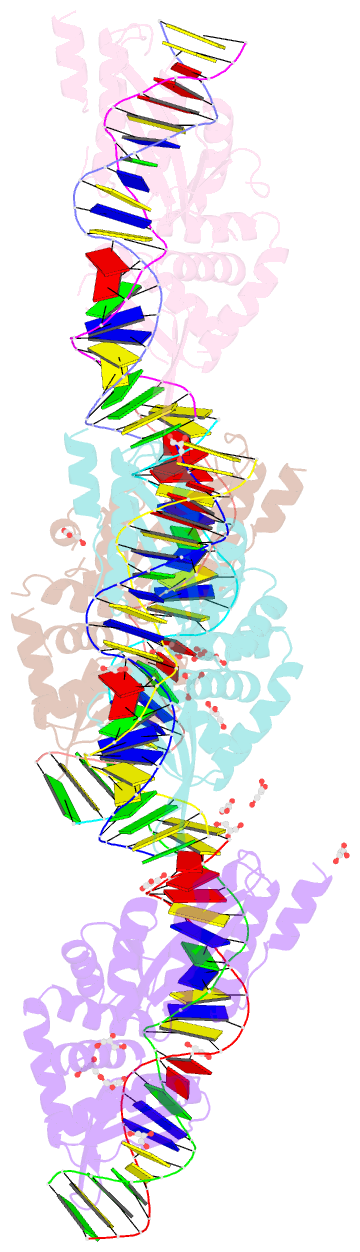
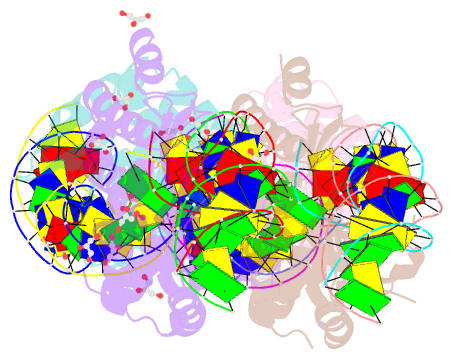
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 1mow; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- hydrolase-DNA
- Method
- X-ray (2.4 Å)
- Summary
- E-drei
- Reference
- Chevalier BS, Kortemme T, Chadsey MS, Baker D, Monnat Jr RJ, Stoddard BL (2002): "Design, Activity and Structure of a Highly Specific Artificial Endonuclease." Mol.Cell, 10, 895-905. doi: 10.1016/S1097-2765(02)00690-1.
- Abstract
- We have generated an artificial highly specific endonuclease by fusing domains of homing endonucleases I-DmoI and I-CreI and creating a new 1400 A(2) protein interface between these domains. Protein engineering was accomplished by combining computational redesign and an in vivo protein-folding screen. The resulting enzyme, E-DreI (Engineered I-DmoI/I-CreI), binds a long chimeric DNA target site with nanomolar affinity, cleaving it precisely at a rate equivalent to its natural parents. The structure of an E-DreI/DNA complex demonstrates the accuracy of the protein interface redesign algorithm and reveals how catalytic function is maintained during the creation of the new endonuclease. These results indicate that it may be possible to generate novel highly specific DNA binding proteins from homing endonucleases.