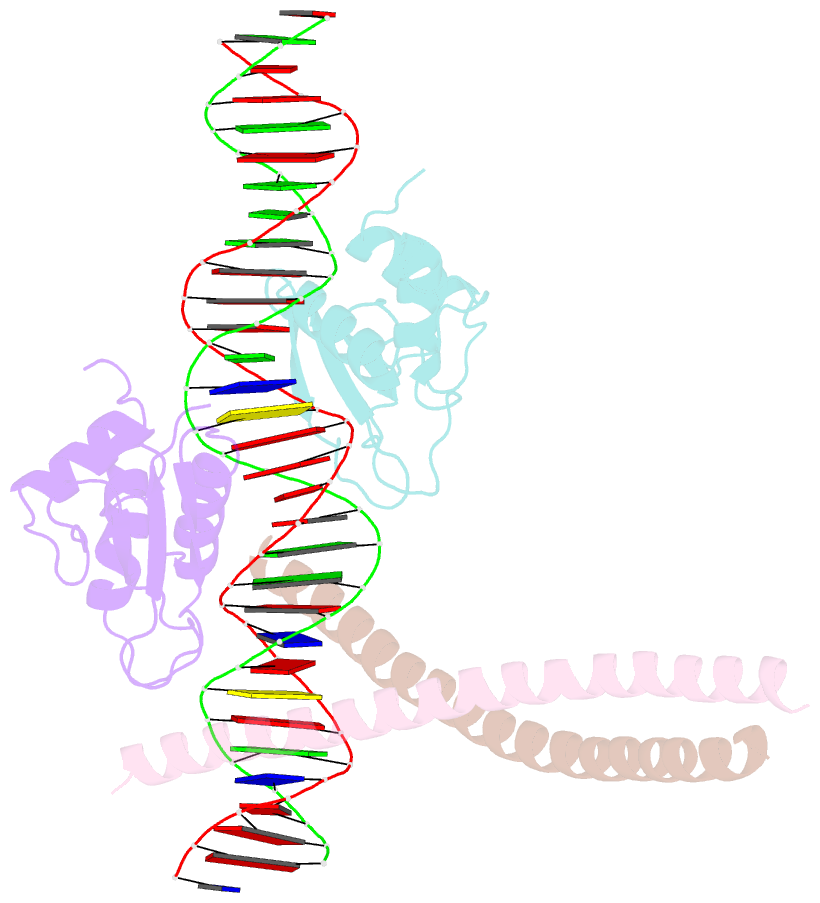
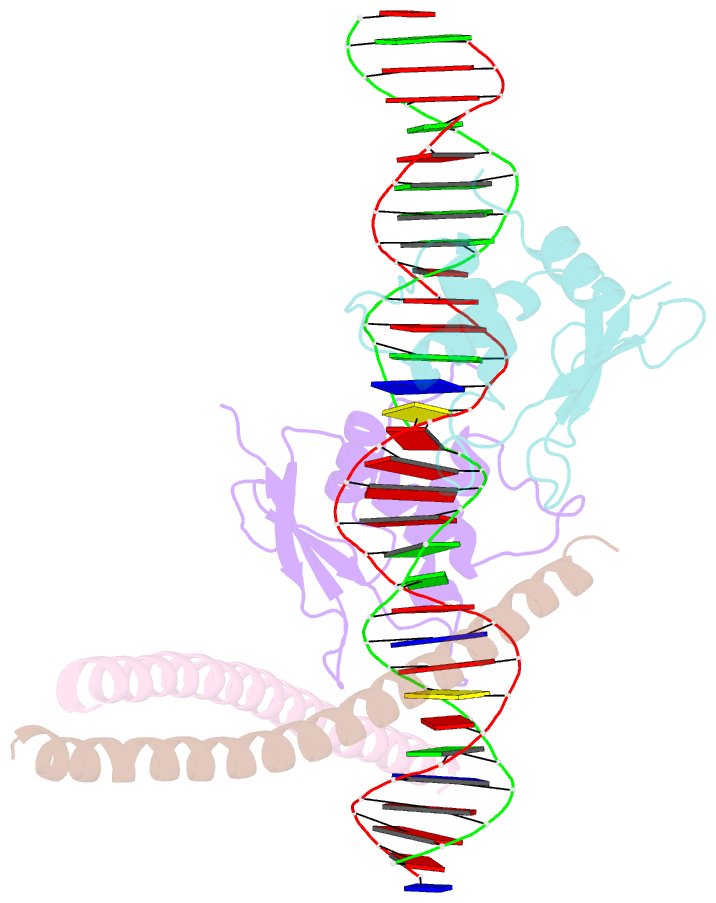
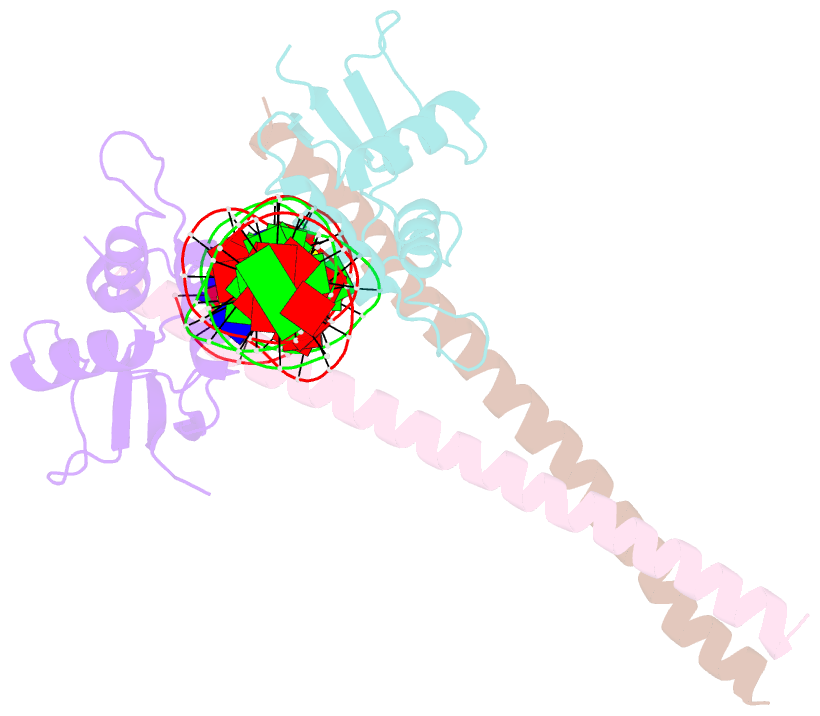
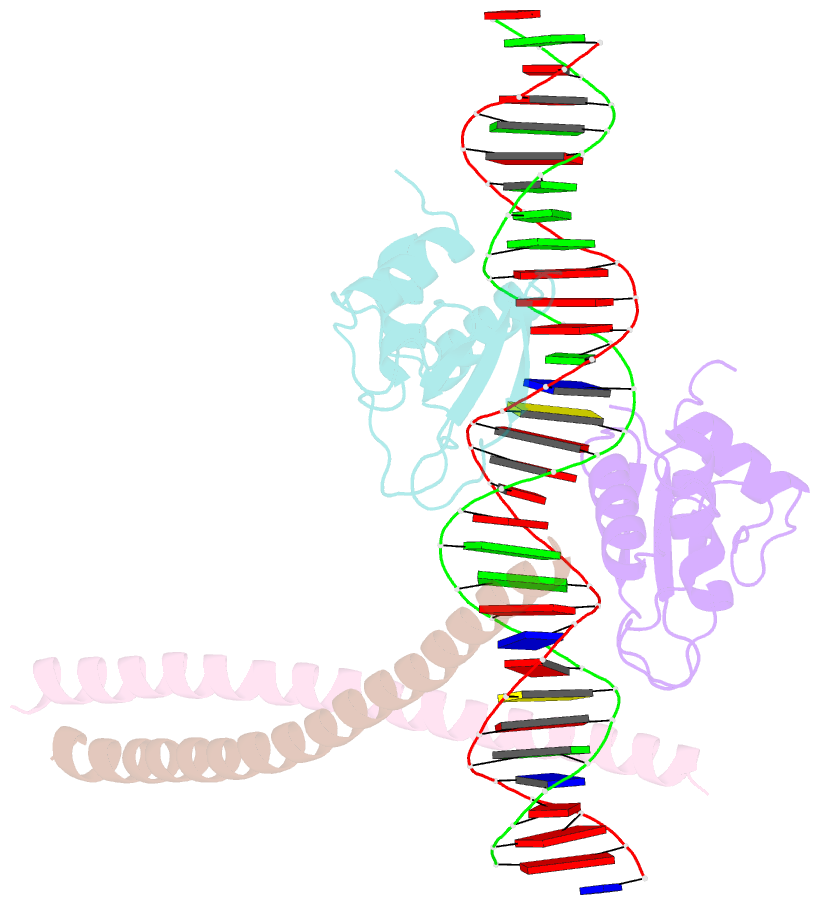
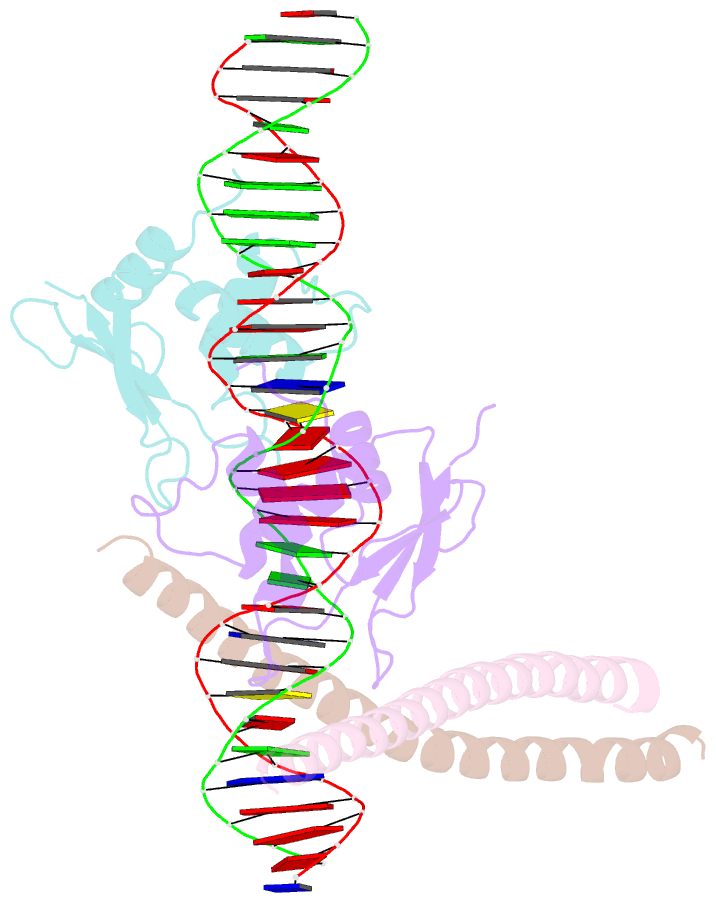
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 1t2k; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- transcription-DNA
- Method
- X-ray (3.0 Å)
- Summary
- Structure of the DNA binding domains of irf3, atf-2 and jun bound to DNA
- Reference
- Panne D, Maniatis T, Harrison SC (2004): "Crystal structure of ATF-2/c-Jun and IRF-3 bound to the interferon-beta enhancer." Embo J., 23, 4384-4393. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600453.
- Abstract
- Transcriptional activation of the interferon-beta (IFN-beta) gene requires assembly of an enhanceosome containing the transcription factors ATF-2/c-Jun, IRF-3/IRF-7, NF-kappaB and HMGI(Y). These factors cooperatively bind a composite DNA site and activate expression of the IFN-beta gene. The 3.0 A crystal structure of the DNA-binding domains of ATF-2/c-Jun and two IRF-3 molecules in a complex with 31 base pairs (bp) of the PRDIV-PRDIII region of the IFN-beta enhancer shows that association of the four proteins with DNA creates a continuous surface for the recognition of 24 bp. The structure, together with in vitro binding studies and protein mutagenesis, shows that protein-protein interactions are not critical for cooperative binding. Instead, cooperativity arises mainly through nucleotide sequence-dependent structural changes in the DNA that allow formation of complementary DNA conformations. Because the binding sites overlap on the enhancer, the unit of recognition is the entire nucleotide sequence, not the individual subsites.