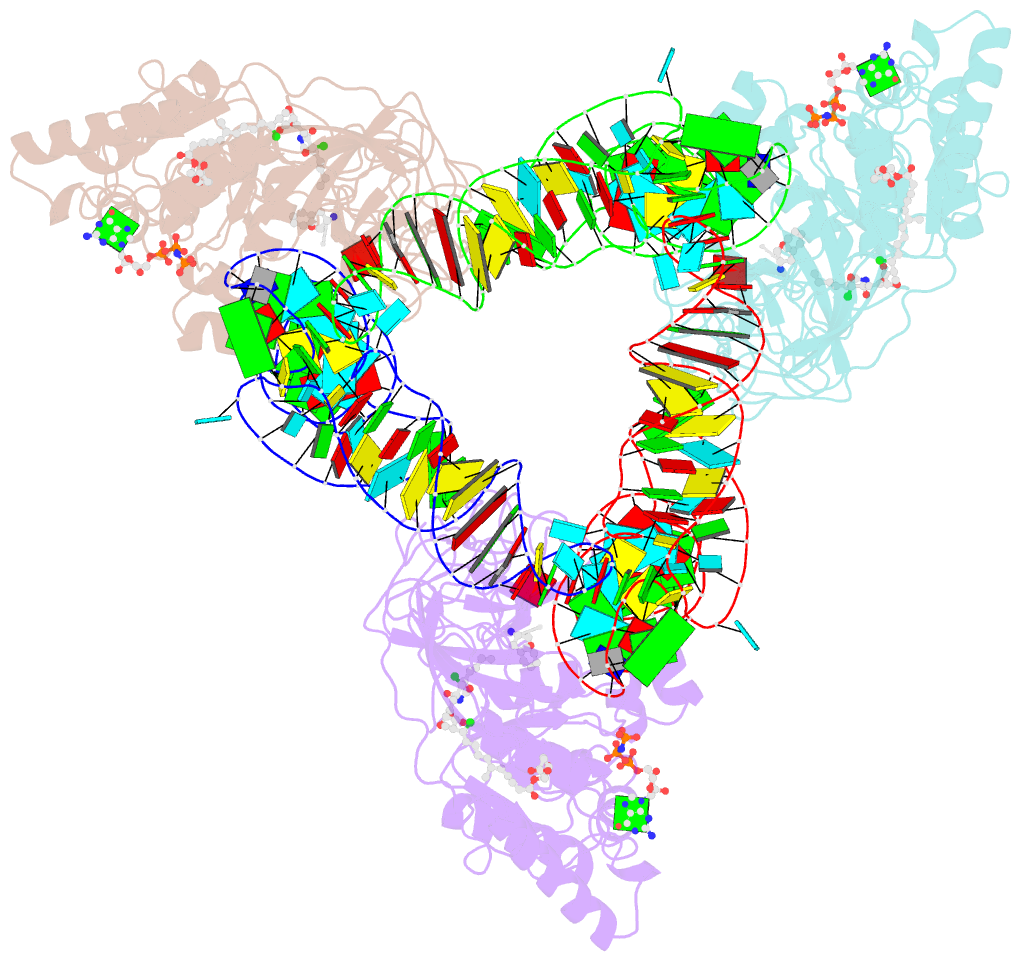
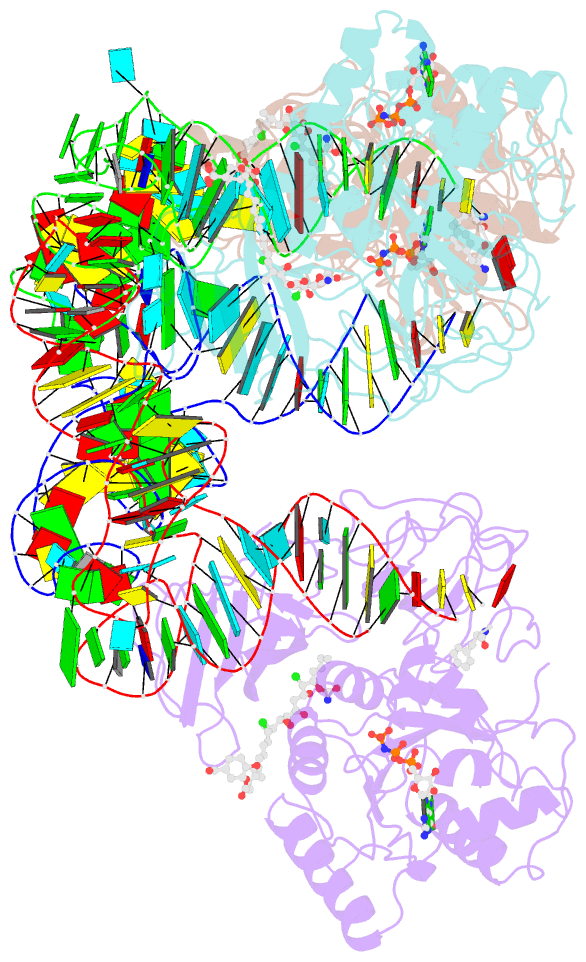
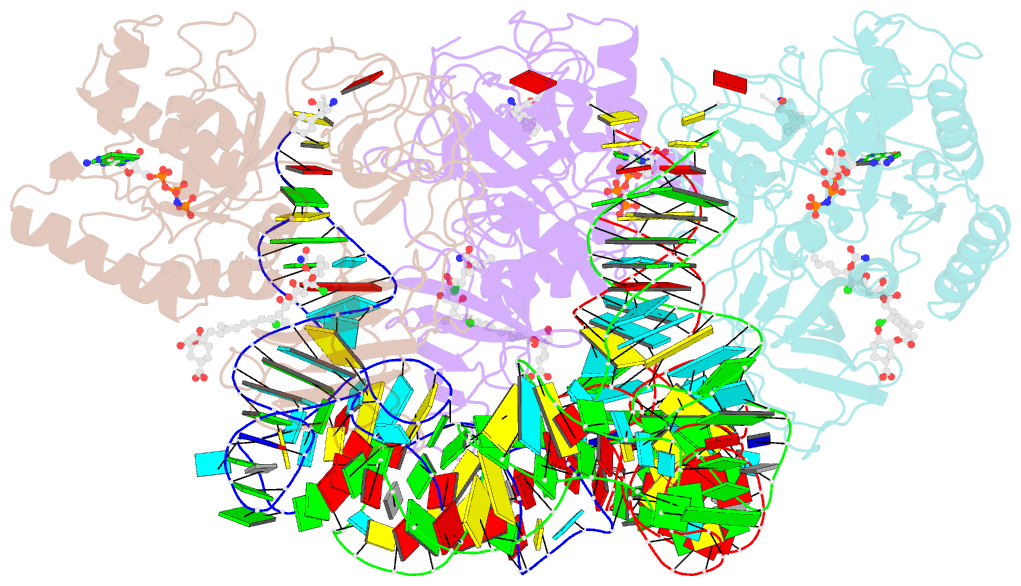
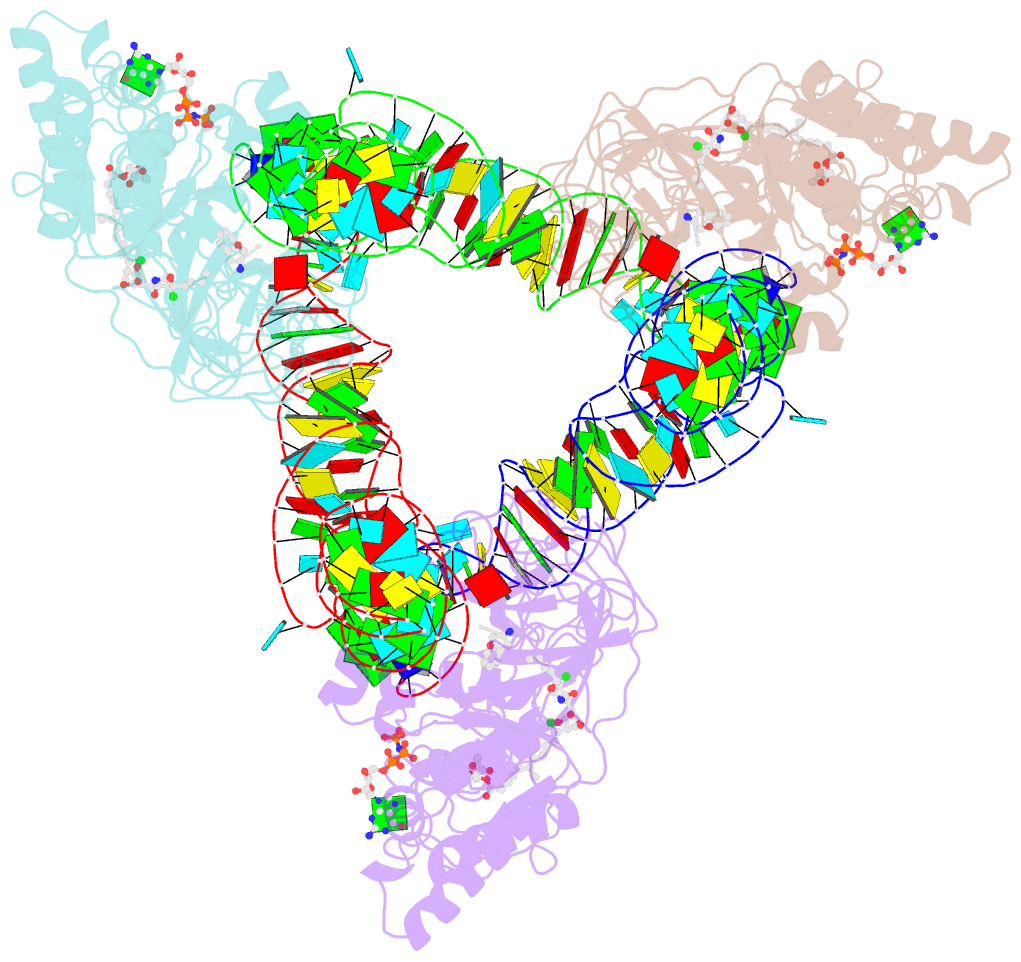
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 1ob5; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- hydrolase
- Method
- X-ray (3.1 Å)
- Summary
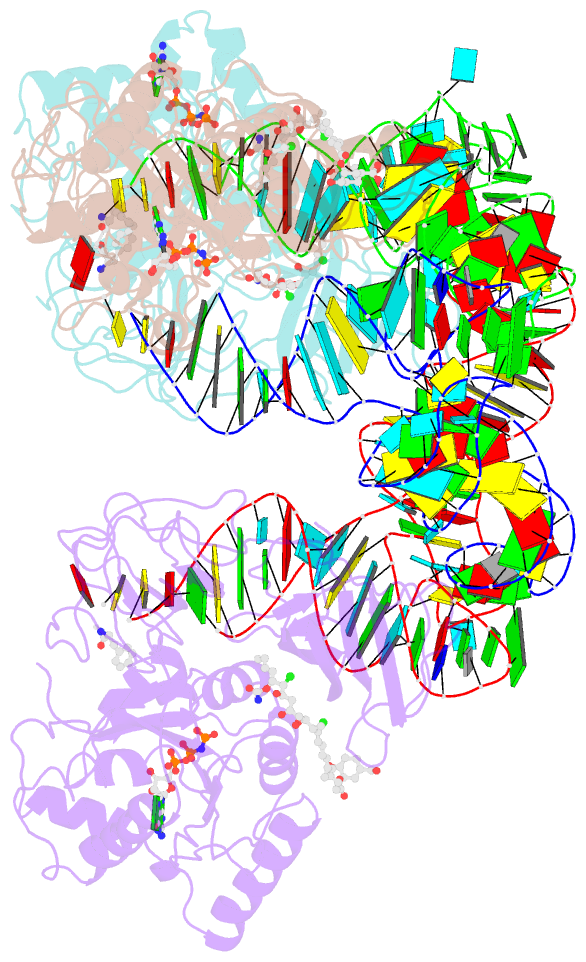
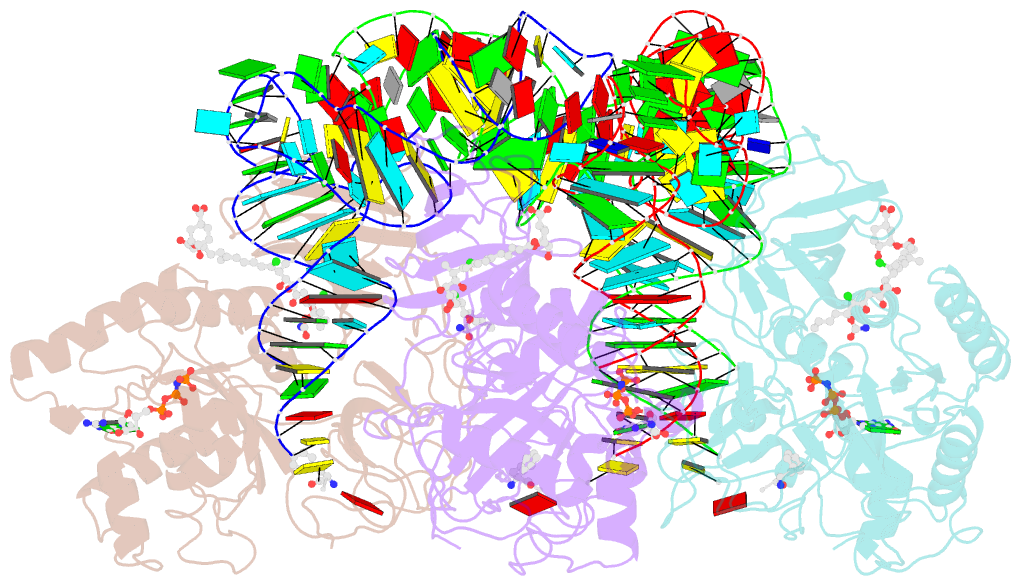
- T. aquaticus elongation factor ef-tu complexed with the antibiotic enacyloxin iia, a gtp analog, and phe-trna
- Reference
- Parmeggiani A, Krab IM, Watanabe T, Nielsen RC, Dahlberg C, Nyborg J, Nissen P (2006): "Enacyloxin Iia Pinpoints a Binding Pocket of Elongation Factor TU for Development of Novel Antibiotics." J.Biol.Chem., 281, 2893. doi: 10.1074/JBC.M505951200.
- Abstract
- Elongation factor (EF-) Tu.GTP is the carrier of aminoacyl-tRNA to the programmed ribosome. Enacyloxin IIa inhibits bacterial protein synthesis by hindering the release of EF-Tu.GDP from the ribosome. The crystal structure of the Escherichia coli EF-Tu.guanylyl iminodiphosphate (GDPNP).enacyloxin IIa complex at 2.3 A resolution presented here reveals the location of the antibiotic at the interface of domains 1 and 3. The binding site overlaps that of kirromycin, an antibiotic with a structure that is unrelated to enacyloxin IIa but that also inhibits EF-Tu.GDP release. As one of the major differences, the enacyloxin IIa tail borders a hydrophobic pocket that is occupied by the longer tail of kirromycin, explaining the higher binding affinity of the latter. EF-Tu.GDPNP.enacyloxin IIa shows a disordered effector region that in the Phe-tRNAPhe.EF-Tu (Thermus aquaticus).GDPNP.enacyloxin IIa complex, solved at 3.1 A resolution, is stabilized by the interaction with tRNA. This work clarifies the structural background of the action of enacyloxin IIa and compares its properties with those of kirromycin, opening new perspectives for structure-guided design of novel antibiotics.