Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 1y69; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- ribosome
- Method
- X-ray (3.33 Å)
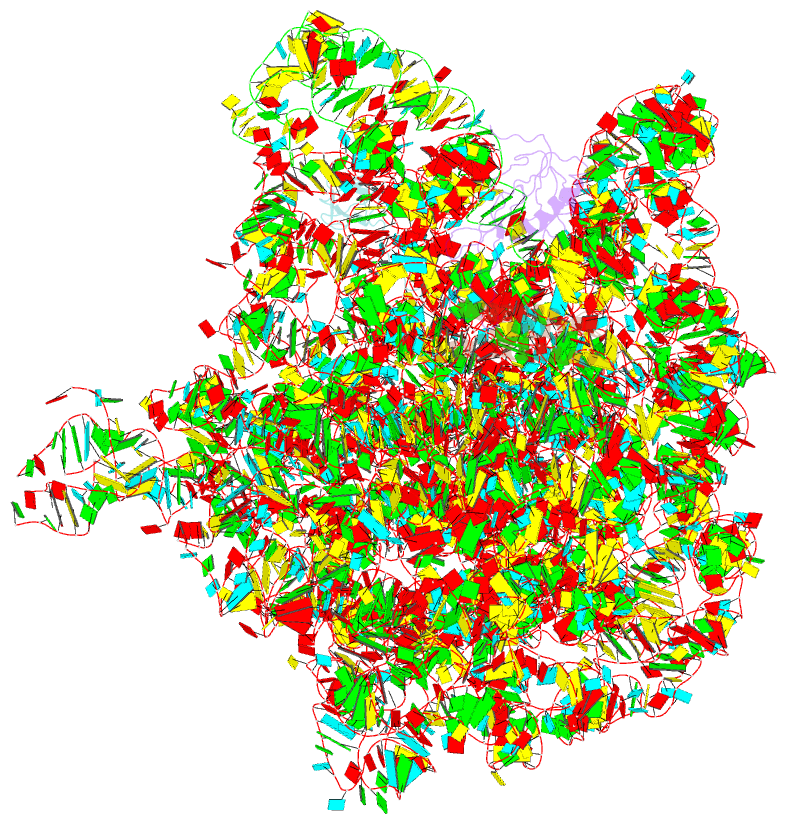
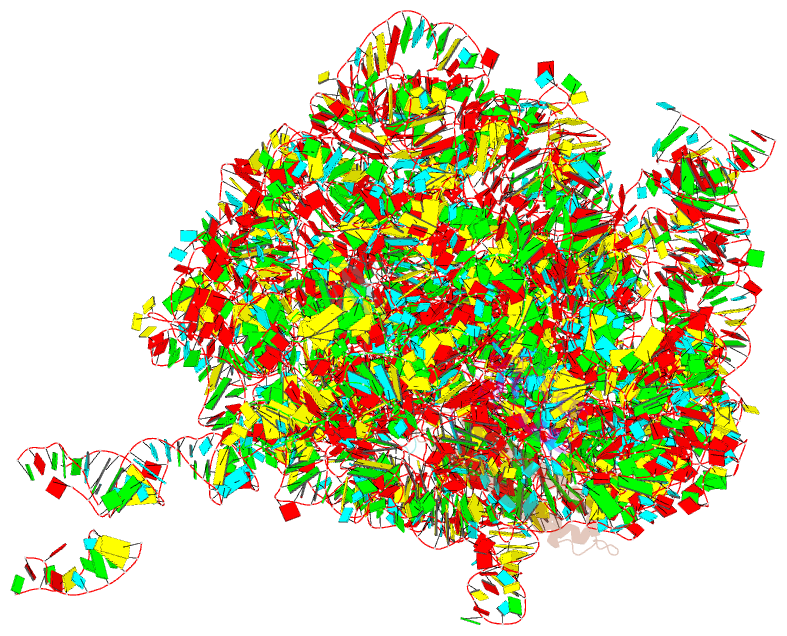
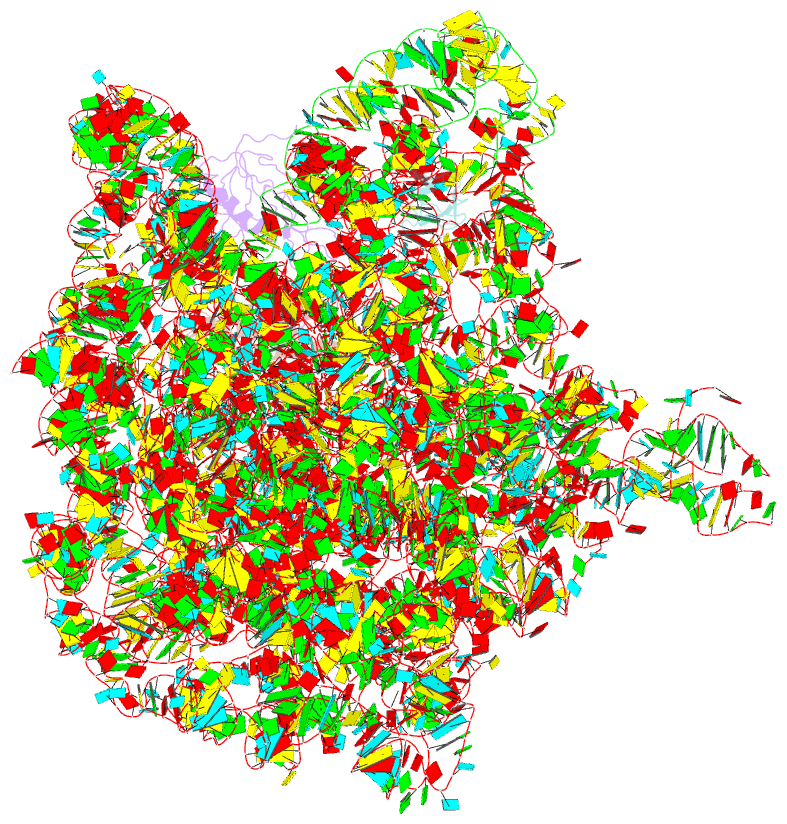
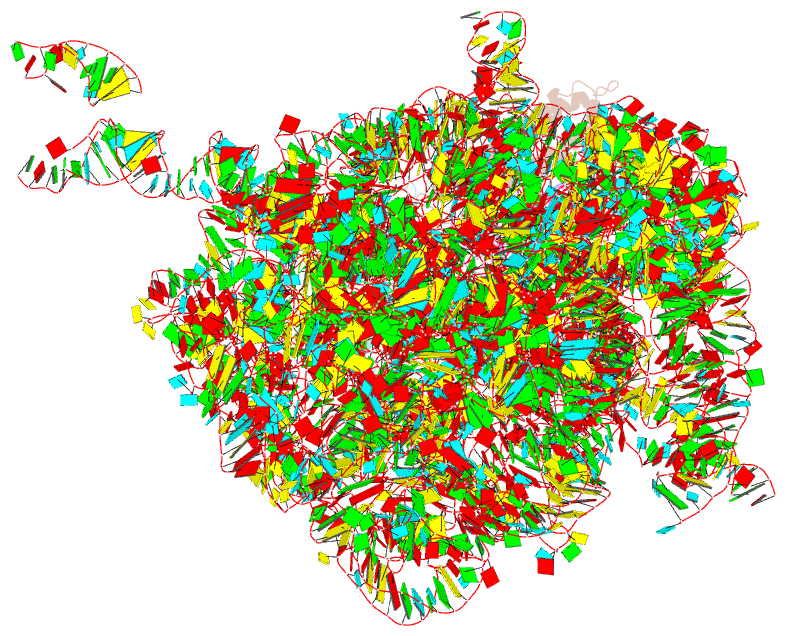
- Summary
- Rrf domain i in complex with the 50s ribosomal subunit from deinococcus radiodurans
- Reference
- Wilson DN, Schluenzen F, Harms JM, Yoshida T, Ohkubo T, Albrecht R, Buerger J, Kobayashi Y, Fucini P (2005): "X-ray crystallography on ribosome recycling: mechanism of binding and action of RRF on the 50S ribosomal subunit." EMBO J., 24, 251-260. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600525.
- Abstract
- This study presents the crystal structure of domain I of the Escherichia coli ribosome recycling factor (RRF) bound to the Deinococcus radiodurans 50S subunit. The orientation of RRF is consistent with the position determined on a 70S-RRF complex by cryoelectron microscopy (cryo-EM). Alignment, however, requires a rotation of 7 degrees and a shift of the cryo-EM RRF by a complete turn of an alpha-helix, redefining the contacts established with ribosomal components. At 3.3 A resolution, RRF is seen to interact exclusively with ribosomal elements associated with tRNA binding and/or translocation. Furthermore, these results now provide a high-resolution structural description of the conformational changes that were suspected to occur on the 70S-RRF complex, which has implications for the synergistic action of RRF with elongation factor G (EF-G). Specifically, the tip of the universal bridge element H69 is shifted by 20 A toward h44 of the 30S subunit, suggesting that RRF primes the intersubunit bridge B2a for the action of EF-G. Collectively, our data enable a model to be proposed for the dual action of EF-G and RRF during ribosome recycling.