Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 1r4r; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- transcription-DNA
- Method
- X-ray (3.0 Å)
- Summary
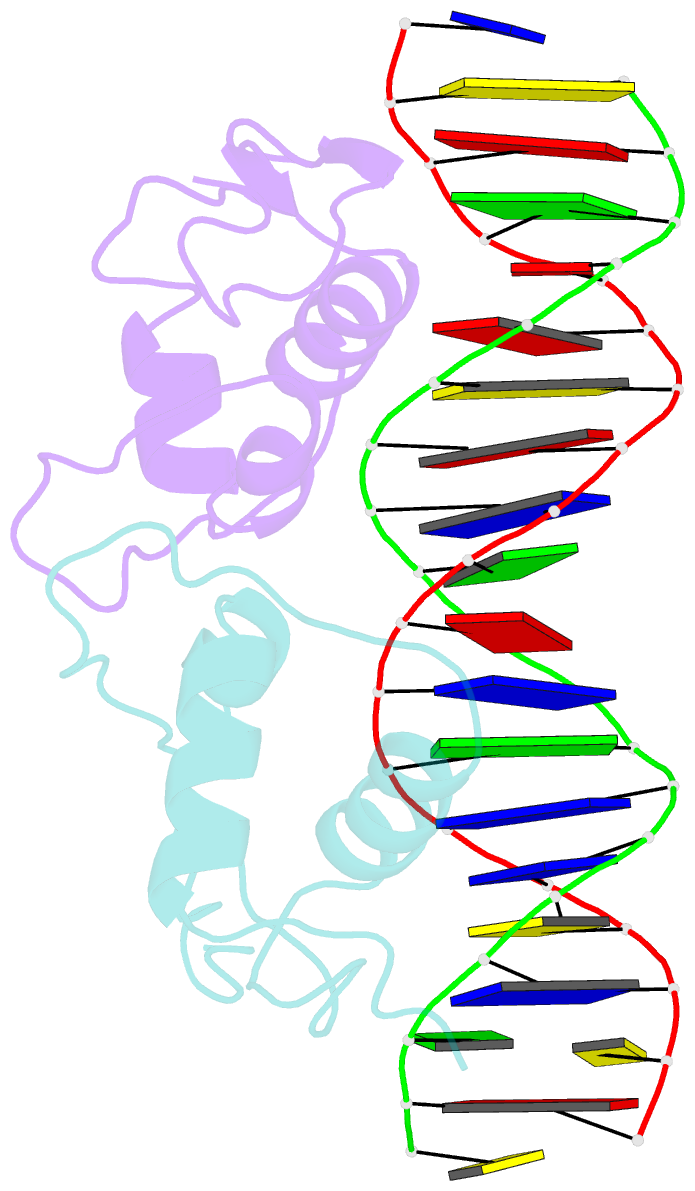
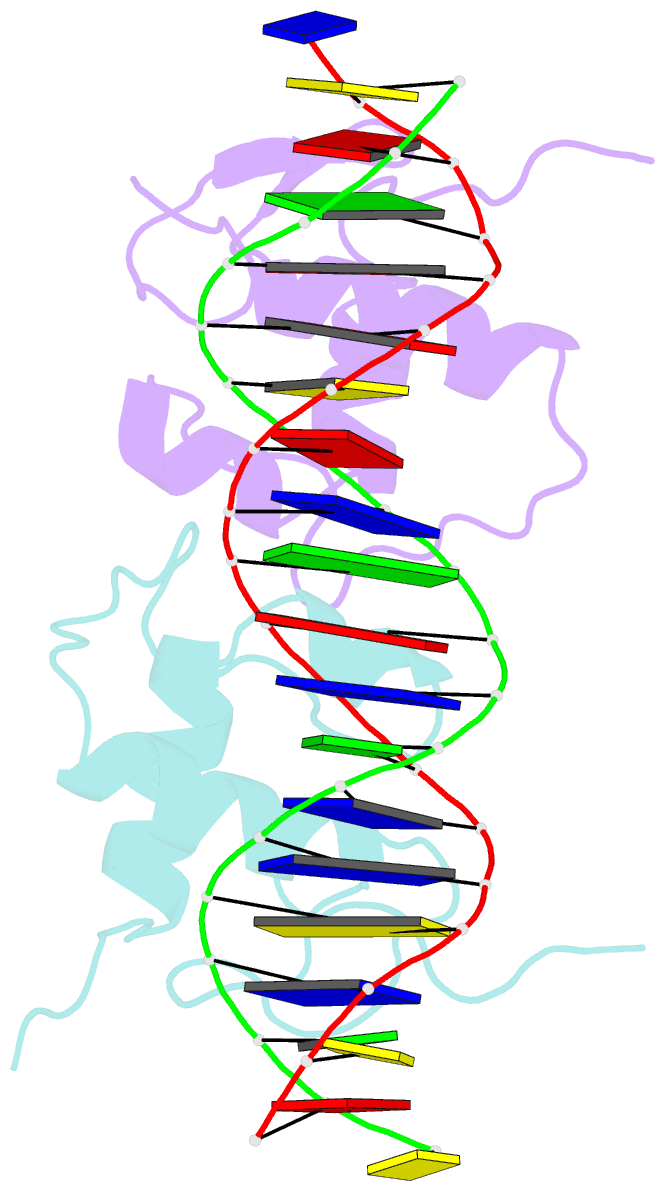
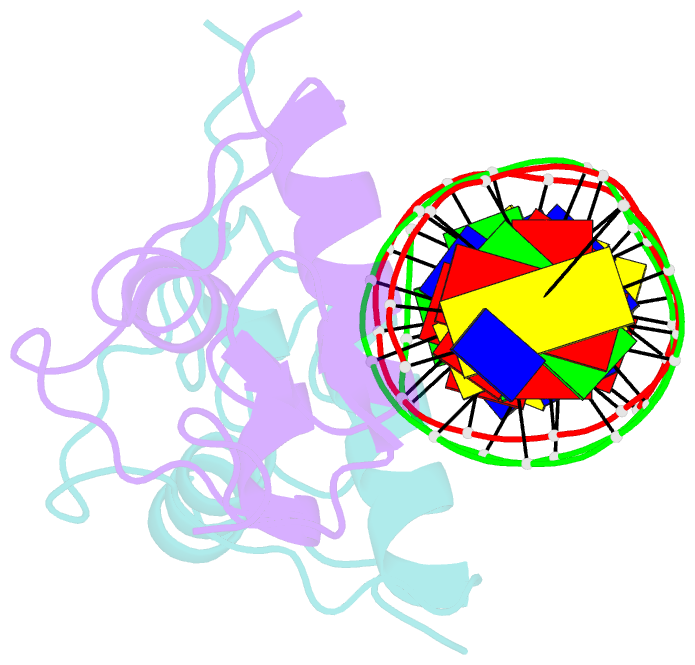
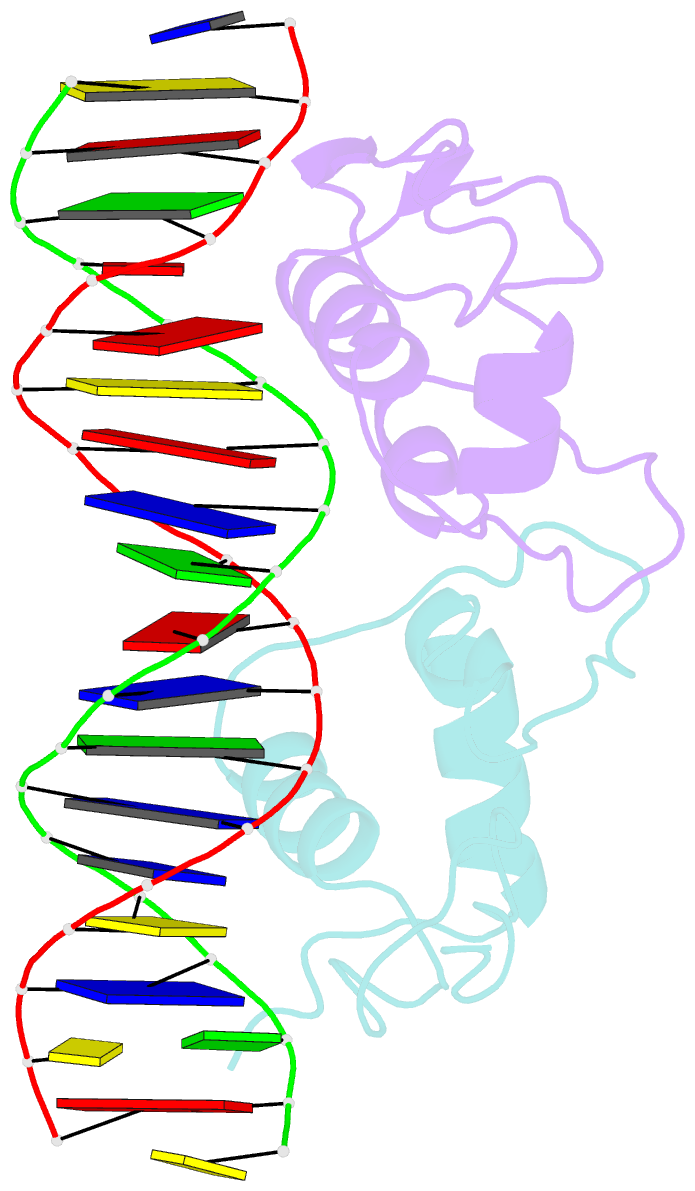
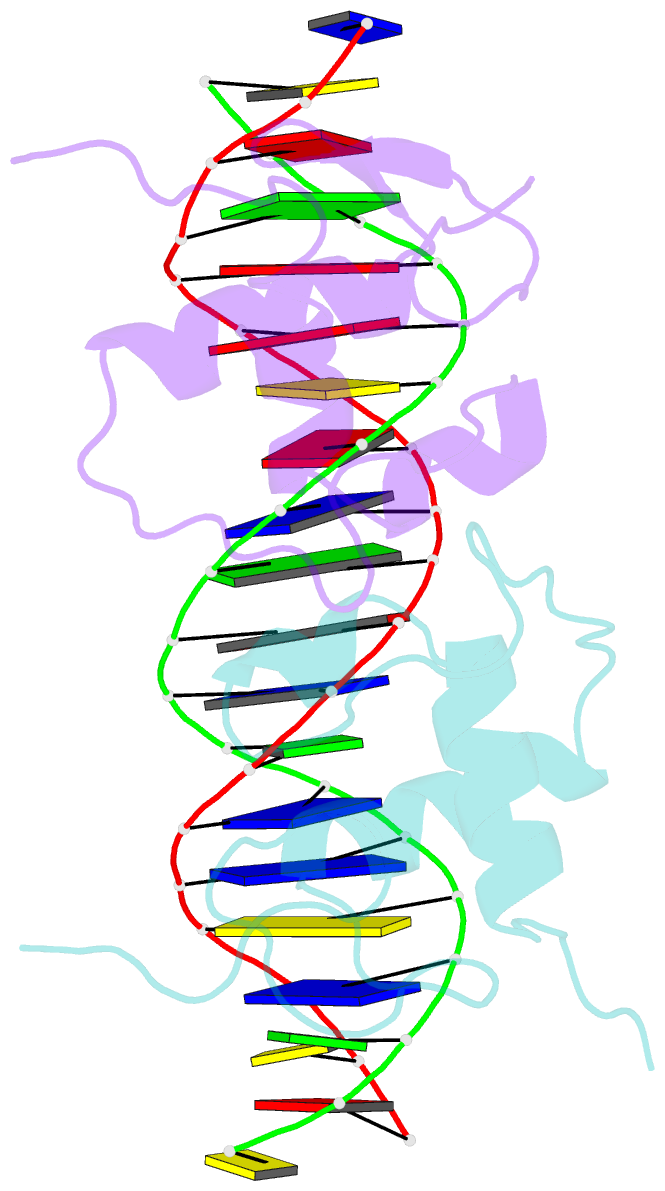
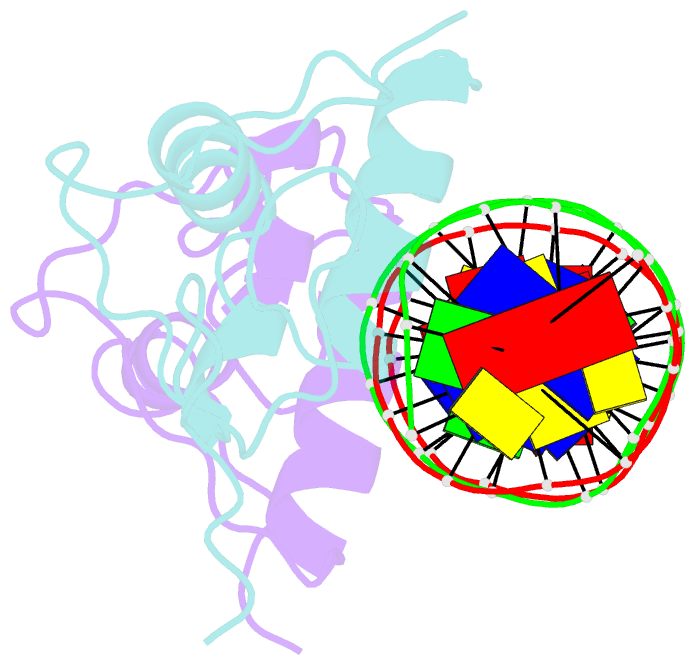
- Crystallographic analysis of the interaction of the glucocorticoid receptor with DNA
- Reference
- Luisi BF, Xu WX, Otwinowski Z, Freedman LP, Yamamoto KR, Sigler PB (1991): "Crystallographic Analysis of the Interaction of the Glucocorticoid Receptor with DNA." Nature, 352, 497-505. doi: 10.1038/352497a0.
- Abstract
- Two crystal structures of the glucocorticoid receptor DNA-binding domain complexed with DNA are reported. The domain has a globular fold which contains two Zn-nucleated substructures of distinct conformation and function. When it binds DNA, the domain dimerizes, placing the subunits in adjacent major grooves. In one complex, the DNA has the symmetrical consensus target sequence; in the second, the central spacing between the target's half-sites is larger by one base pair. This results in one subunit interacting specifically with the consensus target half-site and the other nonspecifically with a noncognate element. The DNA-induced dimer fixes the separation of the subunits' recognition surfaces so that the spacing between the half-sites becomes a critical feature of the target sequence's identity.