Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 1p7d; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- DNA binding protein-DNA
- Method
- X-ray (2.95 Å)
- Summary
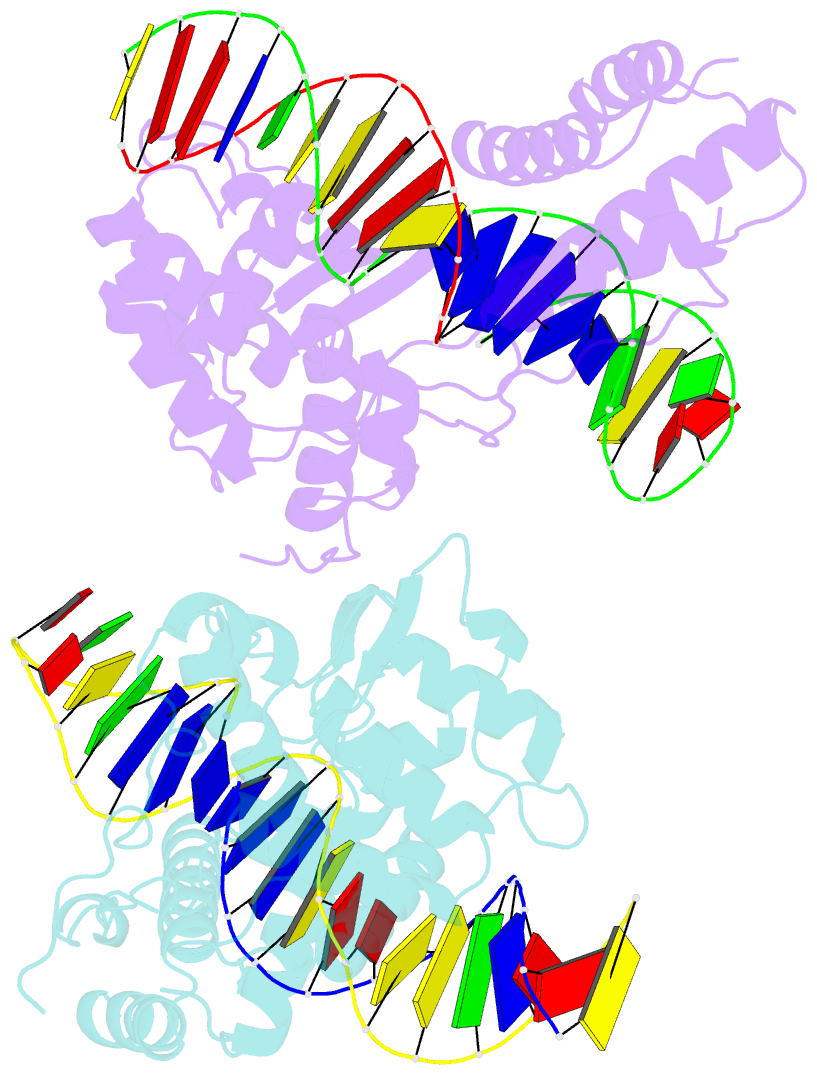
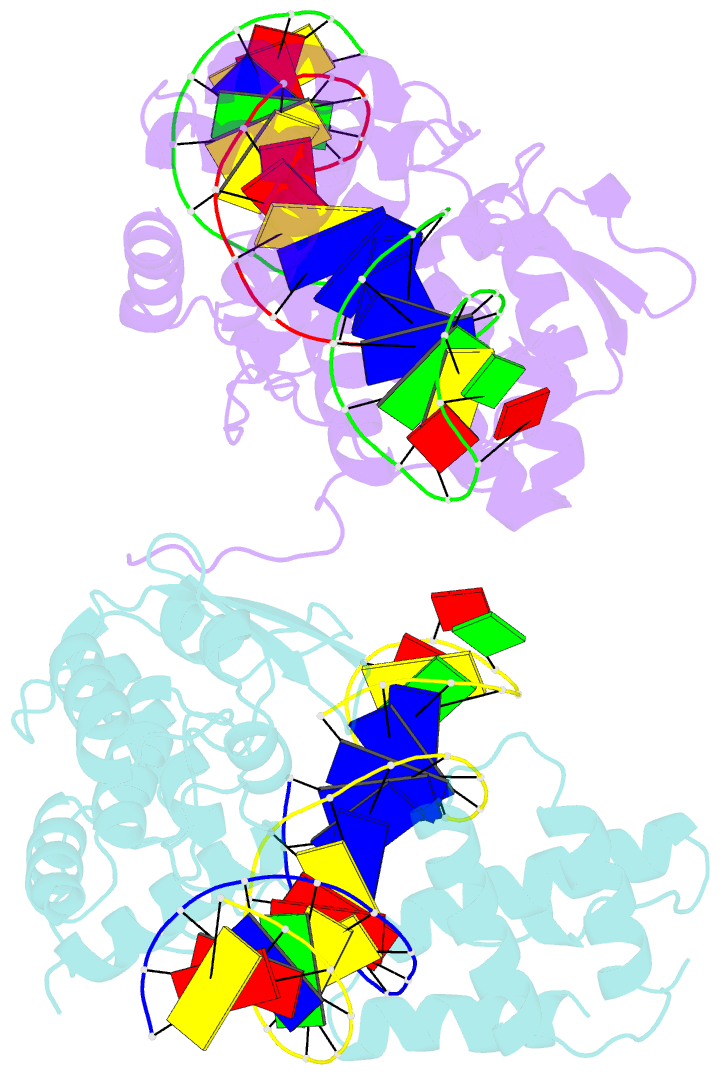
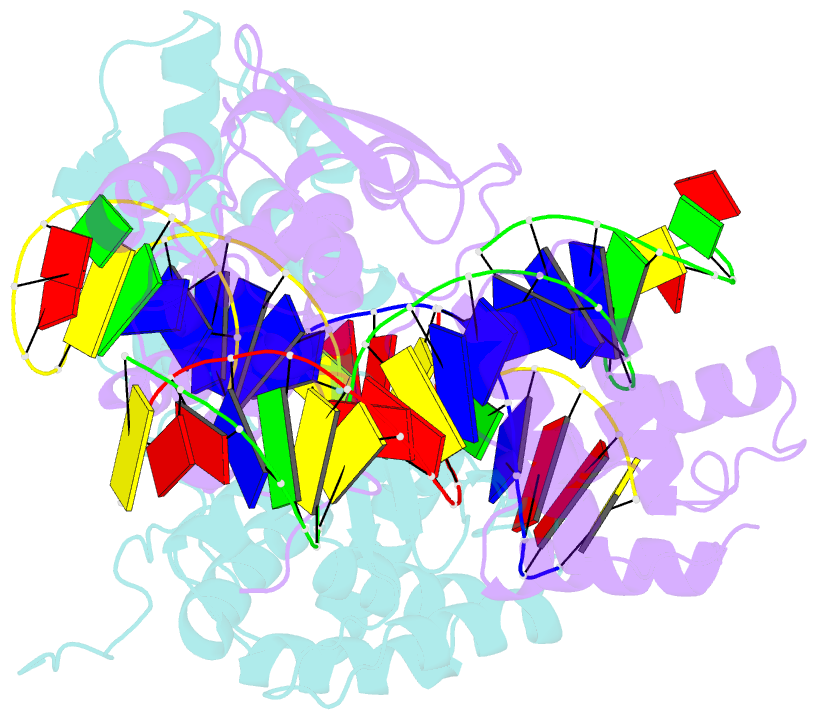
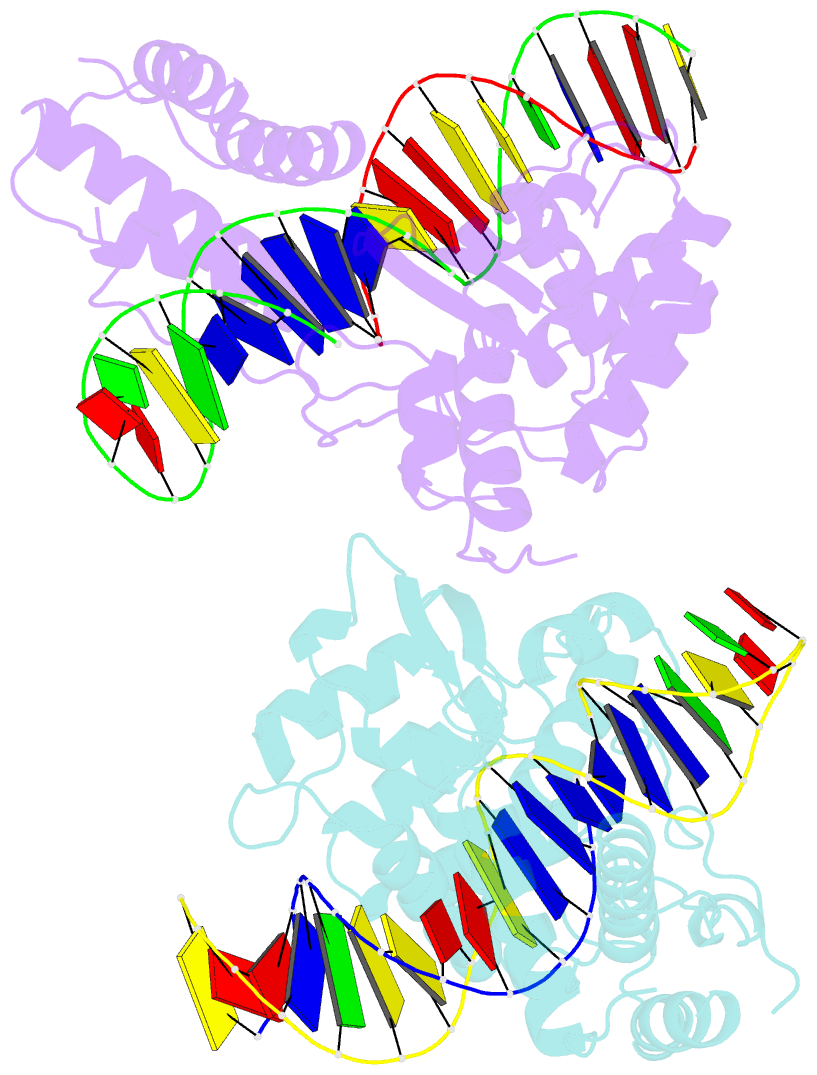
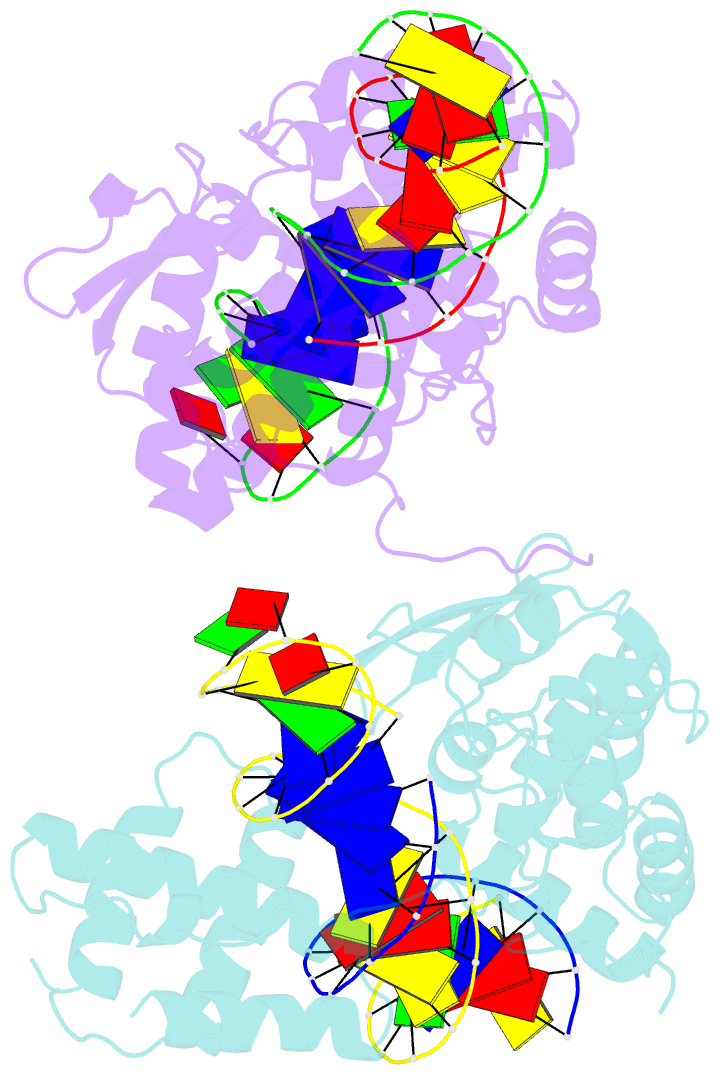
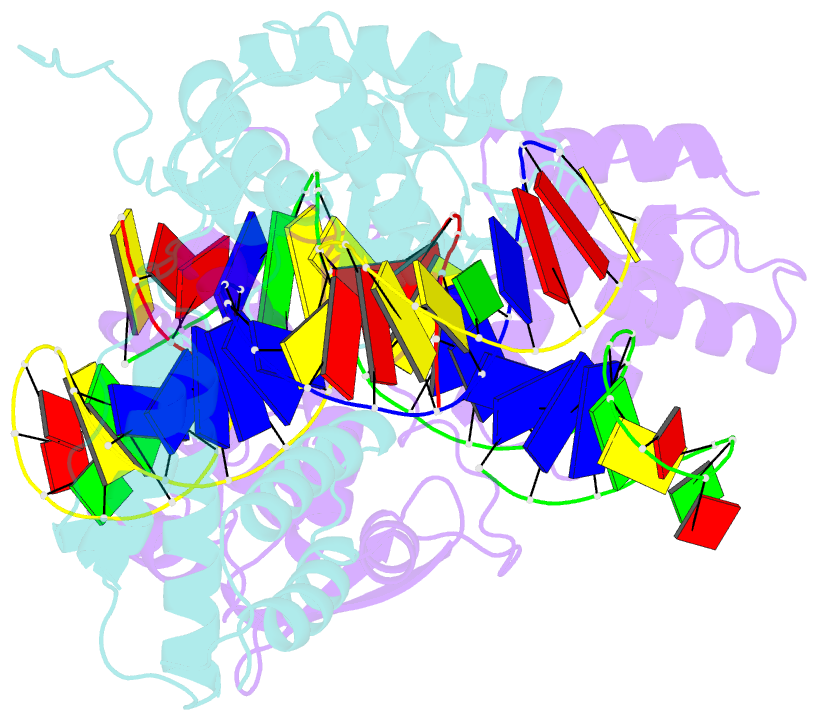
- Crystal structure of the lambda integrase (residues 75-356) bound to DNA
- Reference
- Aihara H, Kwon HJ, Nunes-Duby SE, Landy A, Ellenberger T (2003): "A Conformational Switch Controls the DNA Cleavage Activity of Lambda Integrase." Mol.Cell, 12, 187-198. doi: 10.1016/S1097-2765(03)00268-5.
- Abstract
- The bacteriophage lambda integrase protein (lambda Int) belongs to a family of tyrosine recombinases that catalyze DNA rearrangements. We have determined a crystal structure of lambda Int complexed with a cleaved DNA substrate through a covalent phosphotyrosine bond. In comparison to an earlier unliganded structure, we observe a drastic conformational change in DNA-bound lambda Int that brings Tyr342 into the active site for cleavage of the DNA in cis. A flexible linker connects the central and the catalytic domains, allowing the protein to encircle the DNA. Binding specificity is achieved through direct interactions with the DNA and indirect readout of the flexibility of the att site. The conformational switch that activates lambda Int for DNA cleavage exposes the C-terminal 8 residues for interactions with a neighboring Int molecule. The protein interactions mediated by lambda Int's C-terminal tail offer a mechanism for the allosteric control of cleavage activity in higher order lambda Int complexes.