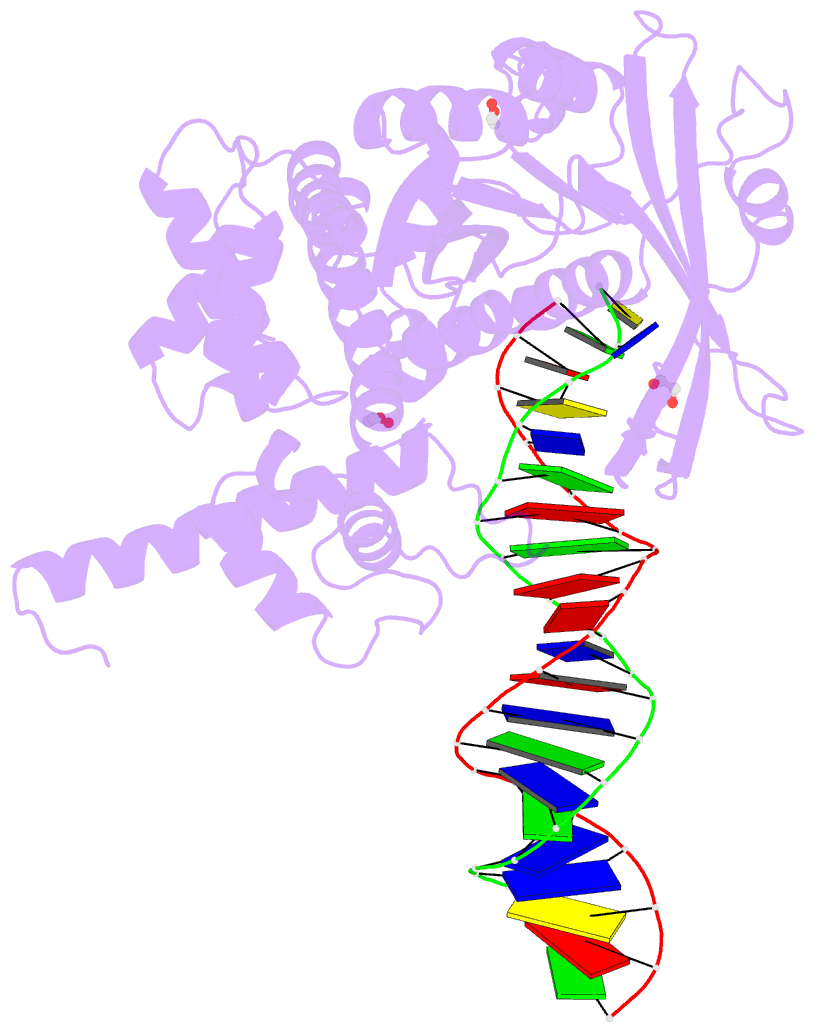
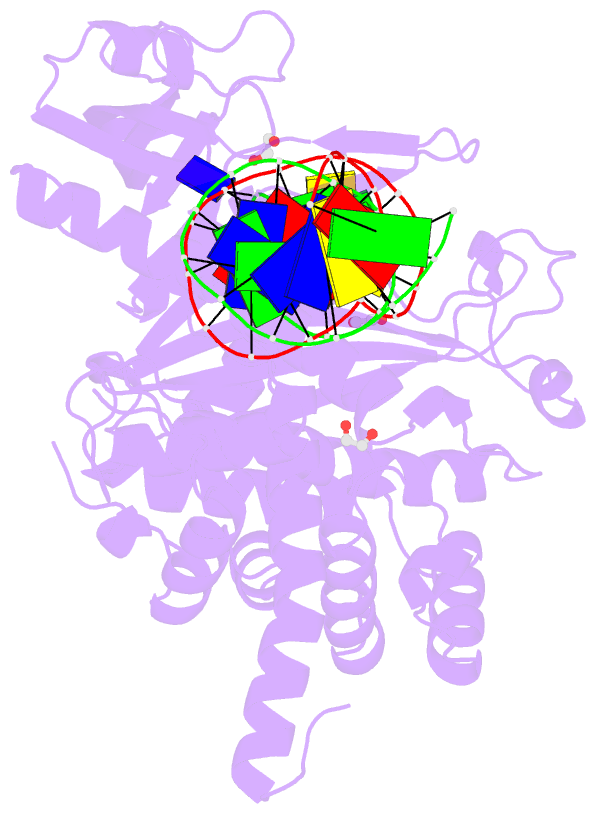
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 1mus; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- transcription-DNA
- Method
- X-ray (1.9 Å)
- Summary
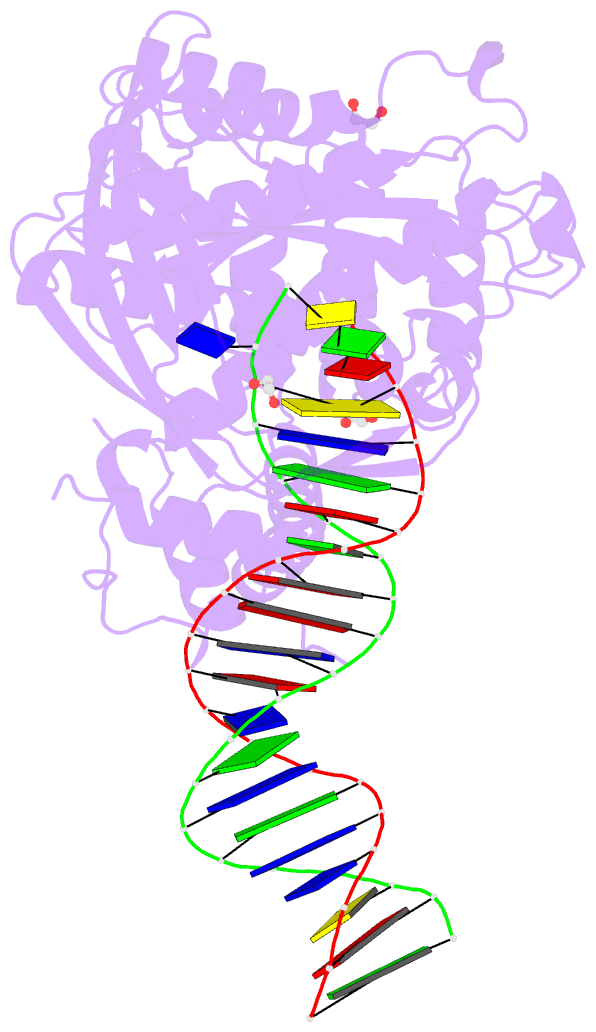
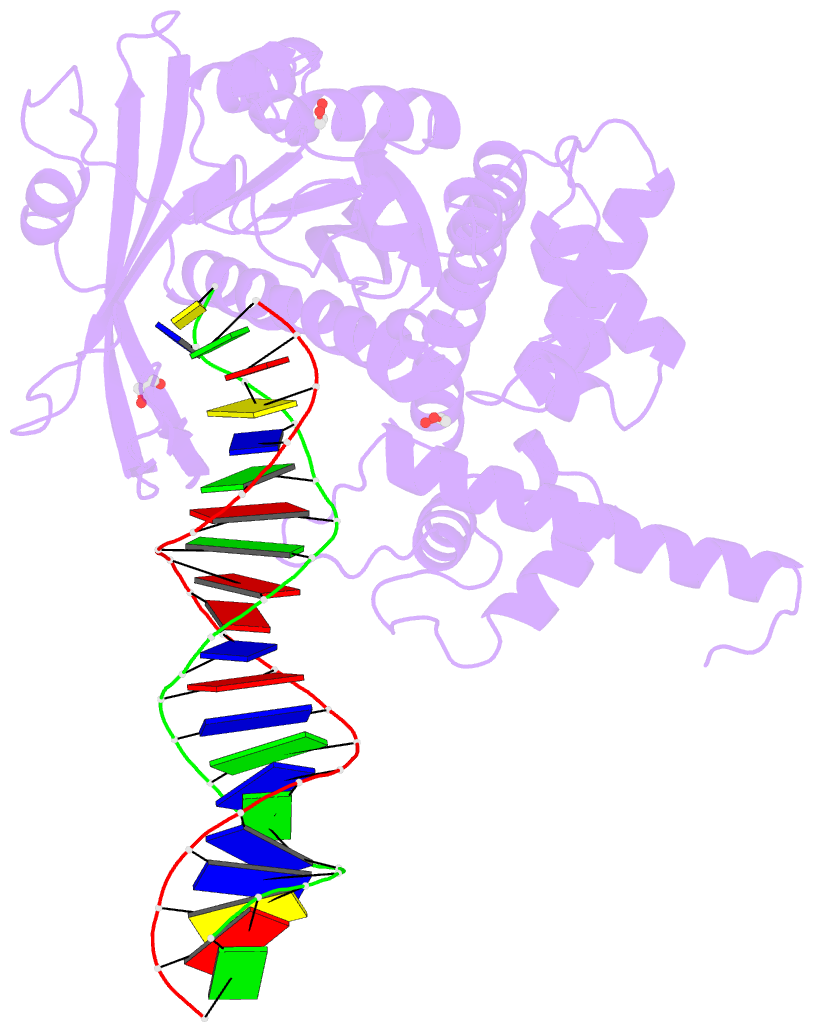
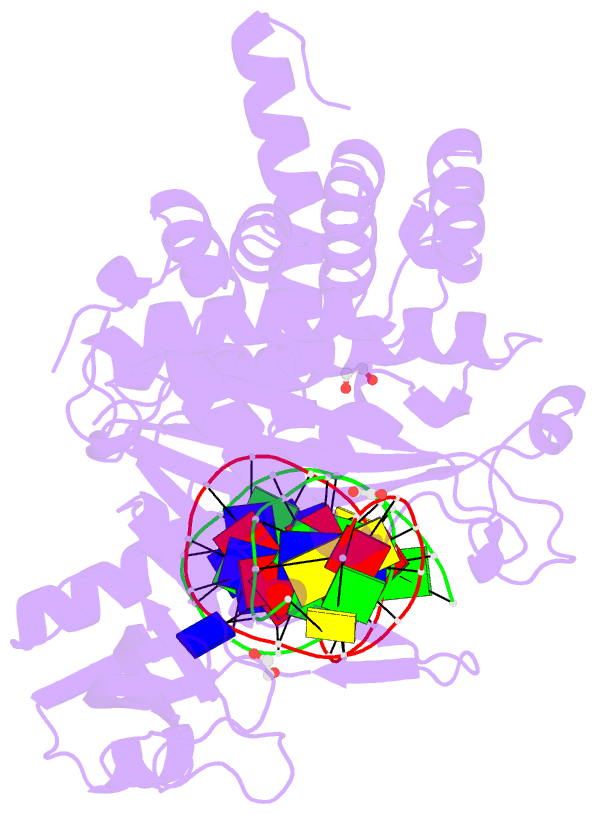
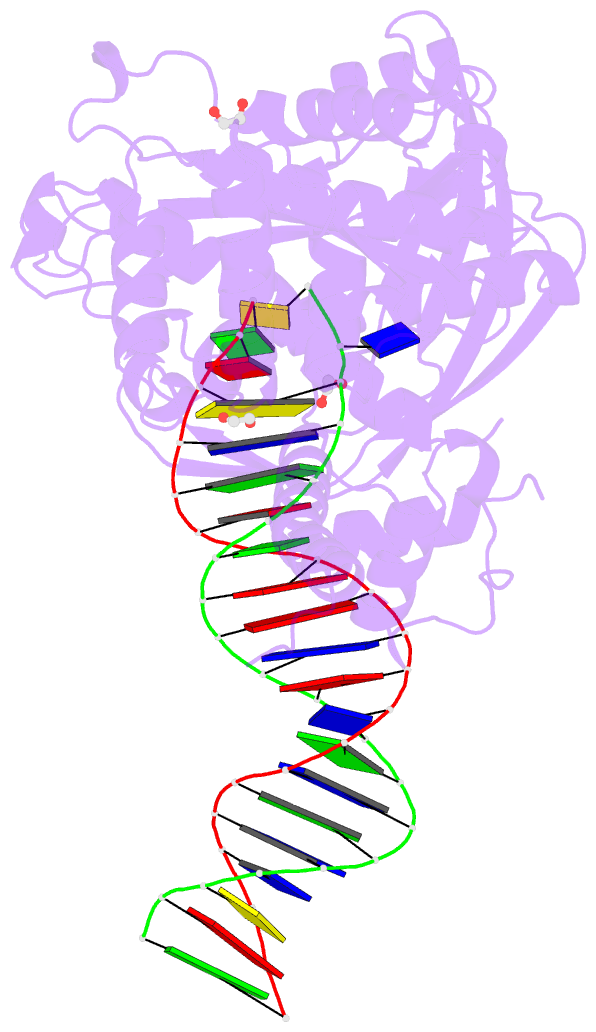
- Crystal structure of tn5 transposase complexed with resolved outside end DNA
- Reference
- Steiniger-White M, Rayment I, Reznikoff WS (2004): "Structure/function insights into Tn5 transposition." Curr.Opin.Struct.Biol., 14, 50-57. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2004.01.008.
- Abstract
- Prokaryotic transposon 5 (Tn5) serves as a model system for studying the molecular mechanism of DNA transposition. Elucidation of the X-ray co-crystal structure of Tn5 transposase complexed with a DNA recognition end sequence provided the first three-dimensional picture of an intermediate in a transposition/retroviral integration pathway. The many Tn5 transposase-DNA co-crystal structures now available complement biochemical and genetic studies, allowing a comprehensive and detailed understanding of transposition mechanisms. Specifically, the structures reveal two different types of protein-DNA contacts: cis contacts, required for initial DNA recognition, and trans contacts, required for catalysis. Protein-protein contacts required for synapsis are also seen. Finally, the two divalent metals in the active site of the transposase support a 'two-metal-ion' mechanism for Tn5 transposition.