Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 1p7h; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- transcription-DNA
- Method
- X-ray (2.6 Å)
- Summary
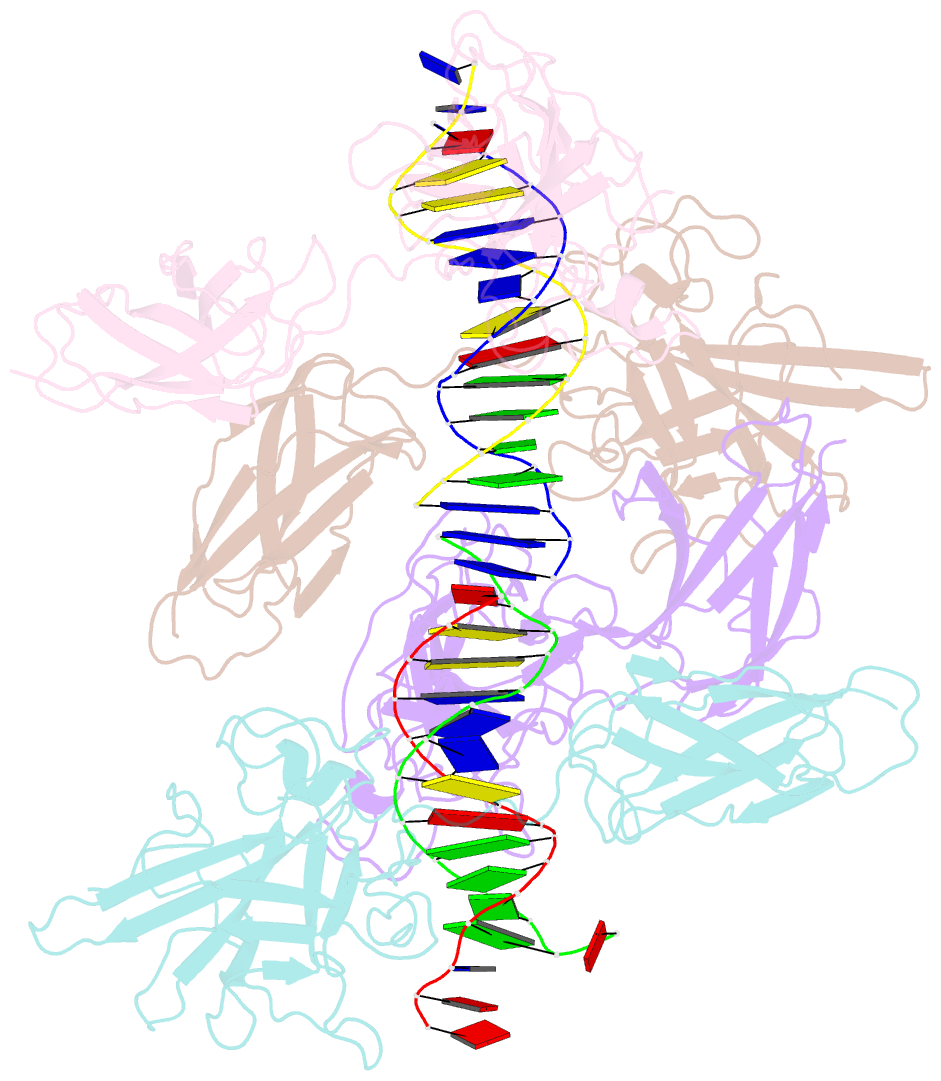
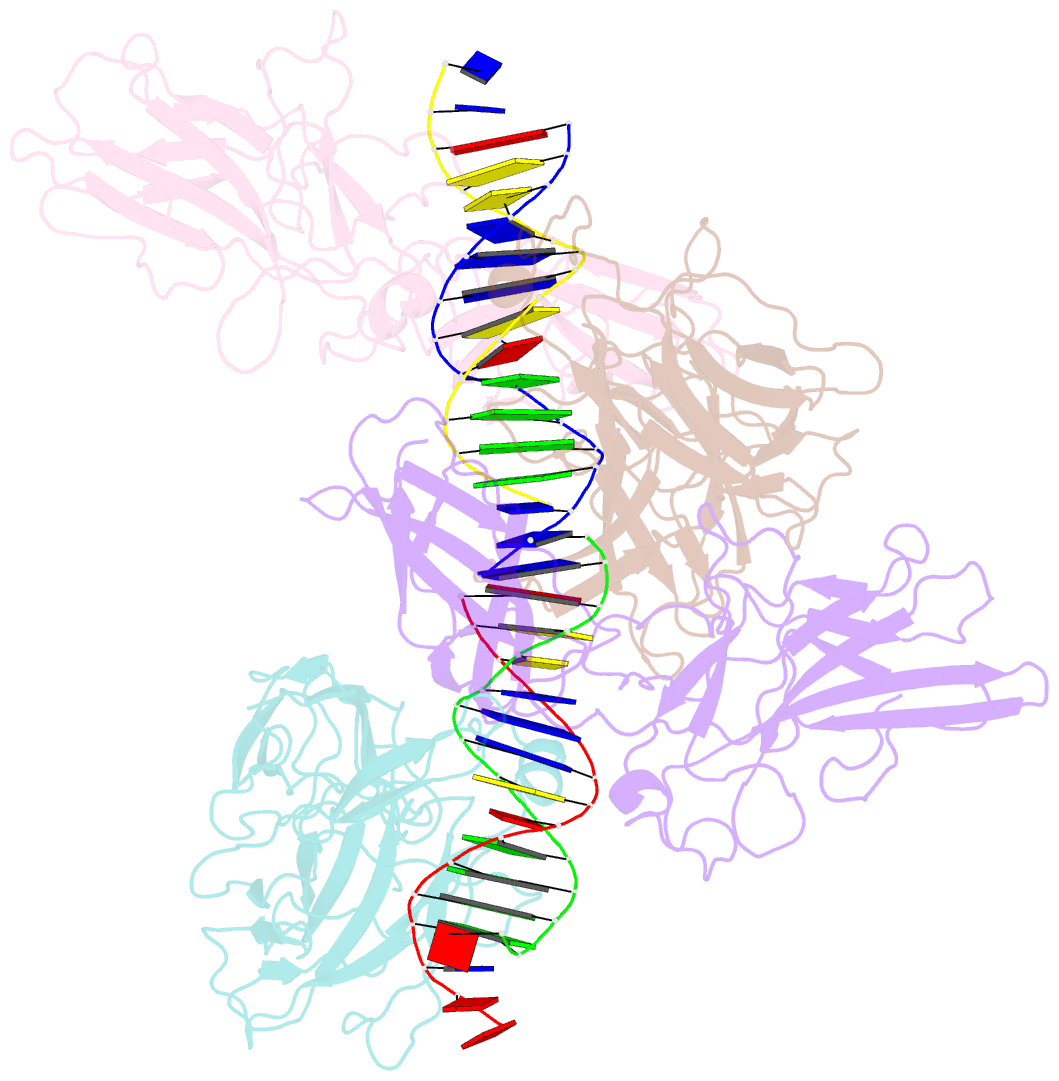
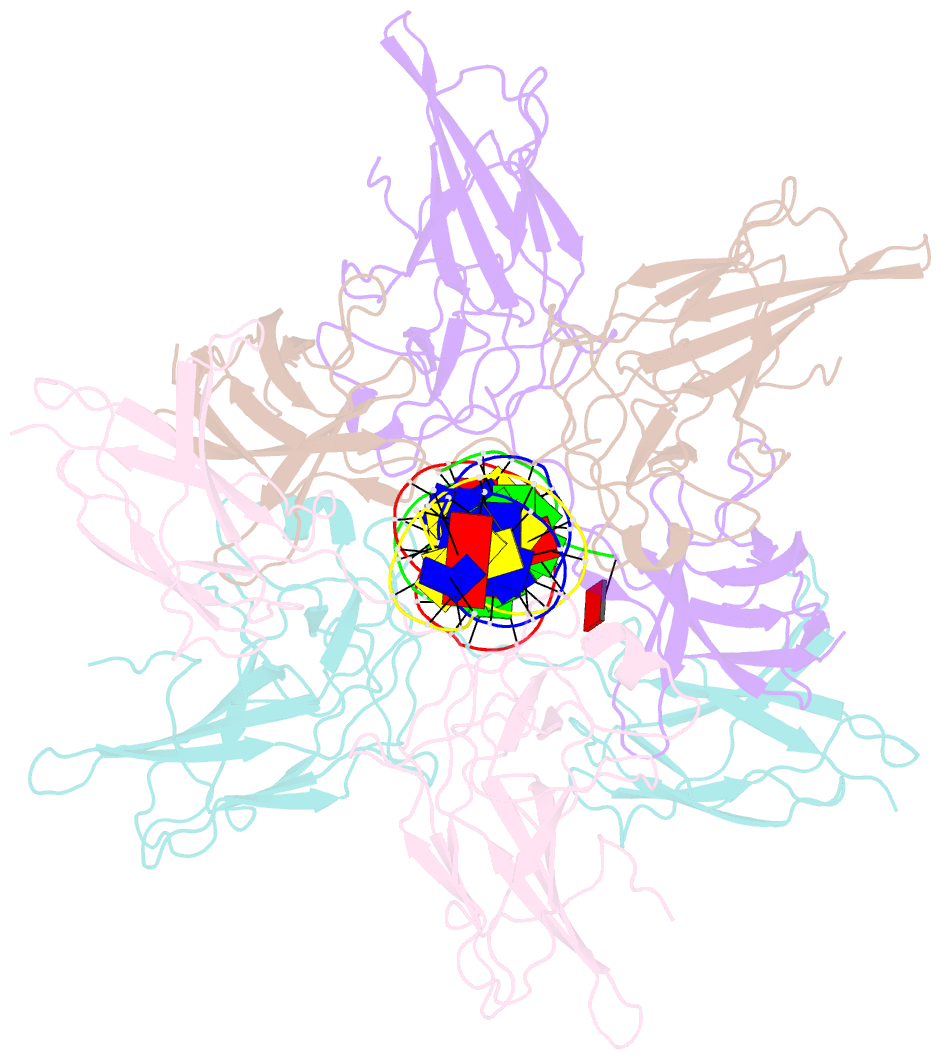
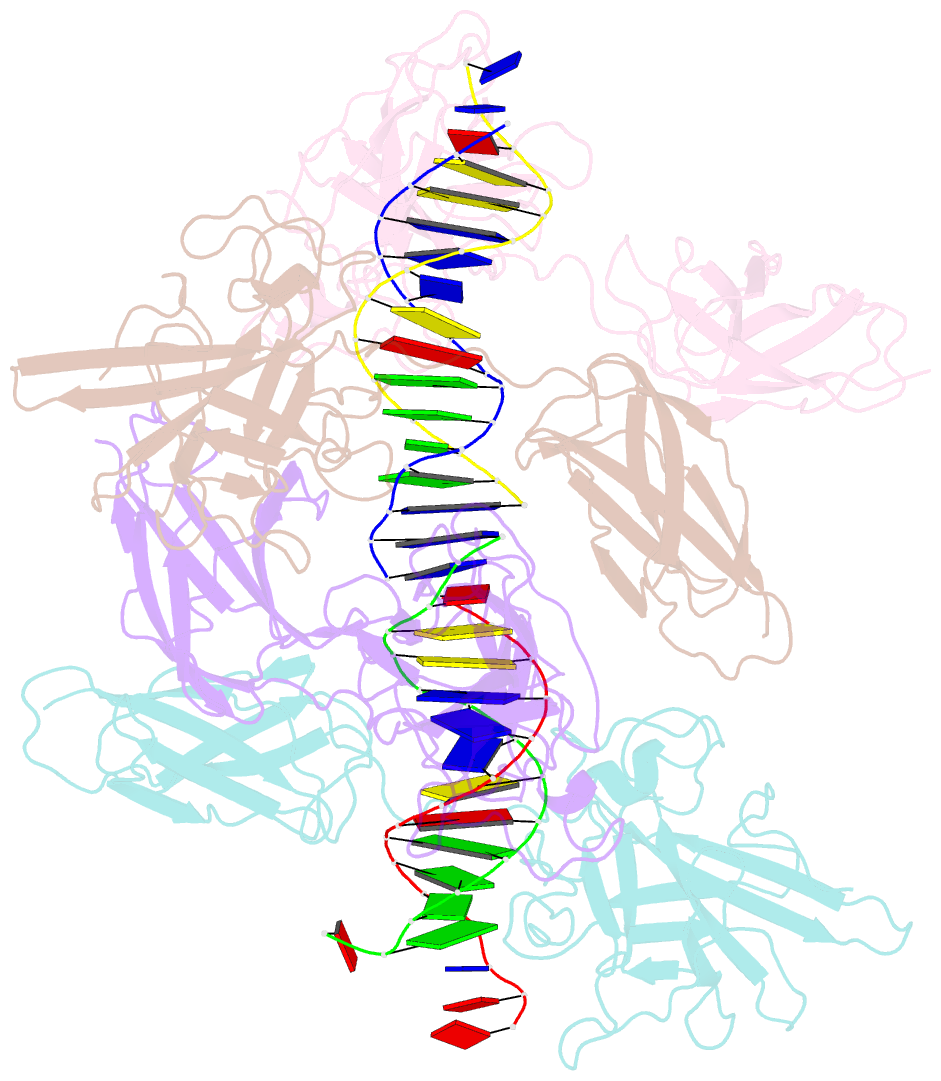
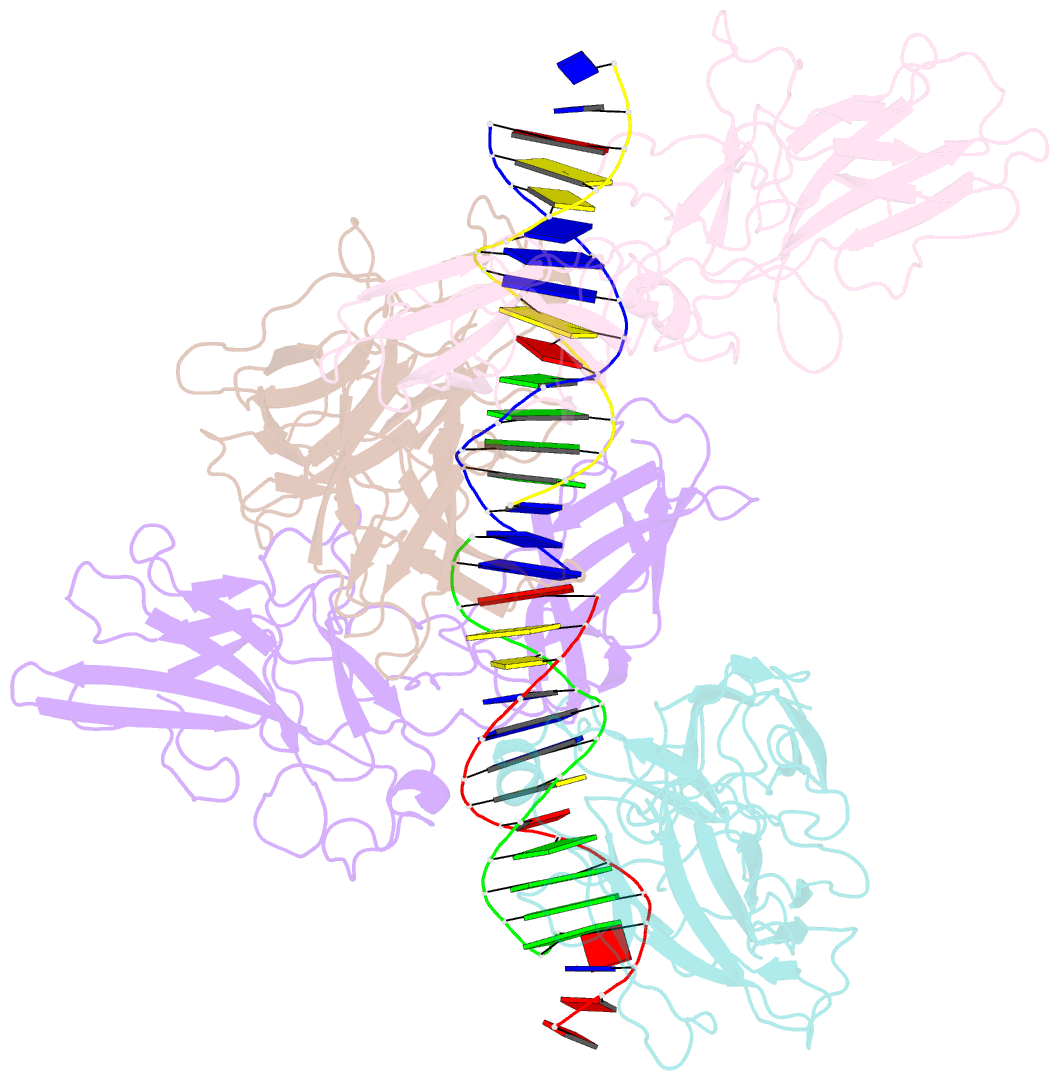
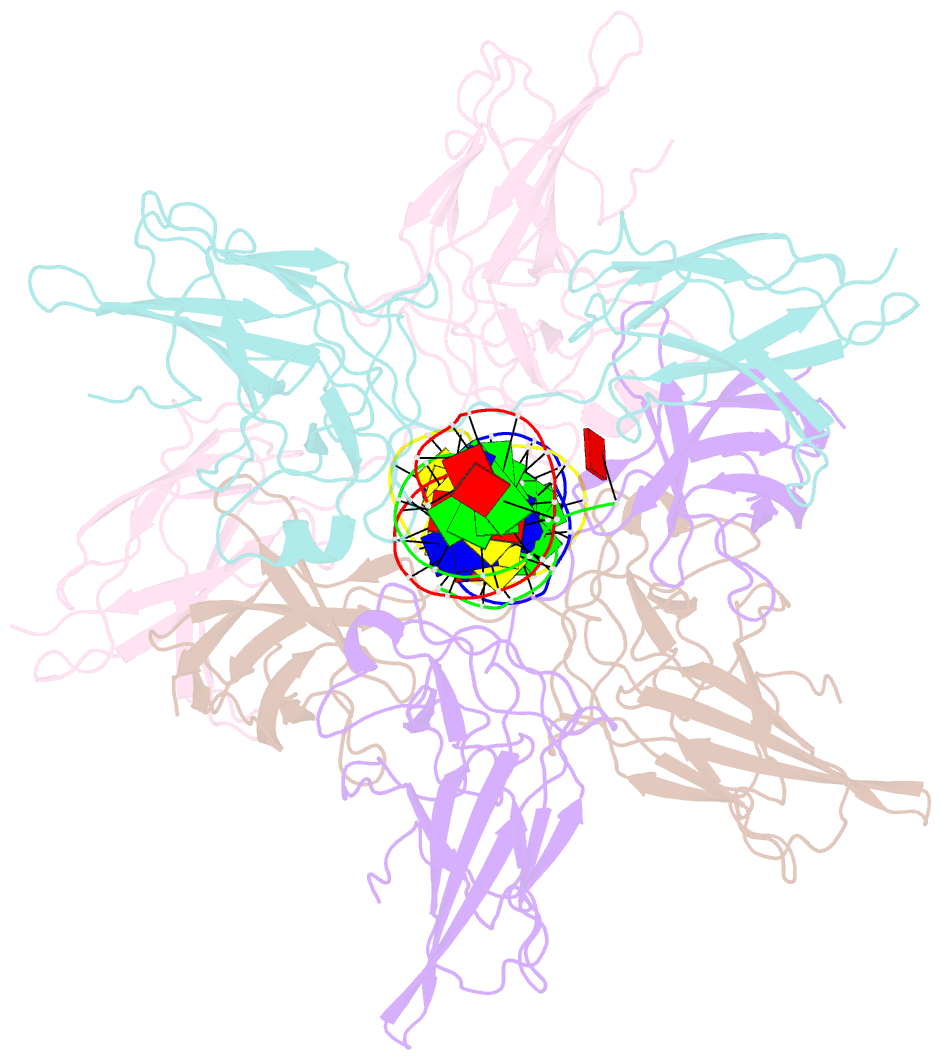
- Structure of nfat1 bound as a dimer to the hiv-1 ltr kb element
- Reference
- Giffin MJ, Stroud JC, Bates DL, von Koenig KD, Hardin J, Chen L (2003): "Structure of NFAT1 bound as a dimer to the HIV-1 LTR kappa B element." Nat.Struct.Biol., 10, 800-806. doi: 10.1038/nsb981.
- Abstract
- DNA binding by NFAT1 as a dimer has been implicated in the activation of host and viral genes. Here we report a crystal structure of NFAT1 bound cooperatively as a dimer to the highly conserved kappa B site from the human immunodeficiency virus 1 (HIV-1) long terminal repeat (LTR). This structure reveals a new mode of dimerization and protein-DNA recognition by the Rel homology region (RHR) of NFAT1. The two NFAT1 monomers form a complete circle around the kappa B DNA through protein-protein interactions mediated by both their N- and C-terminal subdomains. The major dimer interface, formed by the C-terminal domain, is asymmetric and substantially different from the symmetric dimer interface seen in other Rel family proteins. Comparison to other NFAT structures, including NFAT5 and the NFAT1-Fos-Jun-ARRE2 complex, reveals that NFAT1 adopts different conformations and its protein surfaces mediate distinct protein-protein interactions in the context of different DNA sites.