Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 1ttt; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- complex (elongation factor-trna)
- Method
- X-ray (2.7 Å)
- Summary
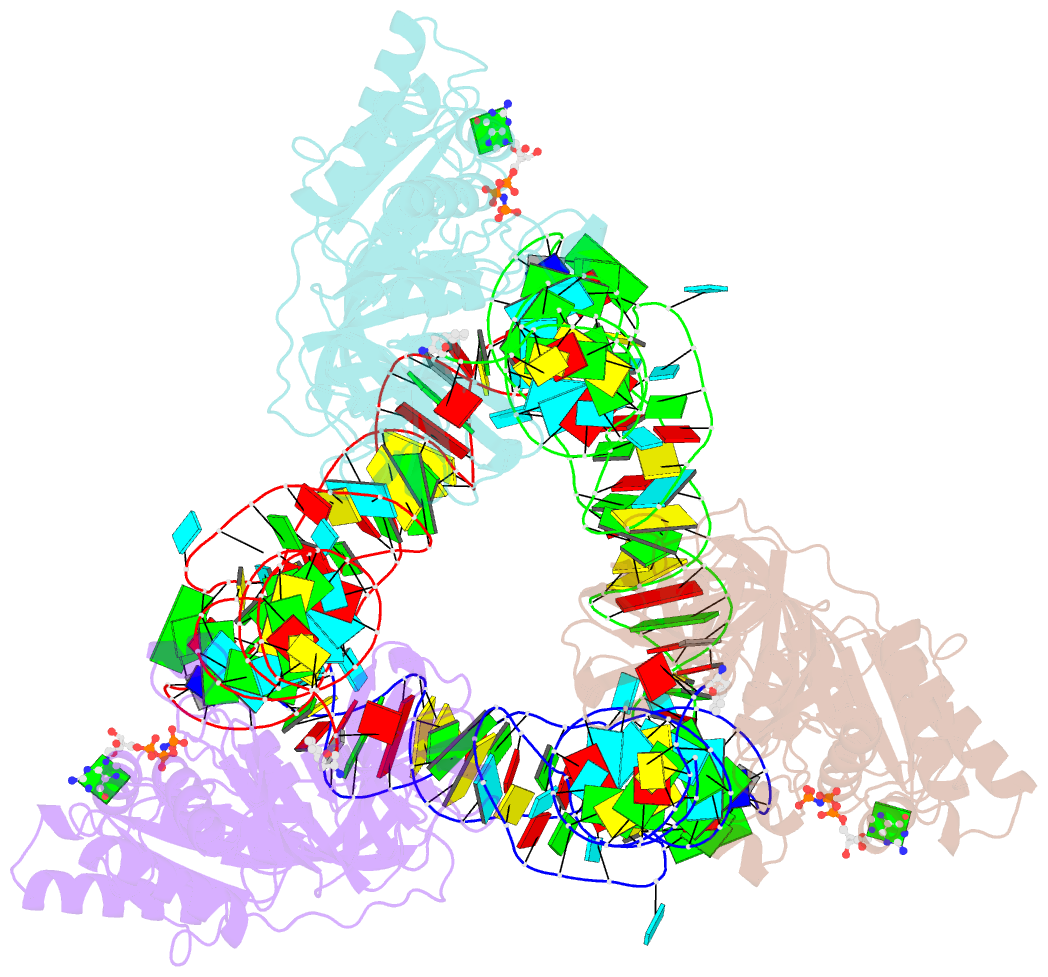
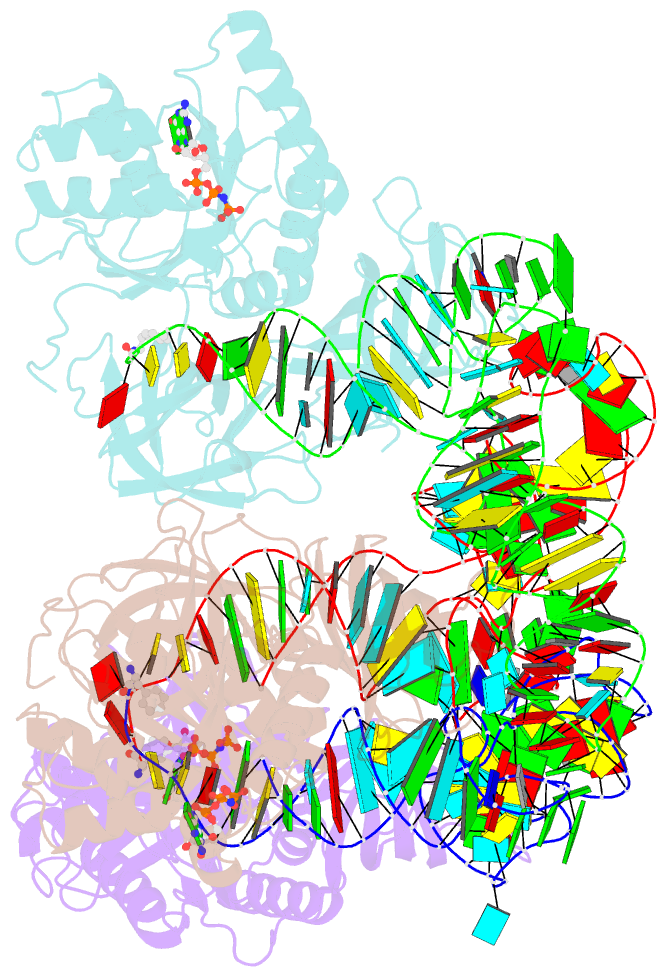
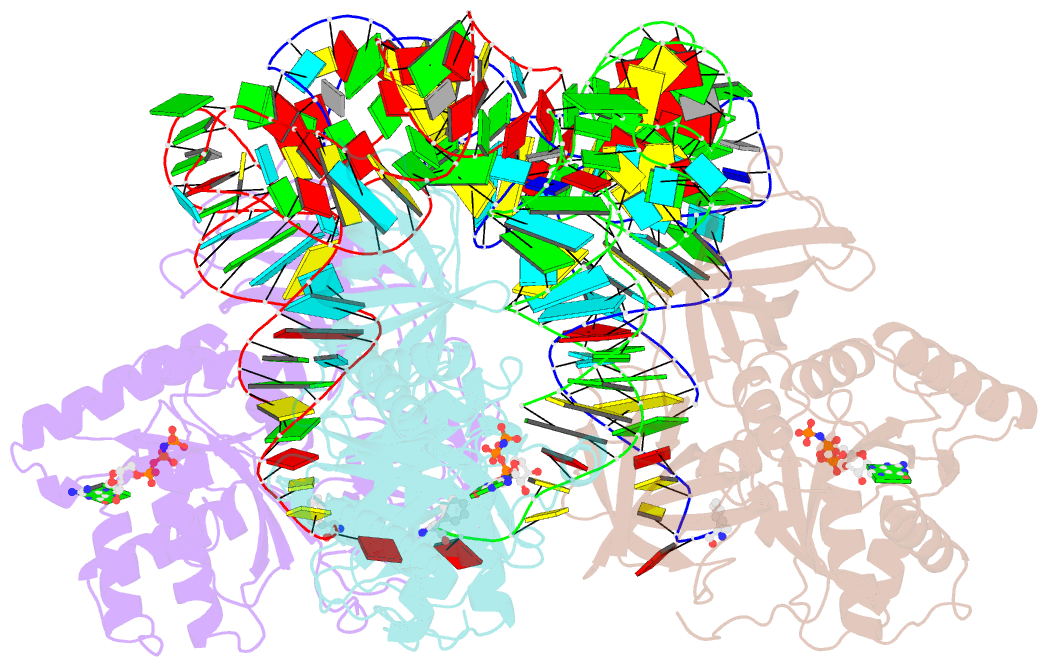
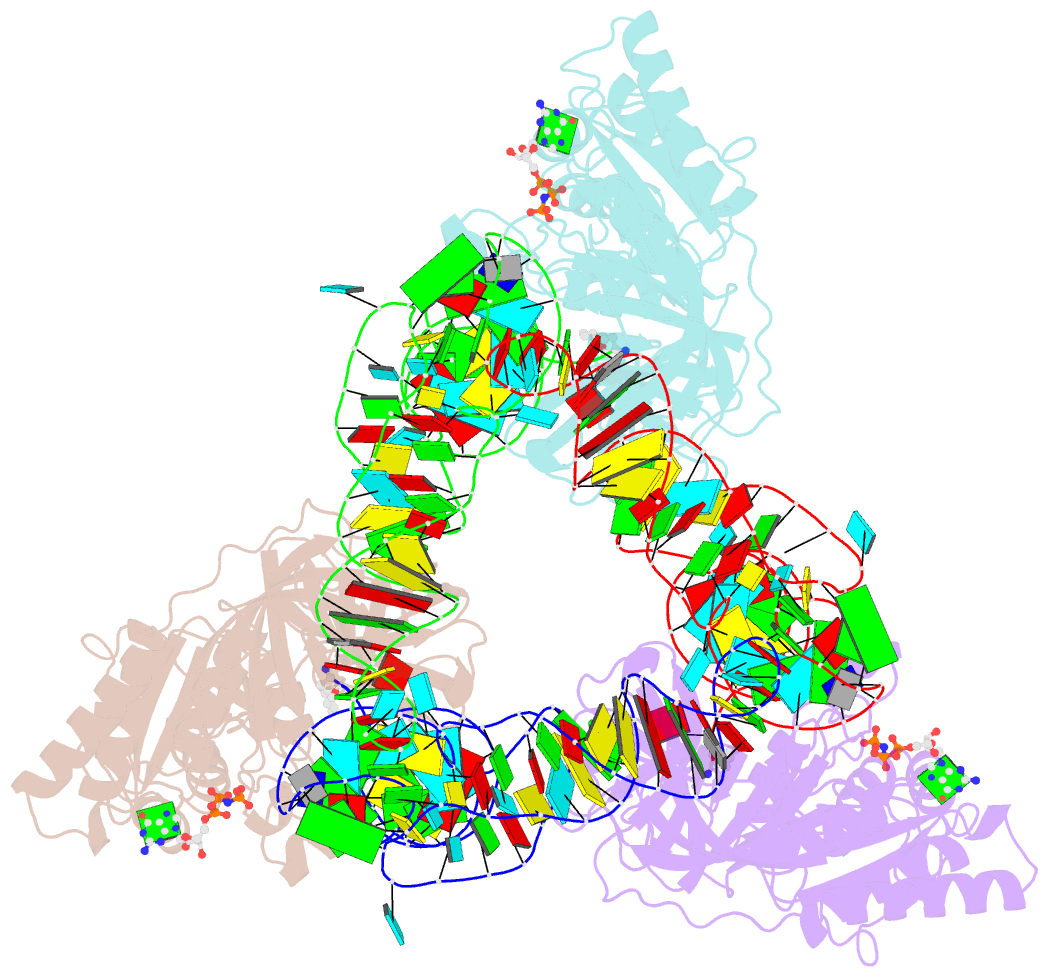
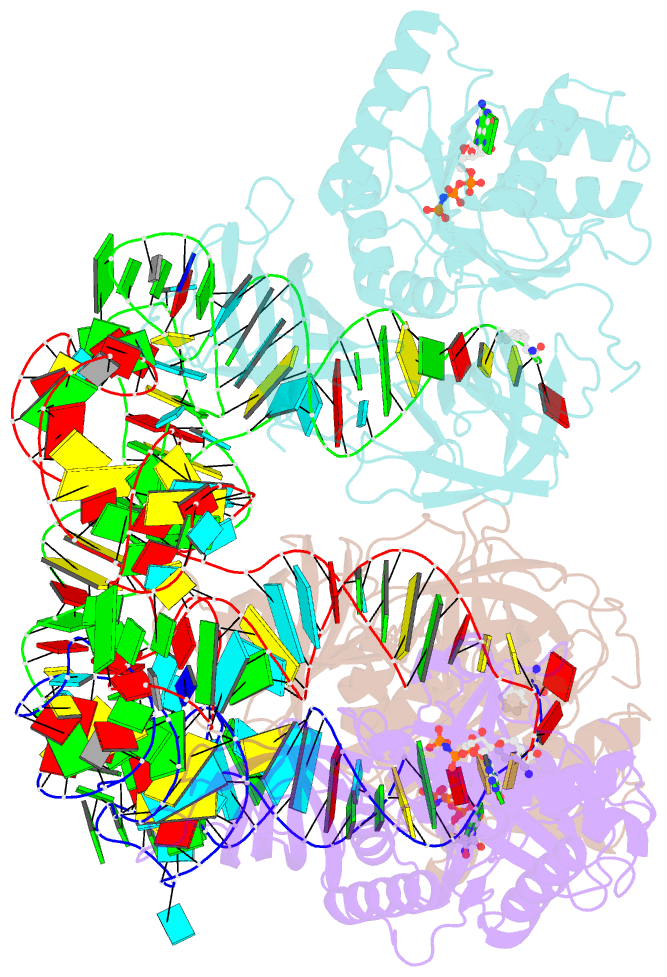
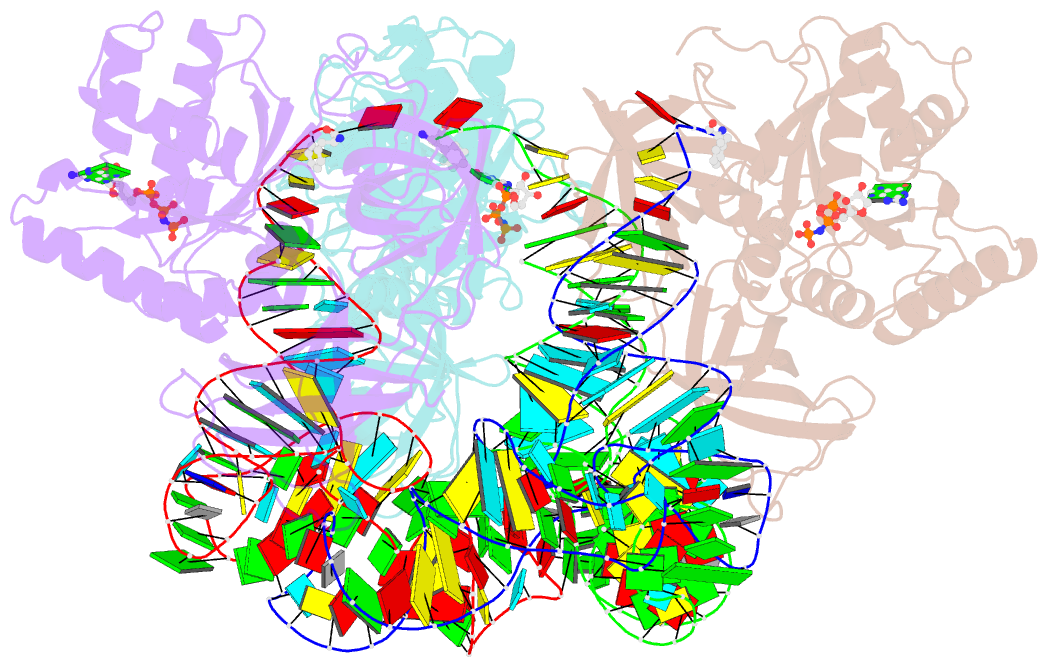
- Phe-trna, elongation factor ef-tu:gdpnp ternary complex
- Reference
- Nissen P, Kjeldgaard M, Thirup S, Polekhina G, Reshetnikova L, Clark BF, Nyborg J (1995): "Crystal structure of the ternary complex of Phe-tRNAPhe, EF-Tu, and a GTP analog." Science, 270, 1464-1472.
- Abstract
- The structure of the ternary complex consisting of yeast phenylalanyl-transfer RNA (Phe-tRNAPhe), Thermus aquaticus elongation factor Tu (EF-Tu), and the guanosine triphosphate (GTP) analog GDPNP was determined by x-ray crystallography at 2.7 angstrom resolution. The ternary complex participates in placing the amino acids in their correct order when messenger RNA is translated into a protein sequence on the ribosome. The EF-Tu-GDPNP component binds to one side of the acceptor helix of Phe-tRNAPhe involving all three domains of EF-Tu. Binding sites for the phenylalanylated CCA end and the phosphorylated 5' end are located at domain interfaces, whereas the T stem interacts with the surface of the beta-barrel domain 3. The binding involves many conserved residues in EF-Tu. The overall shape of the ternary complex is similar to that of the translocation factor, EF-G-GDP, and this suggests a novel mechanism involving "molecular mimicry" in the translational apparatus.