Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 1wmq; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- transcription-RNA
- Method
- X-ray (1.6 Å)
- Summary
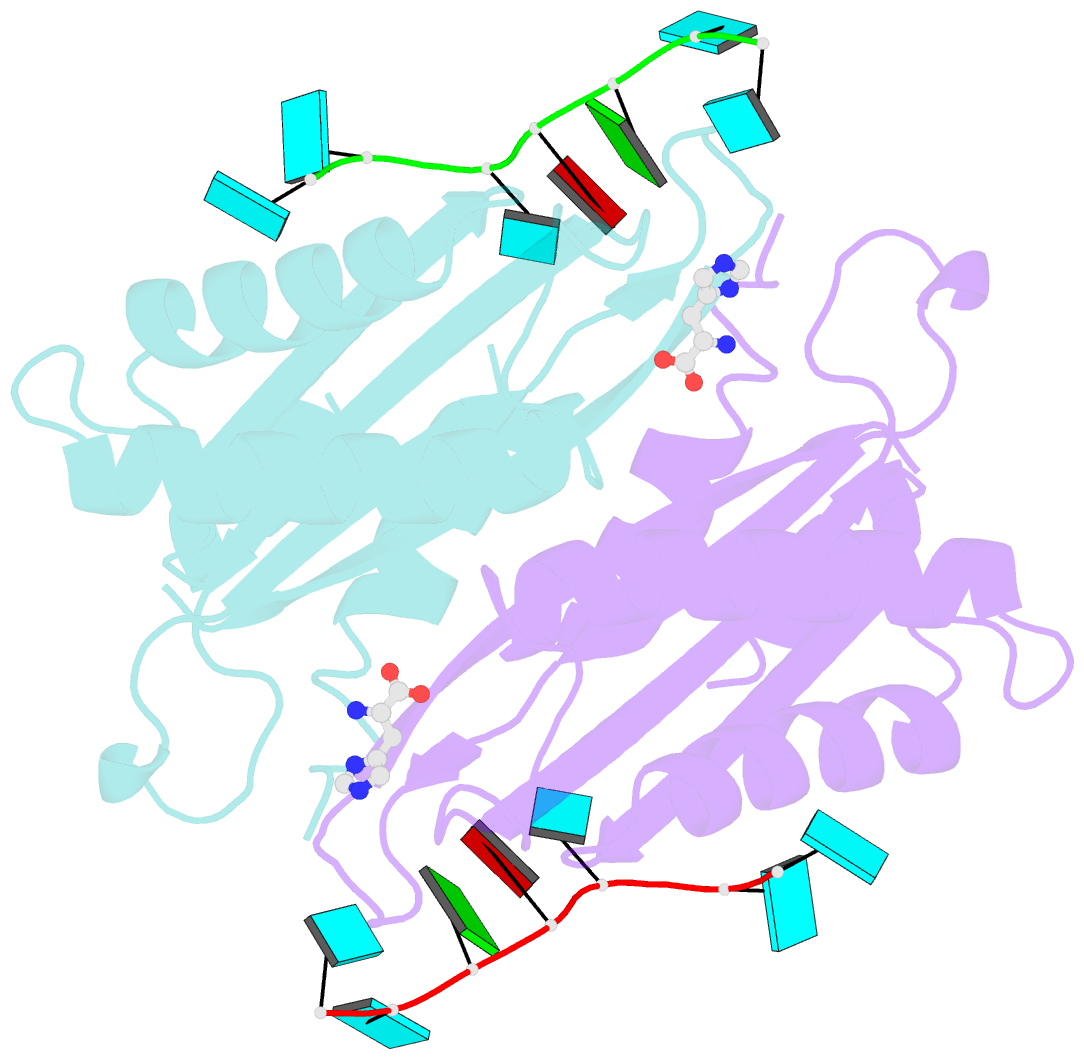
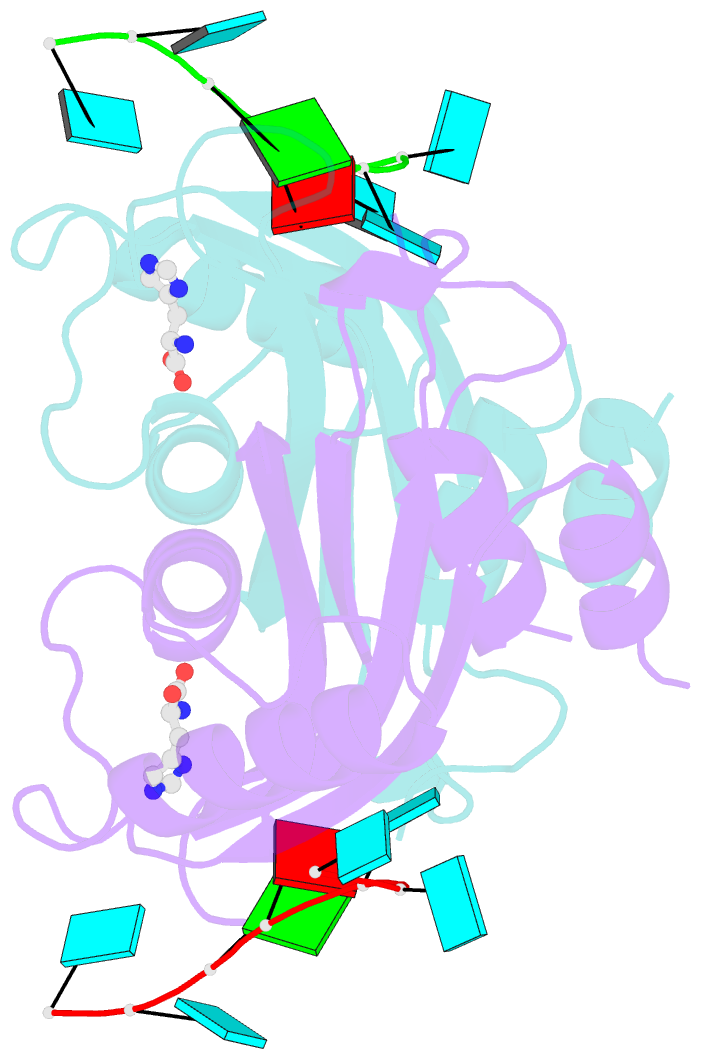
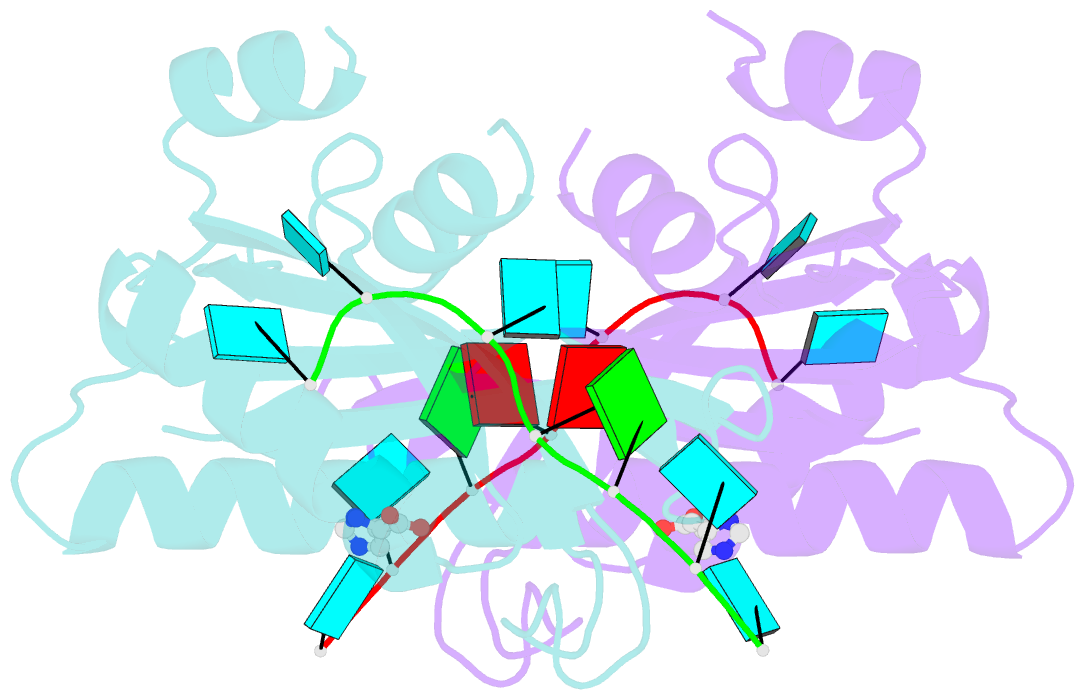
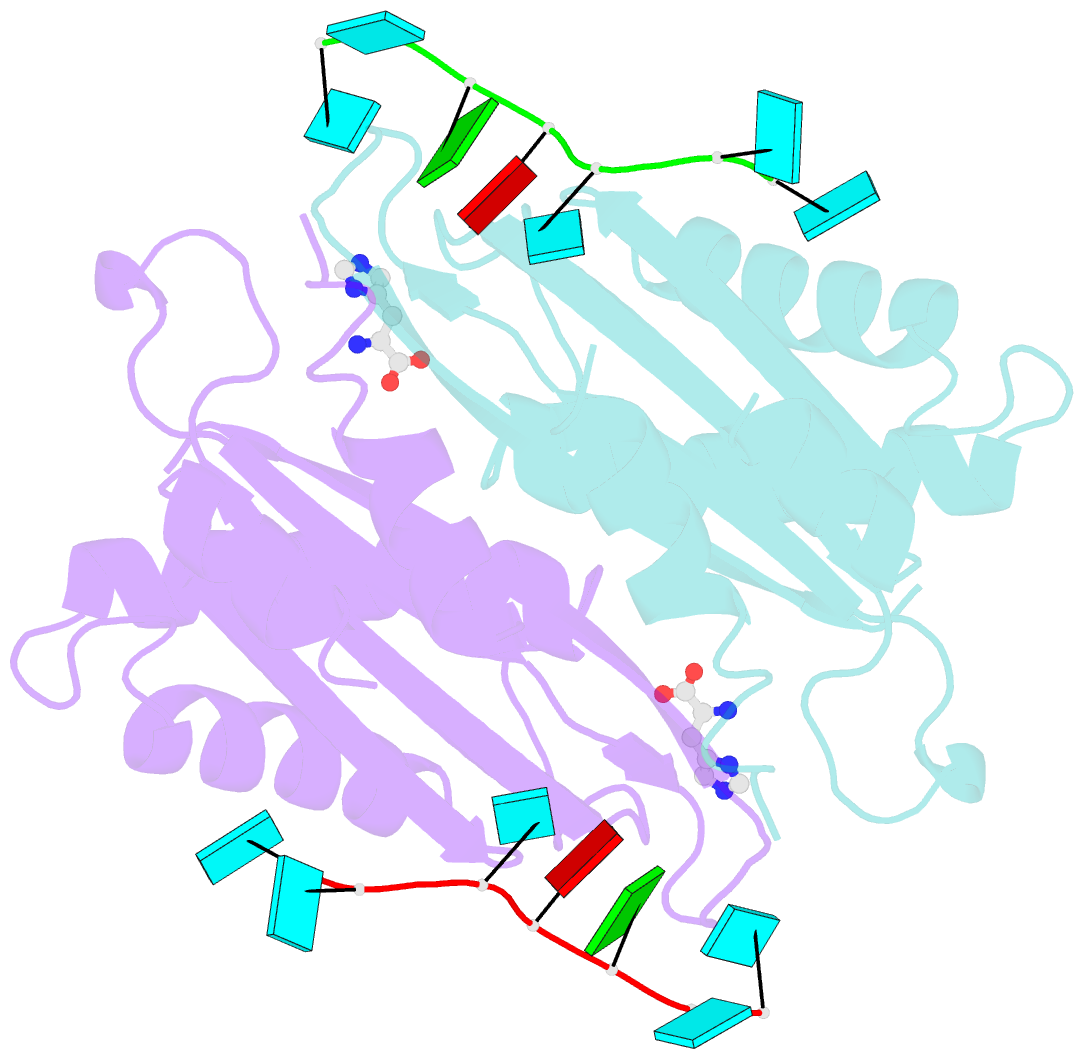
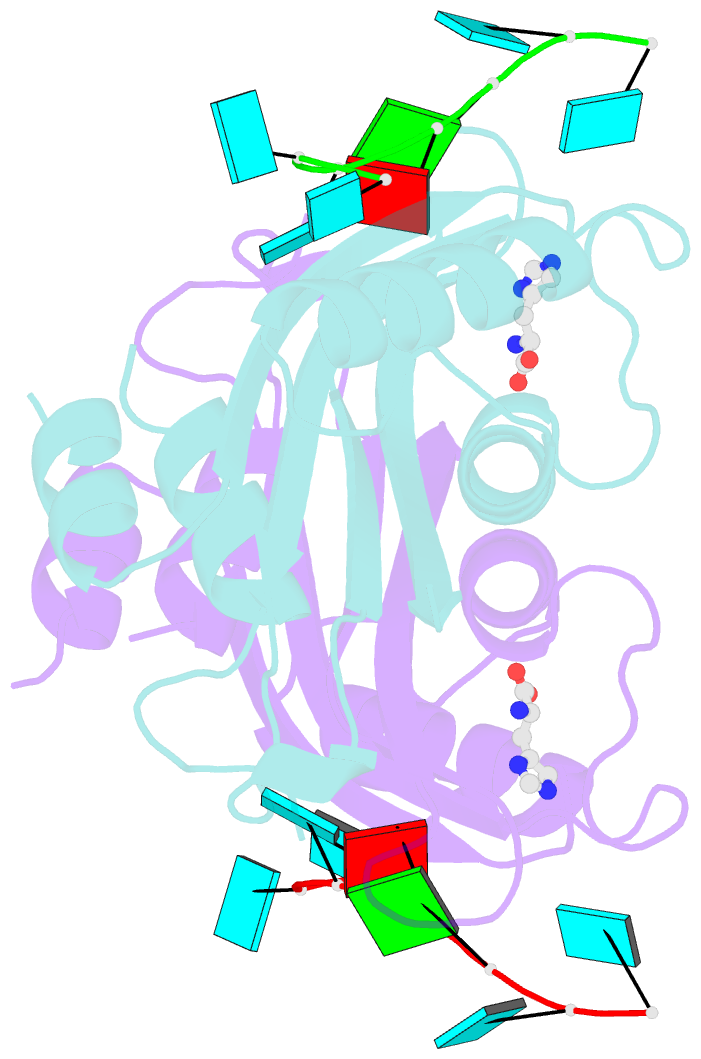
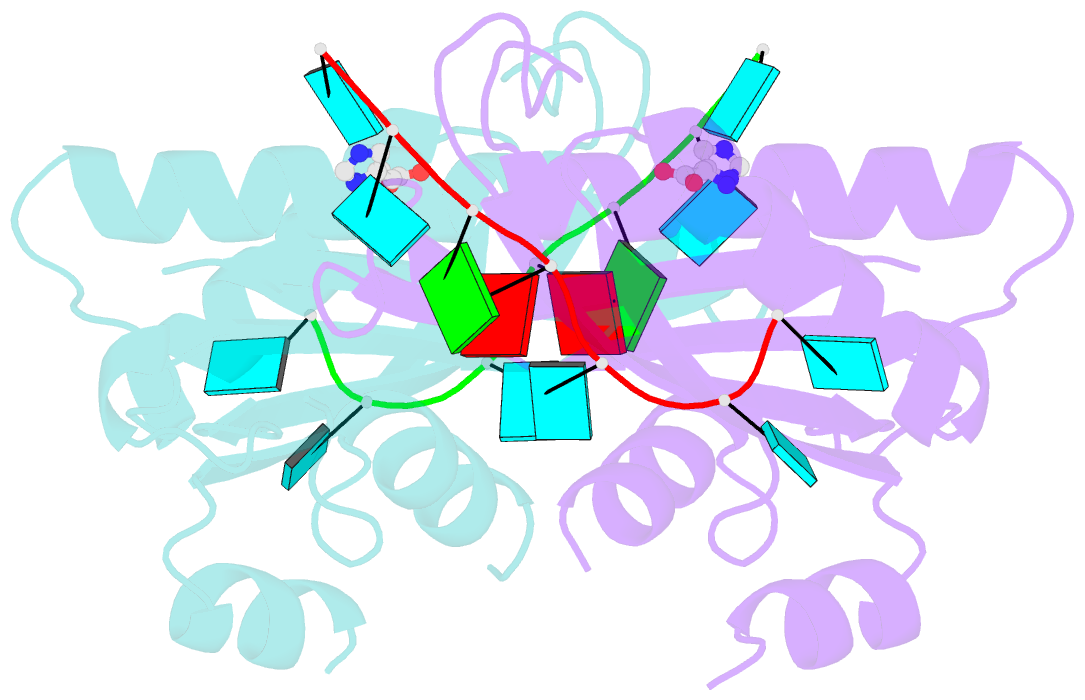
- Structure of the hutp antitermination complex bound to a single stranded region of hut mrna
- Reference
- Kumarevel T, Mizuno H, Kumar PK (2005): "Structural basis of HutP-mediated anti-termination and roles of the Mg2+ ion and L-histidine ligand." Nature, 434, 183-191. doi: 10.1038/nature03355.
- Abstract
- HutP regulates the expression of the hut structural genes of Bacillus subtilis by an anti-termination mechanism and requires two components, Mg2+ ions and L-histidine. HutP recognizes three UAG triplet units, separated by four non-conserved nucleotides on the terminator region. Here we report the 1.60-A resolution crystal structure of the quaternary complex (HutP-L-histidine-Mg2+-21-base single-stranded RNA). In the complex, the RNA adopts a novel triangular fold on the hexameric surface of HutP, without any base-pairing, and binds to the protein mostly by specific protein-base interactions. The structure explains how the HutP and RNA interactions are regulated critically by the l-histidine and Mg2+ ion through the structural rearrangement. To gain insights into these structural rearrangements, we solved two additional crystal structures (uncomplexed HutP and HutP-L-histidine-Mg2+) that revealed the intermediate structures of HutP (before forming an active structure) and the importance of the Mg2+ ion interactions in the complexes.