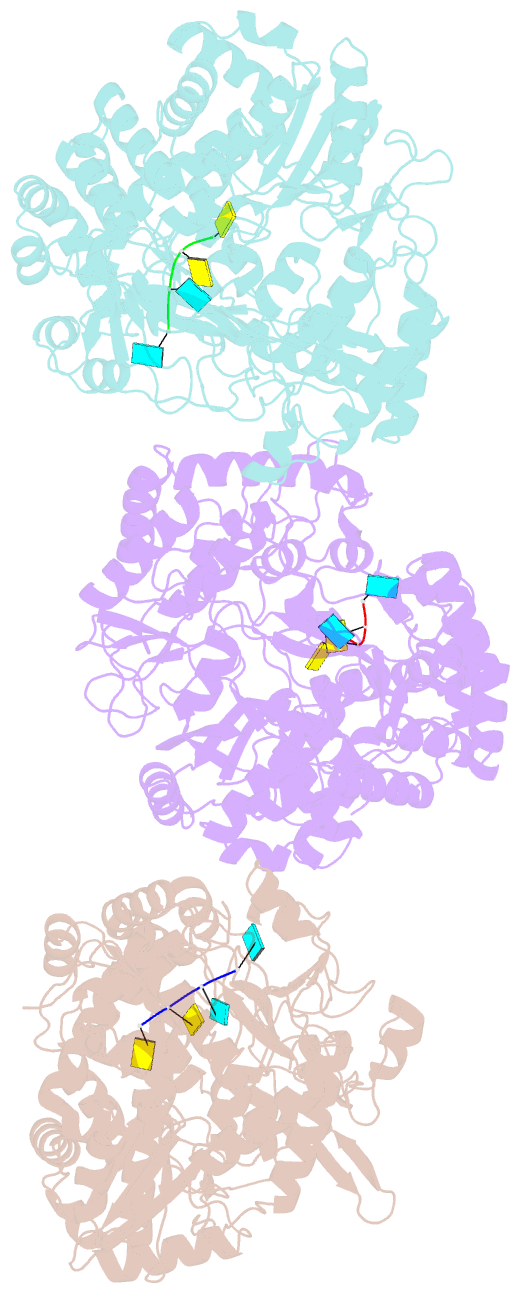
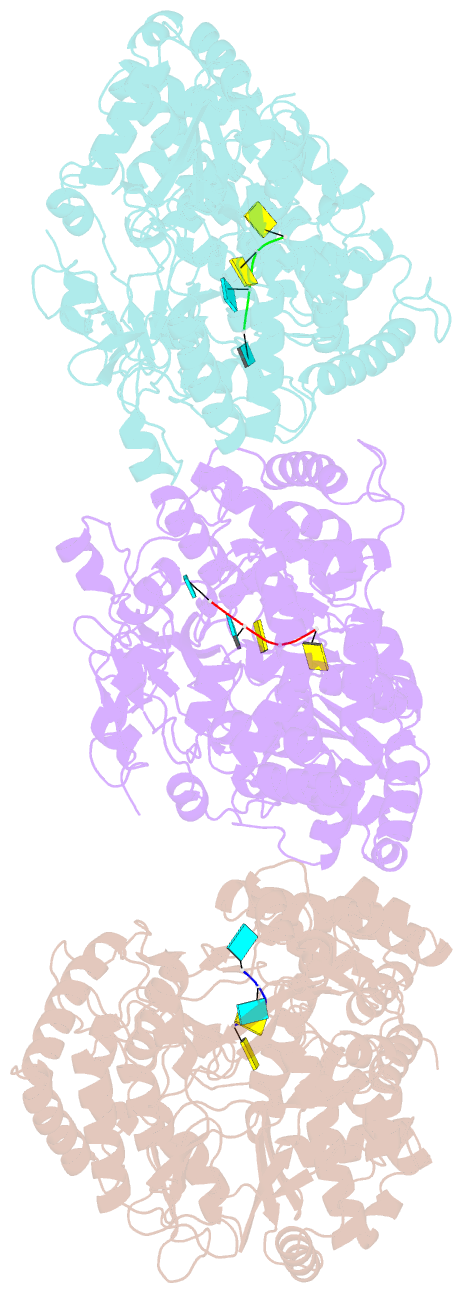
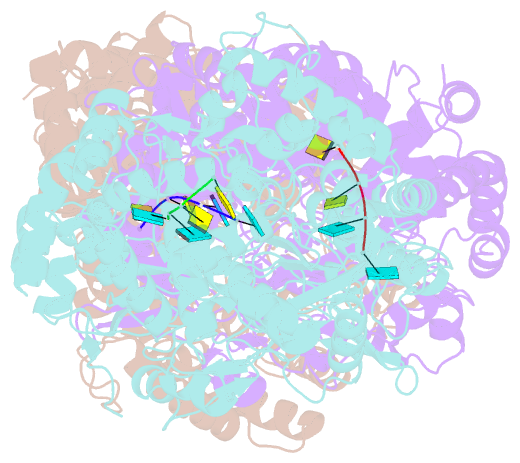
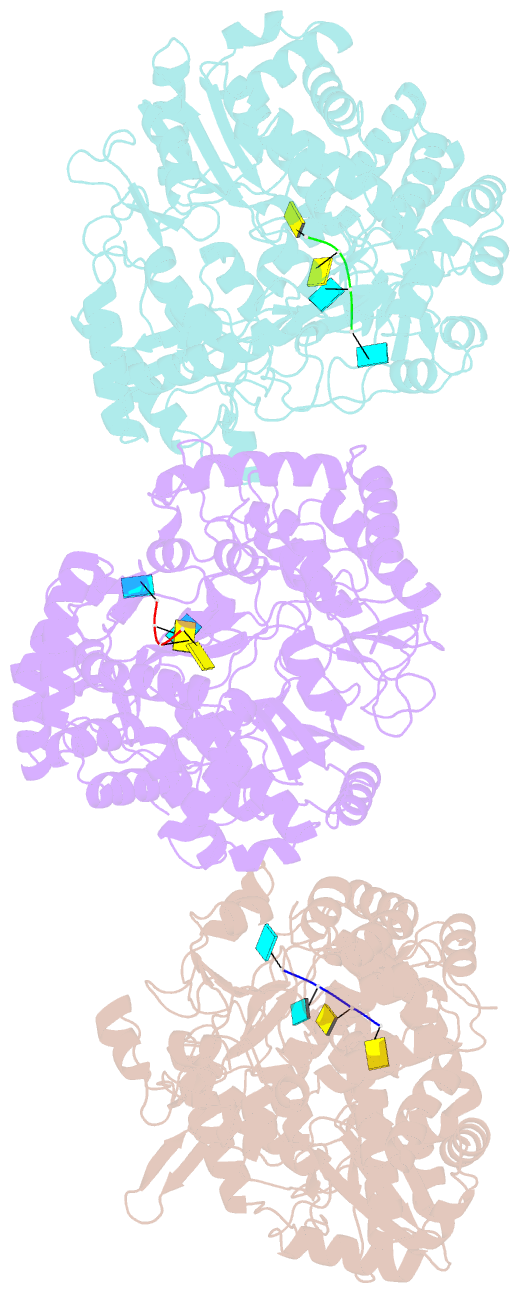
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 1uvj; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- polymerase
- Method
- X-ray (1.9 Å)
- Summary
- The structural basis for RNA specificity and ca2 inhibition of an RNA-dependent RNA polymerase phi6p2 with 7nt RNA
- Reference
- Salgado PS, Makeyev EV, Butcher SJ, Bamford DH, Stuart DI, Grimes JM (2004): "The structural basis for RNA specificity and Ca2+ inhibition of an RNA-dependent RNA polymerase." Structure, 12, 307-316. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2004.01.012.
- Abstract
- The RNA-dependent RNA polymerase of bacteriophage phi6 transcribes mRNA from the three segments of the dsRNA viral genome. We have cocrystallized RNA oligonucleotides with the polymerase, revealing the mode of binding of RNA templates. This binding is somewhat different from that previously seen for DNA oligomers, leading to additional RNA-protein hydrogen bonds, consistent with a preference for RNA. Activation of the RNA/polymerase complex by the addition of substrate and Mg2+ initiates a single round of reaction within the crystal to form a dead-end complex that partially collapses within the enzyme active site. By replacing Mg2+ with Ca2+, we have been able to capture the inhibited complex which shows distortion that explains the structural basis for the inhibition of such polymerases by Ca2+.