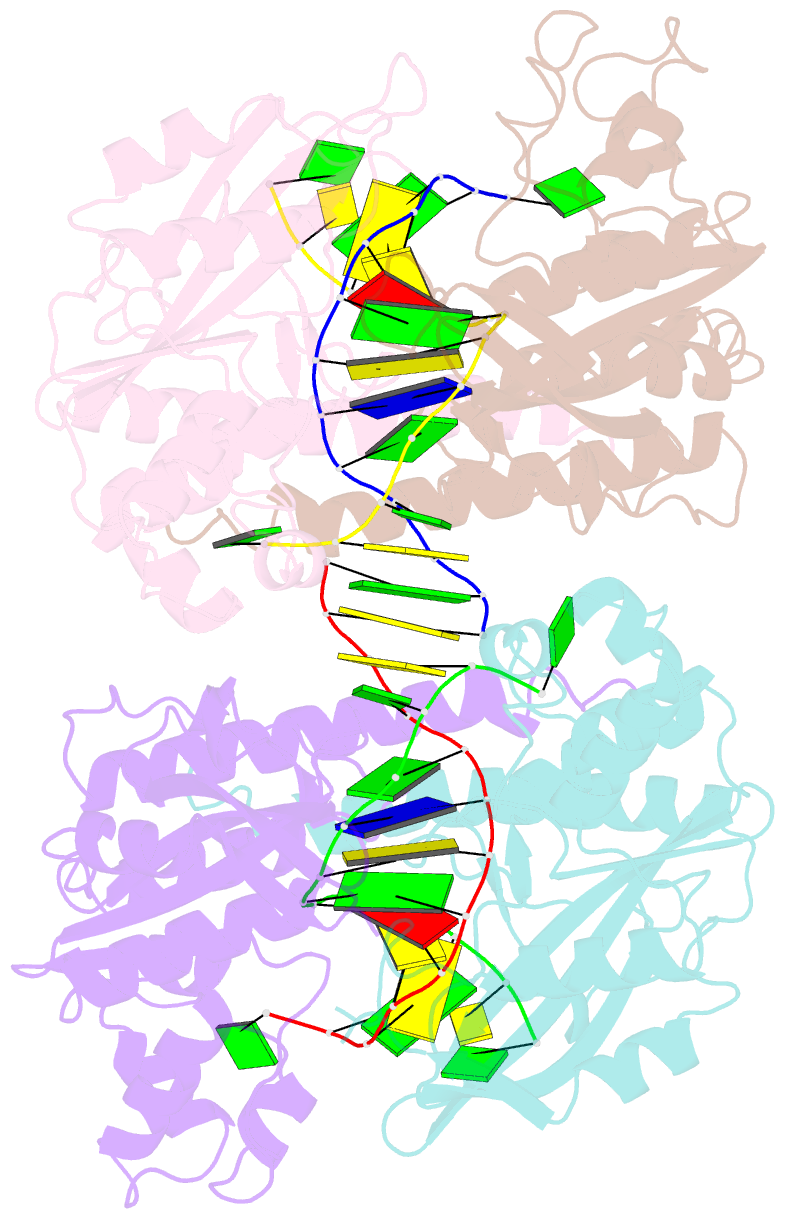
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 1tx3; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- hydrolase-DNA
- Method
- X-ray (2.5 Å)
- Summary
- Hincii bound to cognate DNA
- Reference
- Etzkorn C, Horton NC (2004): "Ca2+ binding in the active site of HincII: implications for the catalytic mechanism." Biochemistry, 43, 13256-13270. doi: 10.1021/bi0490082.
- Abstract
- The 2.8 A crystal structure of the type II restriction endonuclease HincII bound to Ca(2+) and cognate DNA containing GTCGAC is presented. The DNA is uncleaved, and one calcium ion is bound per active site, in a position previously described as site I in the related blunt cutting type II restriction endonuclease EcoRV [Horton, N. C., Newberry, K. J., and Perona, J. J. (1998) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 95 (23), 13489-13494], as well as that found in other related enzymes. Unlike the site I metal in EcoRV, but similar to that of PvuII, NgoMIV, BamHI, BglII, and BglI, the observed calcium cation is directly ligated to the pro-S(p) oxygen of the scissile phosphate. A calcium ion-ligated water molecule is well positioned to act as the nucleophile in the phosphodiester bond cleavage reaction, and is within hydrogen bonding distance of the conserved active site lysine (Lys 129), as well as the pro-R(p) oxygen of the phosphate group 3' of the scissile phosphate, suggesting possible roles for these groups in the catalytic mechanism. Kinetic data consistent with an important role for the 3'-phosphate group in DNA cleavage by HincII are presented. The previously observed sodium ion [Horton, N. C., Dorner, L. F., and Perona, J. J. (2002) Nat. Struct. Biol. 9, 42-47] persists in the active sites of the Ca(2+)-bound structure; however, kinetic data show little effect on the single-turnover rate of DNA cleavage in the absence of Na(+) ions.