Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 1nb7; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- transferase-RNA
- Method
- X-ray (2.9 Å)
- Summary
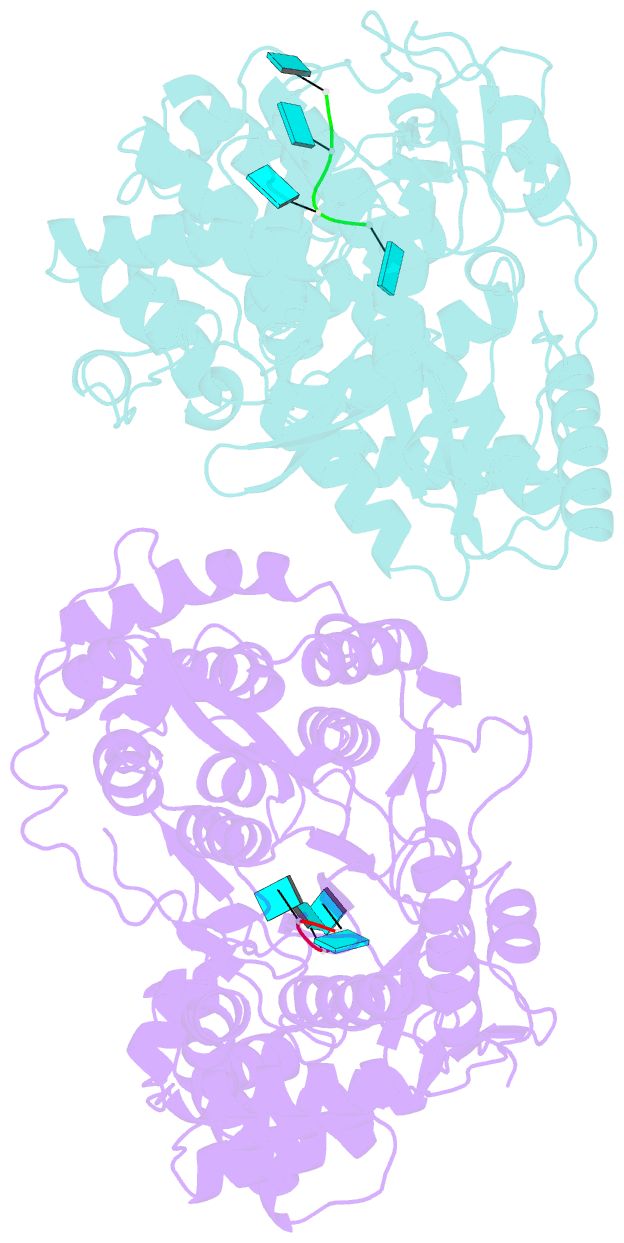
- Hc-j4 RNA polymerase complexed with short RNA template strand
- Reference
- O'Farrell D, Trowbridge R, Rowlands D, Jager J (2003): "Substrate complexes of hepatitis C virus RNA polymerase (HC-J4): structural evidence for nucleotide import and de-novo initiation." J.Mol.Biol., 326, 1025-1035. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(02)01439-0.
- Abstract
- Several crystal structures of the hepatitis C virus NS5B protein (genotype-1b, strain J4) complexed with metal ions, single-stranded RNA or nucleoside-triphosphates have been determined. These complexes illustrate how conserved amino acid side-chains, together with essential structural features within the active site, control nucleotide binding and likely mediate de-novo initiation. The incoming nucleotide interacts with several basic residues from an extension on the NS5B fingers domain, a beta-hairpin from the NS5B thumb domain and the C-terminal arm. The modular, bi-partite fingers domain carries a long binding groove which guides the template towards the catalytic site. The apo-polymerase structure provides unprecedented insights into potential non-nucleoside inhibitor binding sites located between palm and thumb near motif E, which is unique to RNA polymerases and reverse transcriptases.