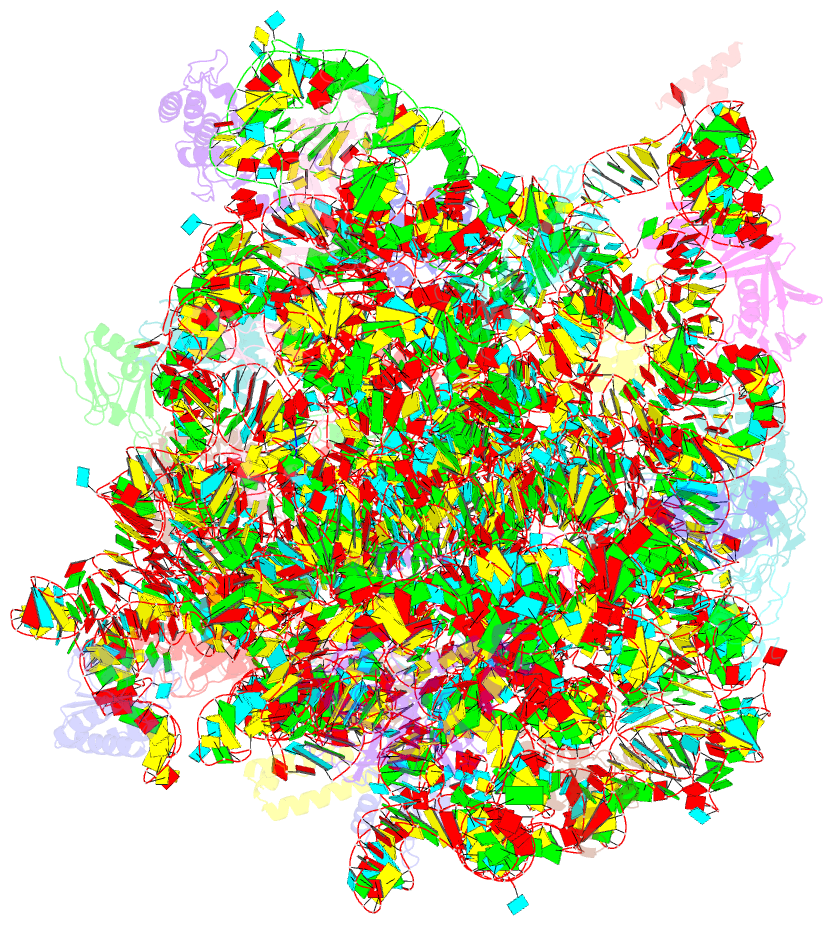
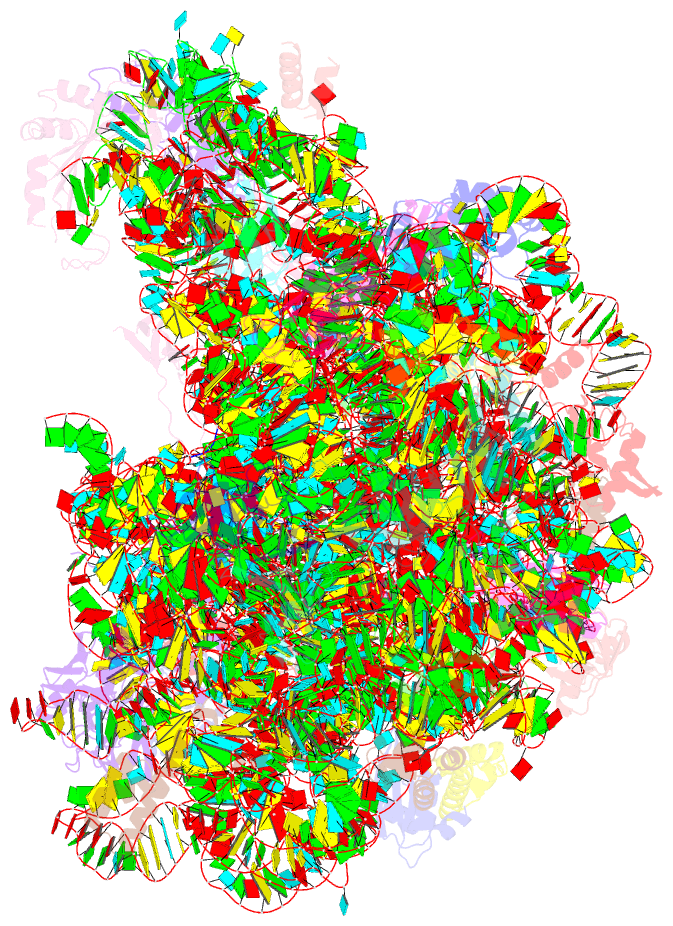
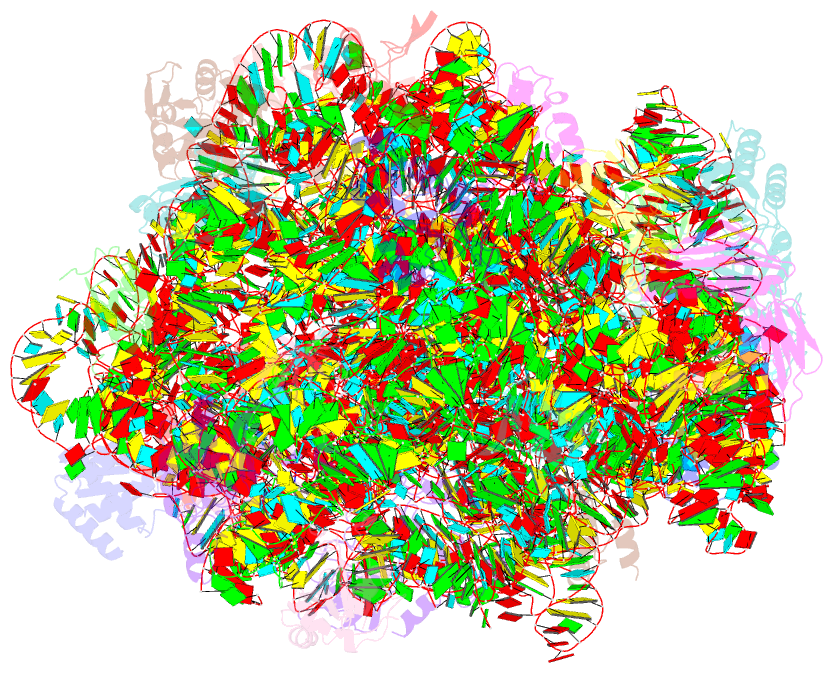
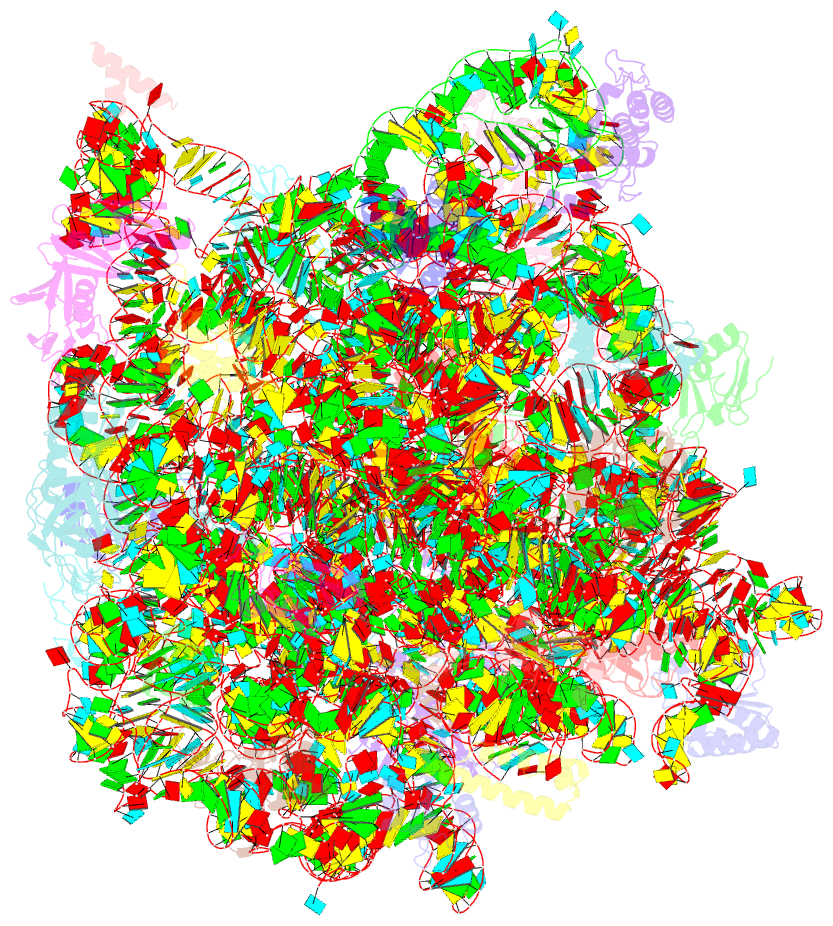
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 1qvg; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- ribosome
- Method
- X-ray (2.9 Å)
- Summary
- Structure of cca oligonucleotide bound to the trna binding sites of the large ribosomal subunit of haloarcula marismortui
- Reference
- Schmeing TM, Moore PB, Steitz TA (2003): "Structures of deacylated tRNA mimics bound to the E site of the large ribosomal subunit." RNA, 9, 1345-1352. doi: 10.1261/rna.5120503.
- Abstract
- During translation, tRNAs cycle through three binding sites on the ribosome: the A, the P, and the E sites. We have determined the structures of complexes between the Haloarcula marismortui large ribosomal subunit and two different E site substrates: a deacylated tRNA acceptor stem minihelix and a CCA-acceptor end. Both of these tRNA mimics contain analogs of adenosine 76, the component responsible for a large proportion of E site binding affinity. They bind in the center of the loop-extension of protein L44e, and make specific contacts with both L44e and 23S rRNA including bases that are conserved in all three kingdoms of life. These contacts are consistent with the footprinting, protection, and cross-linking data that have identified the E site biochemically. These structures explain the specificity of the E site for deacylated tRNAs, as it is too small to accommodate any relevant aminoacyl-tRNA. The orientation of the minihelix suggests that it may mimic the P/E hybrid state. It appears that the E site on the 50S subunit was formed by only RNA in the last common ancestor of the three kingdoms, since the proteins at the E sites of H. marismortui and Deinucoccus radiodurans large subunits are not homologous.