Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 1sds; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- protein-RNA complex
- Method
- X-ray (1.8 Å)
- Summary
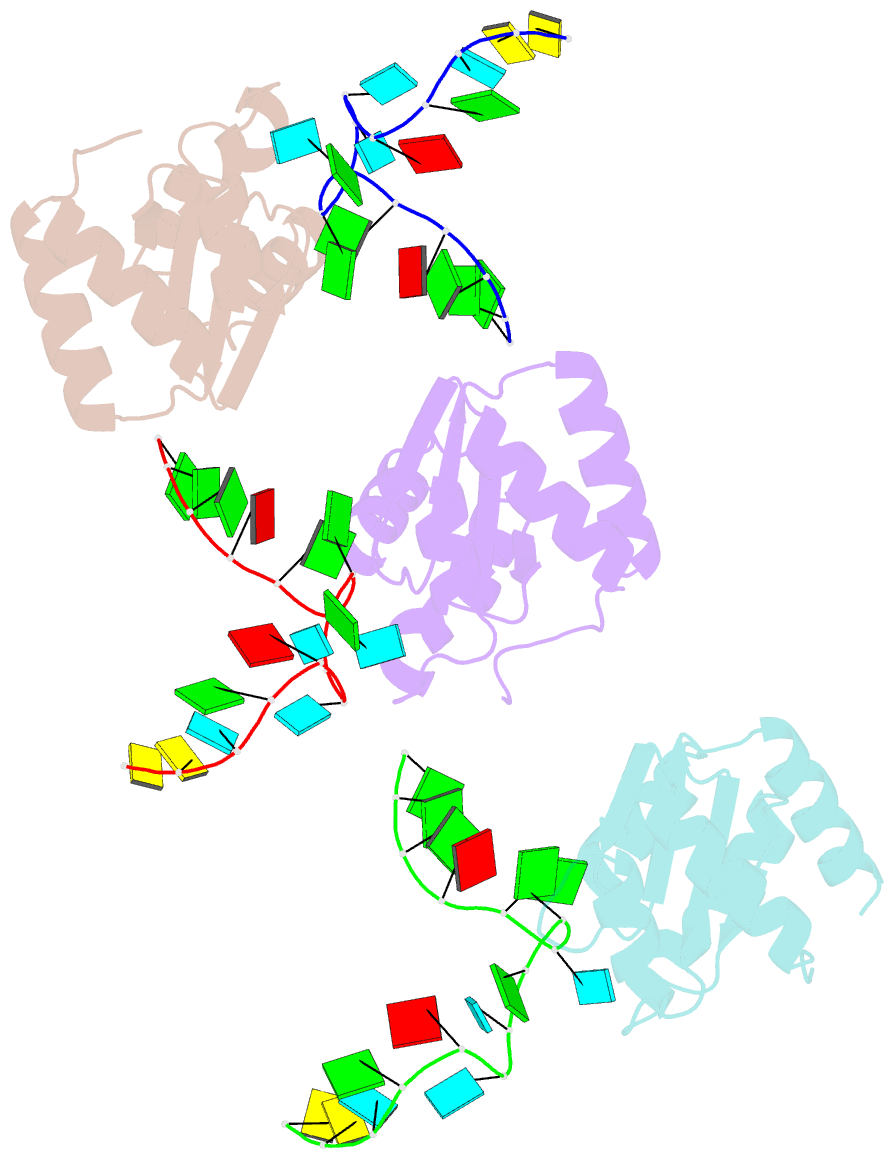
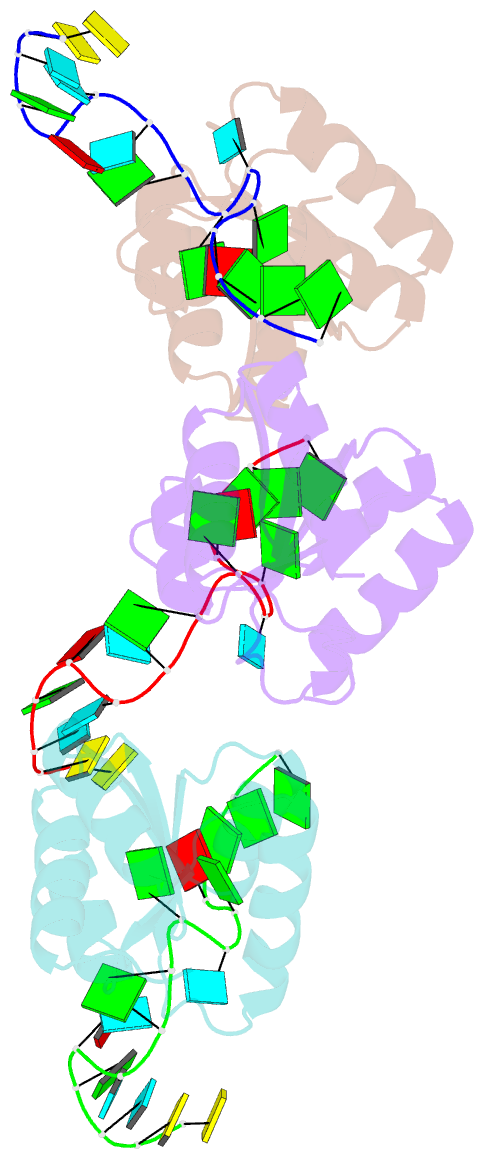
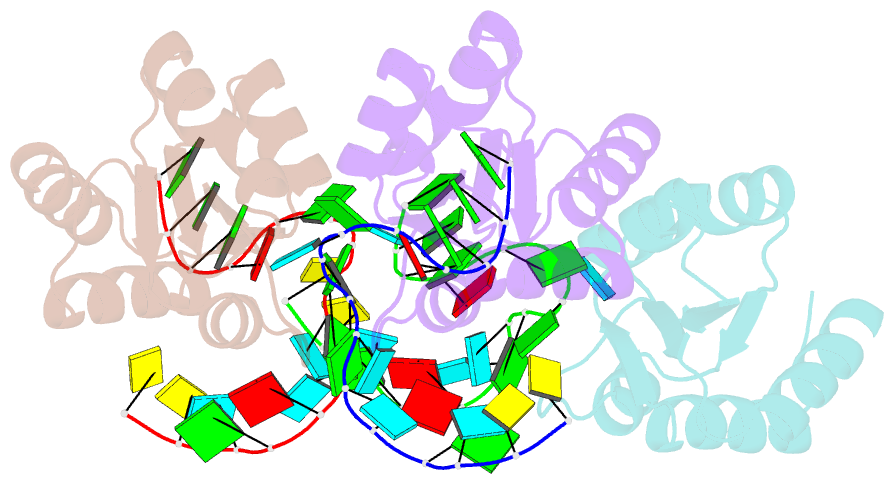
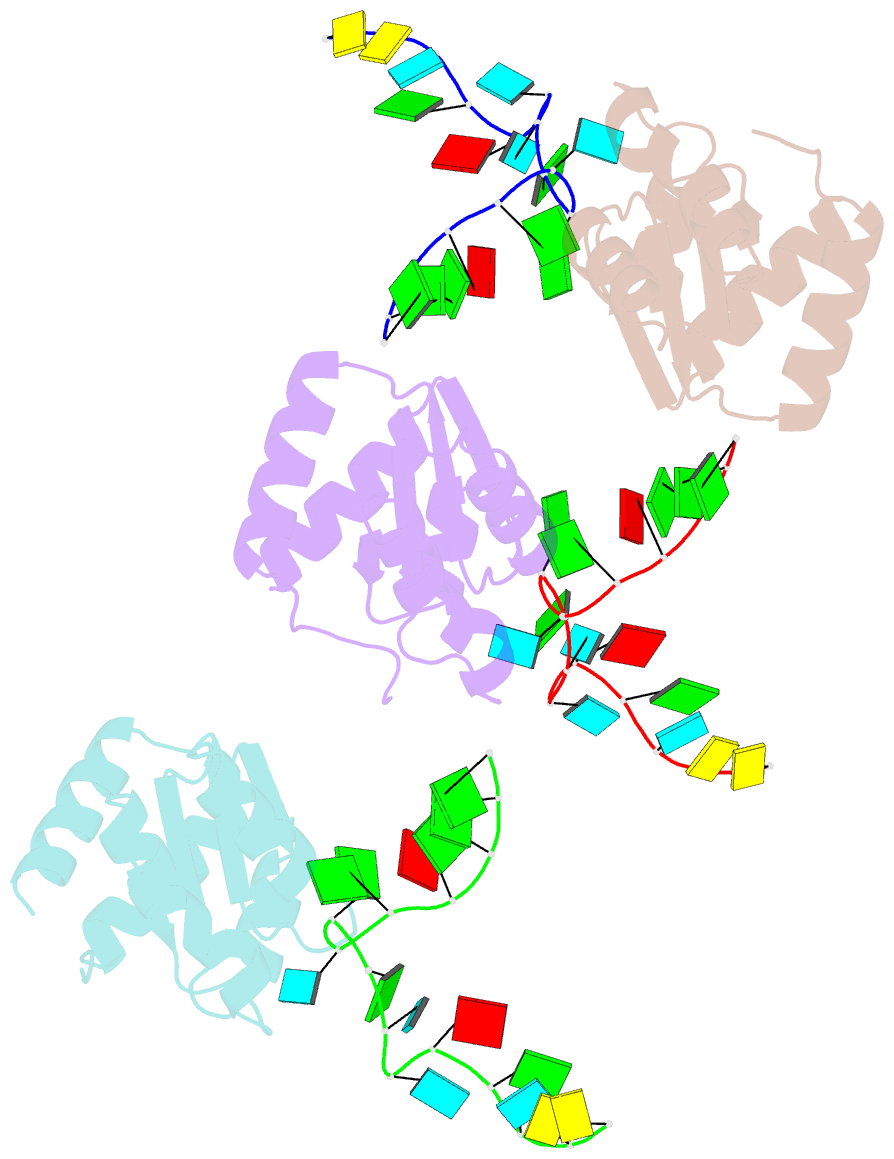
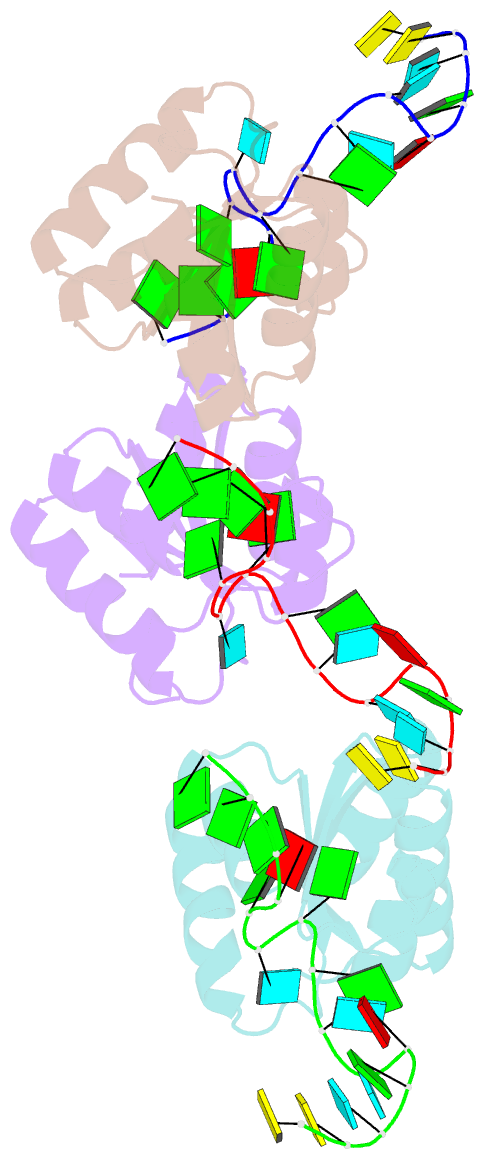
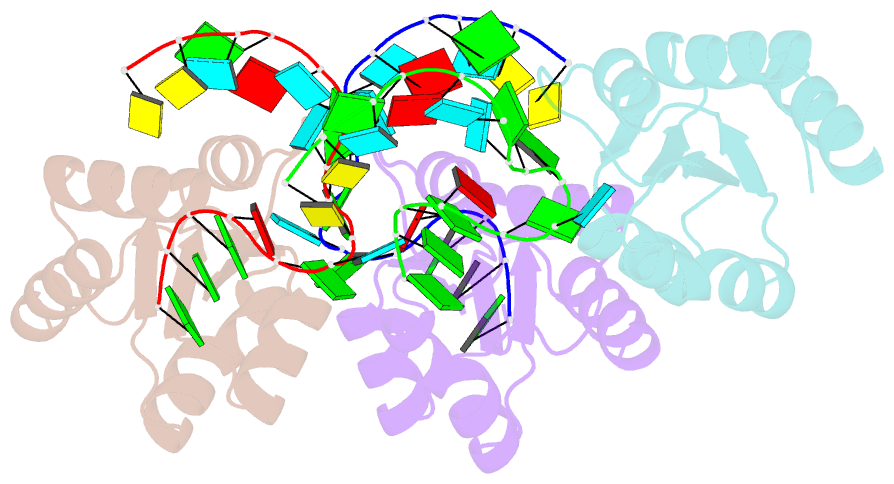
- Structure of protein l7ae bound to a k-turn derived from an archaeal box h-aca srna
- Reference
- Hamma T, Ferre-D'Amare A (2004): "Structure of Protein L7Ae Bound to a K-Turn Derived from an Archaeal Box H/ACA sRNA at 1.8 A Resolution." STRUCTURE, 12, 893-903. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2004.03.015.
- Abstract
- The archaeal RNA binding protein L7Ae and its eukaryotic homolog 15.5 kDa/Snu13 recognize K-turns. This structural motif is canonically comprised of two stems (one with tandem A.G base pairs, the other with Watson-Crick pairs) linked by an asymmetric internal loop. L7Ae recognizes conventional K-turns in ribosomal and box C/D RNAs but also binds specifically to some box H/ACA RNAs at terminal stem loops. These have the A.G paired stem, but lack the Watson-Crick stem. The structure of Methanococcus jannaschii L7Ae bound to a symmetric duplex RNA without Watson-Crick stems demonstrates how a binding site for this component of diverse ribonucleoprotein complexes can be constructed with only the A.G stem and the loop. The RNA adopts a functional conformation with the aid of a base triple and tight binding of divalent cations. Comparison with the 15.5 kDa/Snu13-RNA complex structure suggests why the eukaryotic homolog does not recognize terminal stem loop L7Ae binding sites.