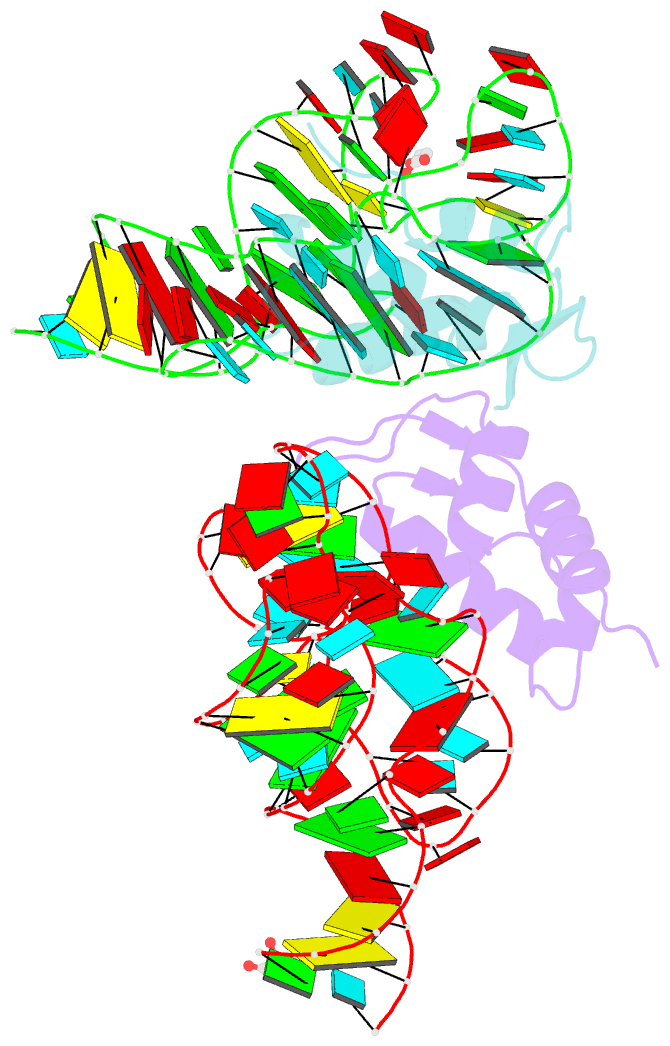
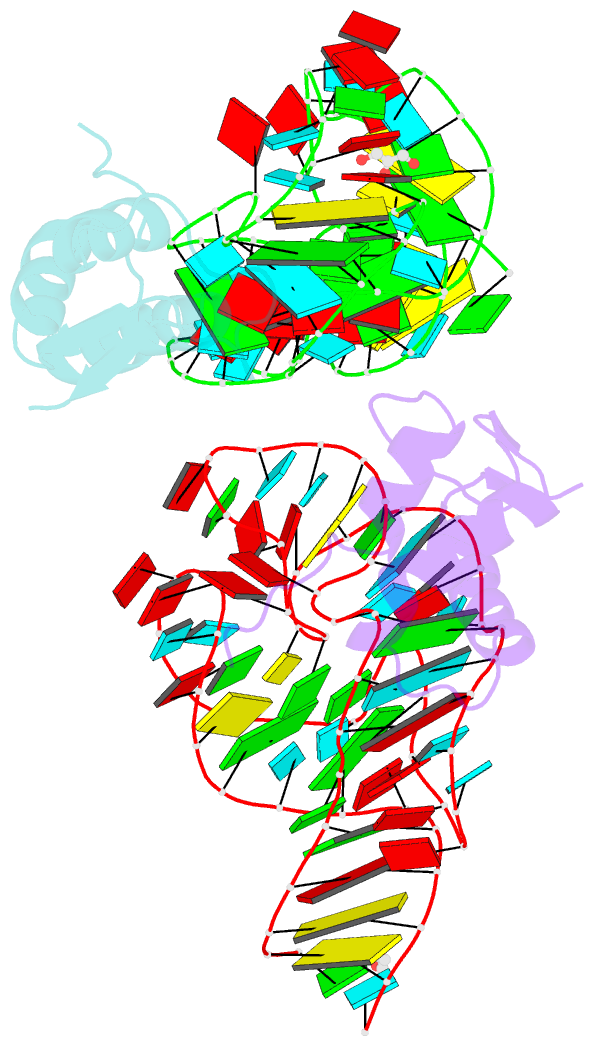
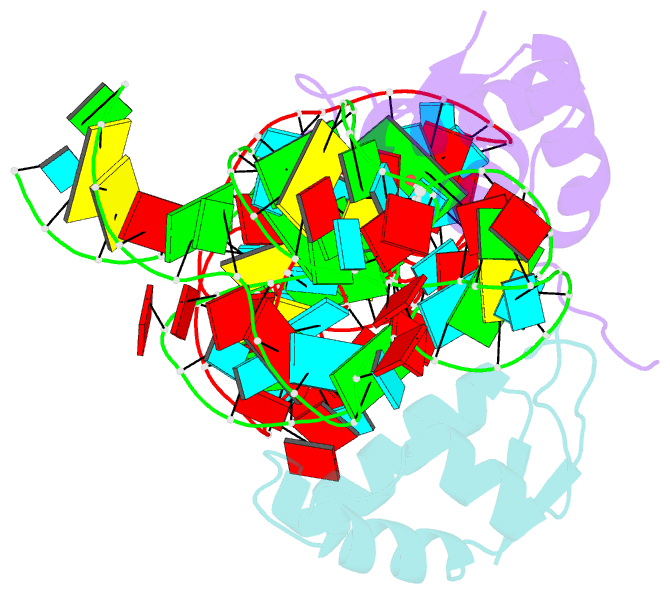
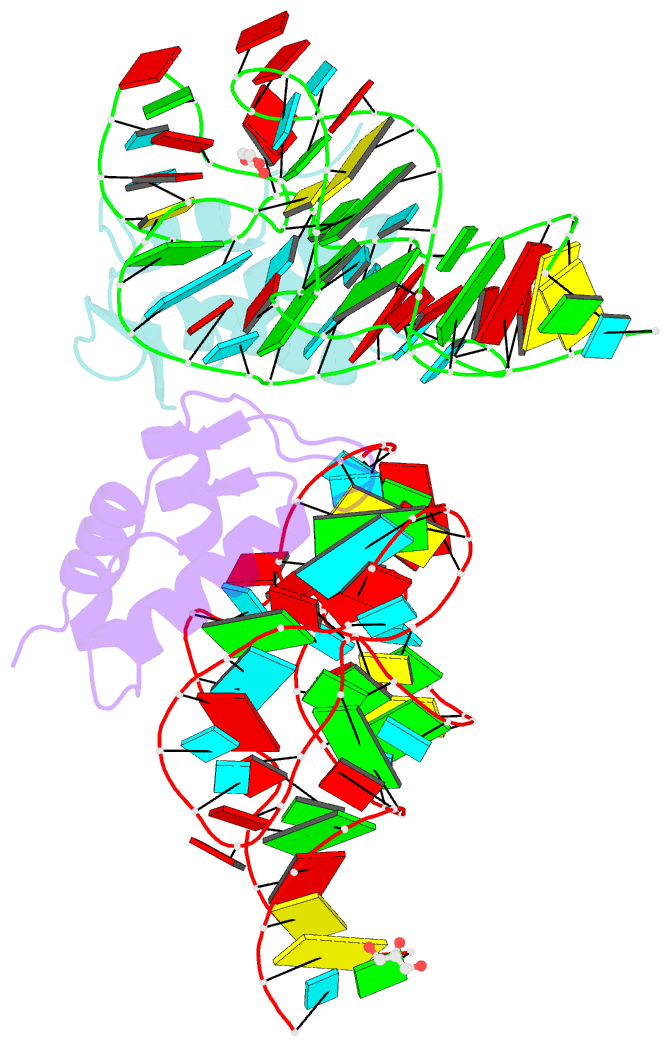
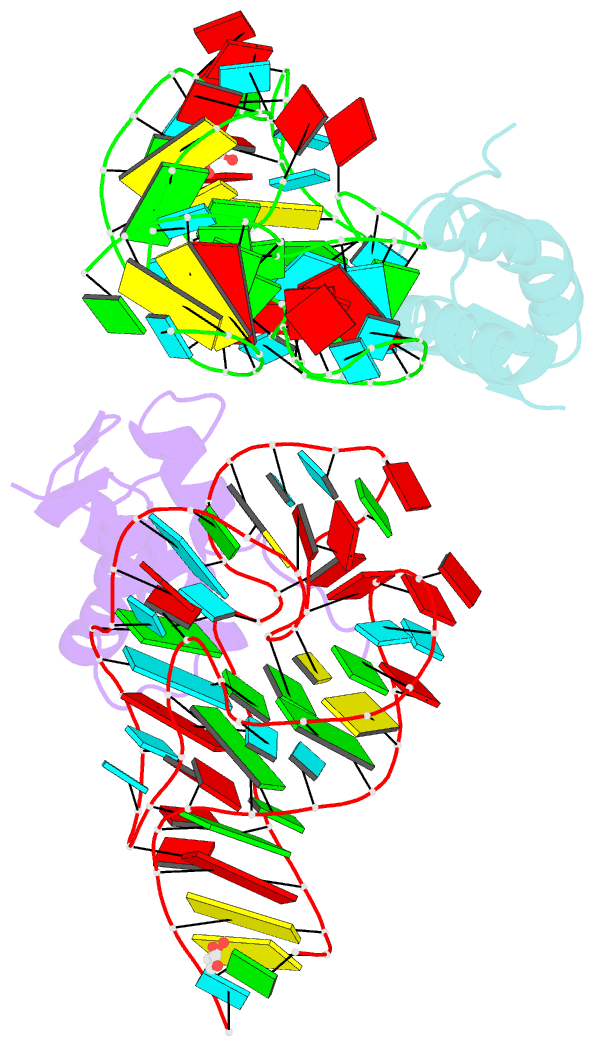
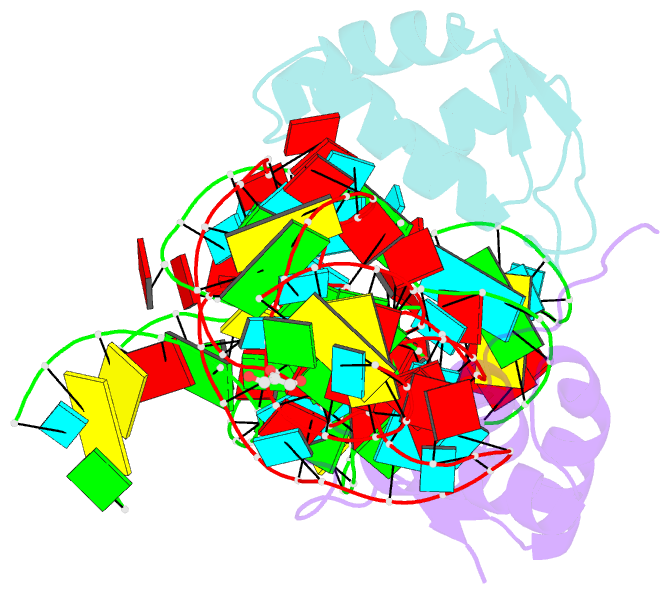
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 1y39; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- structural protein-RNA
- Method
- X-ray (2.8 Å)
- Summary
- Co-evolution of protein and RNA structures within a highly conserved ribosomal domain
- Reference
- Dunstan MS, Guhathakurta D, Draper DE, Conn GL (2005): "Coevolution of Protein and RNA Structures within a Highly Conserved Ribosomal Domain." Chem.Biol., 12, 201-206. doi: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2004.11.019.
- Abstract
- The X-ray crystal structure of a ribosomal L11-rRNA complex with chloroplast-like mutations in both protein and rRNA is presented. The global structure is almost identical to that of the wild-type (bacterial) complex, with only a small movement of the protein alpha helix away from the surface of the RNA required to accommodate the altered protein residue. In contrast, the specific hydrogen bonding pattern of the mutated residues is substantially different, and now includes a direct interaction between the protein side chain and an RNA base edge and a water-mediated contact. Comparison of the two structures allows the observations of sequence variation and relative affinities of wild-type and mutant complexes to be clearly rationalized, but reinforces the concept that there is no single simple code for protein-RNA recognition.