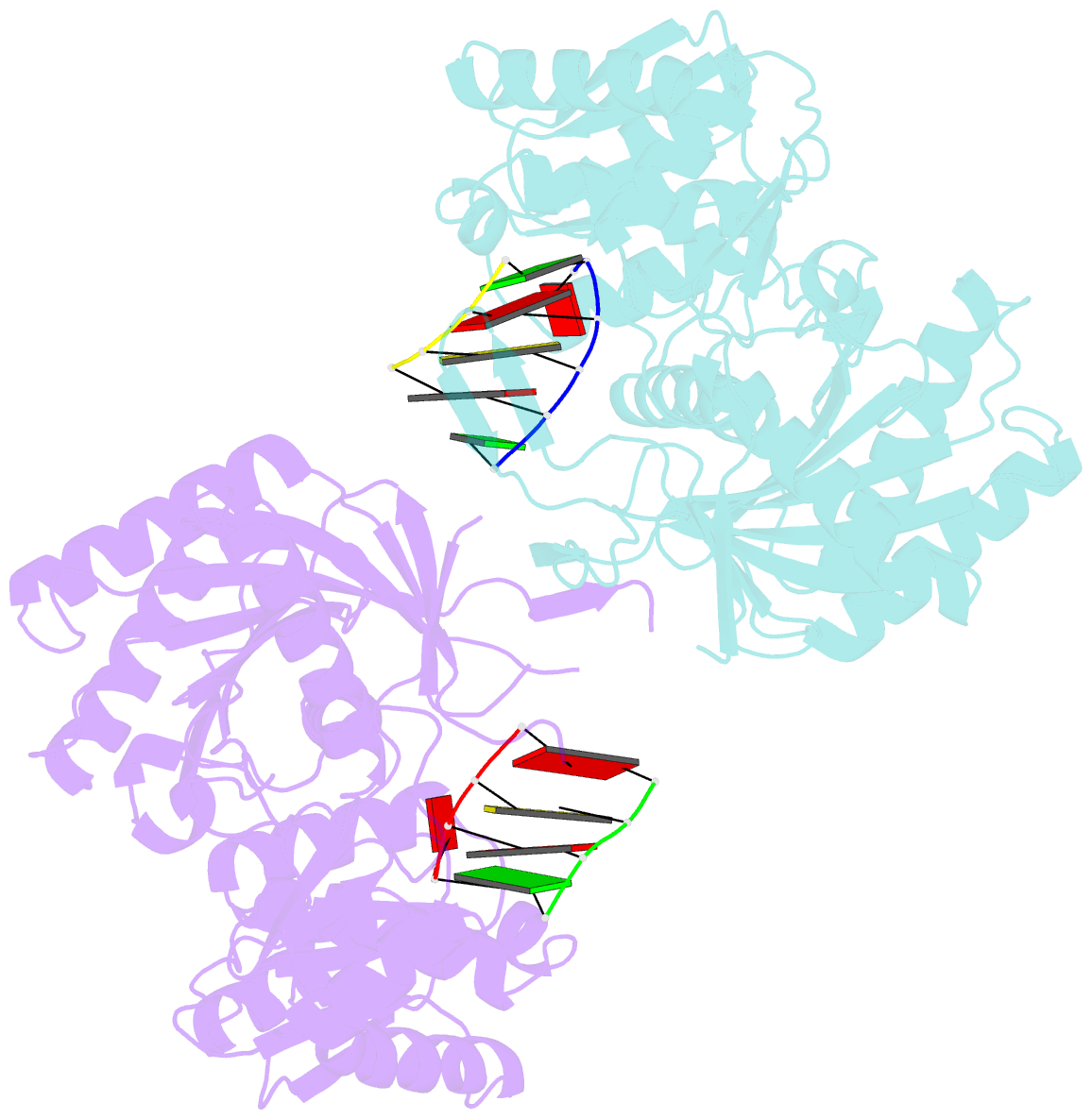
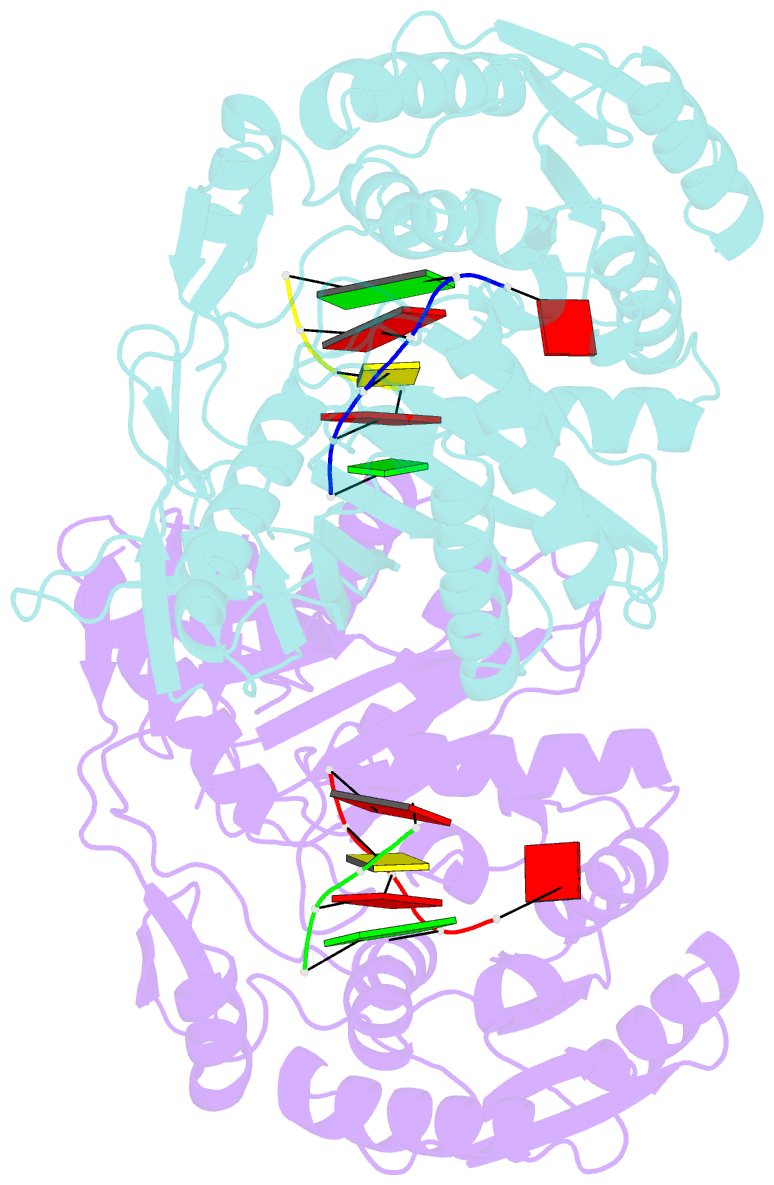
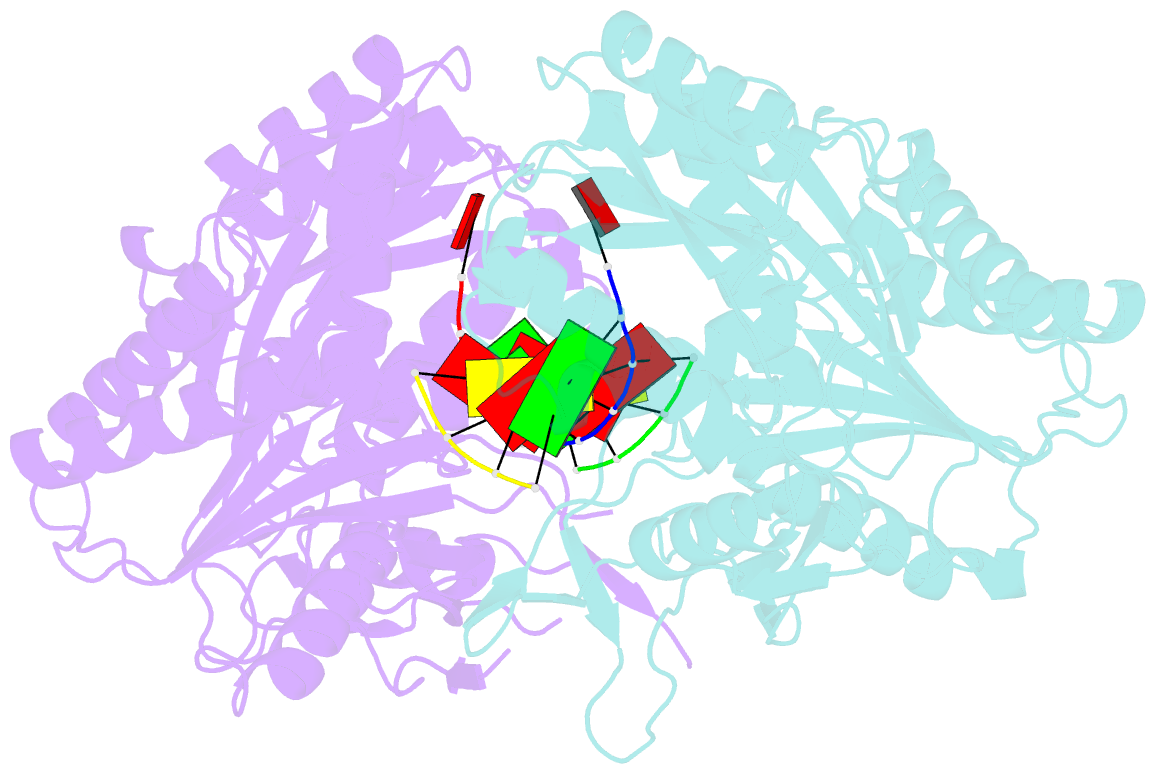
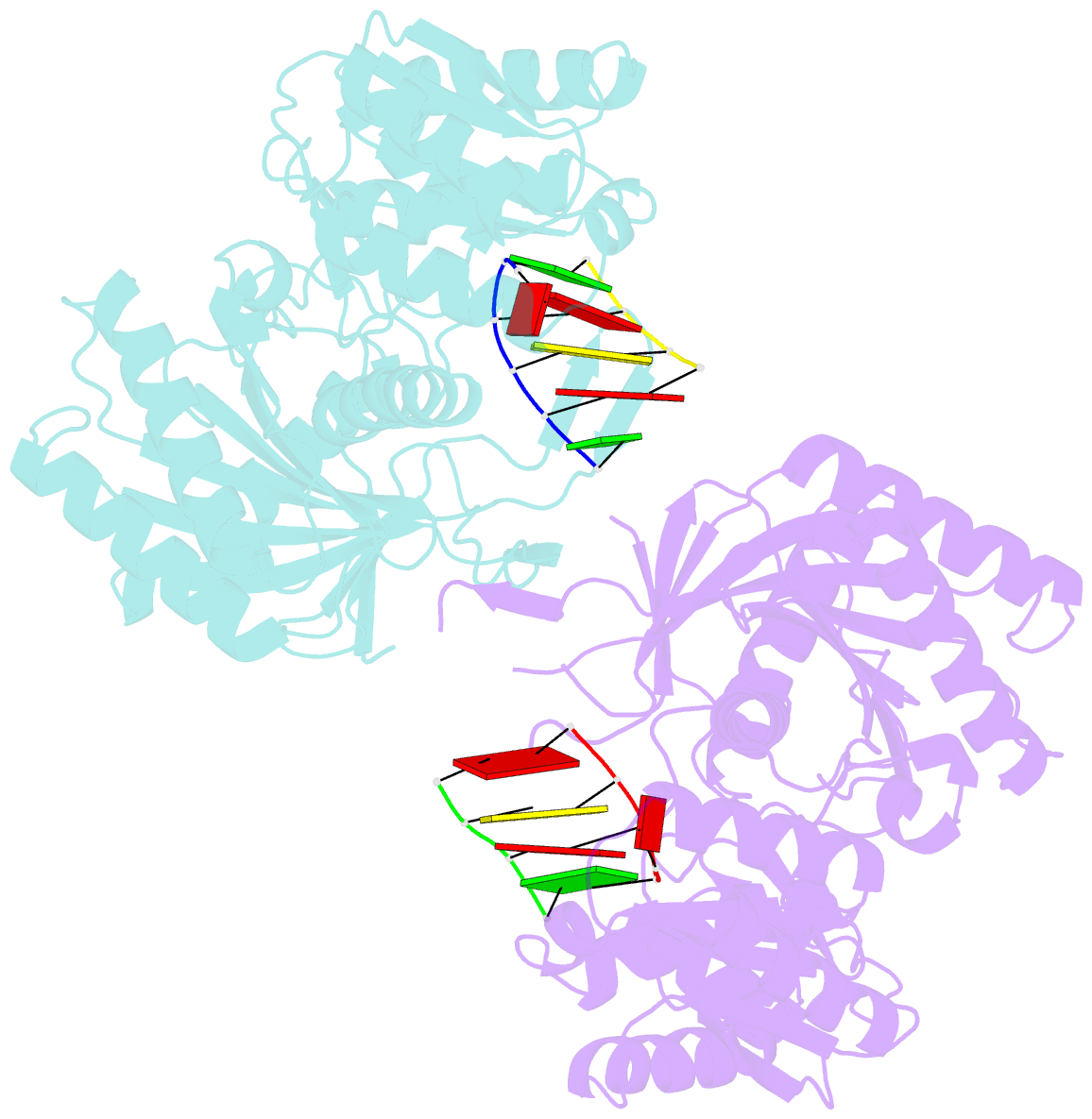
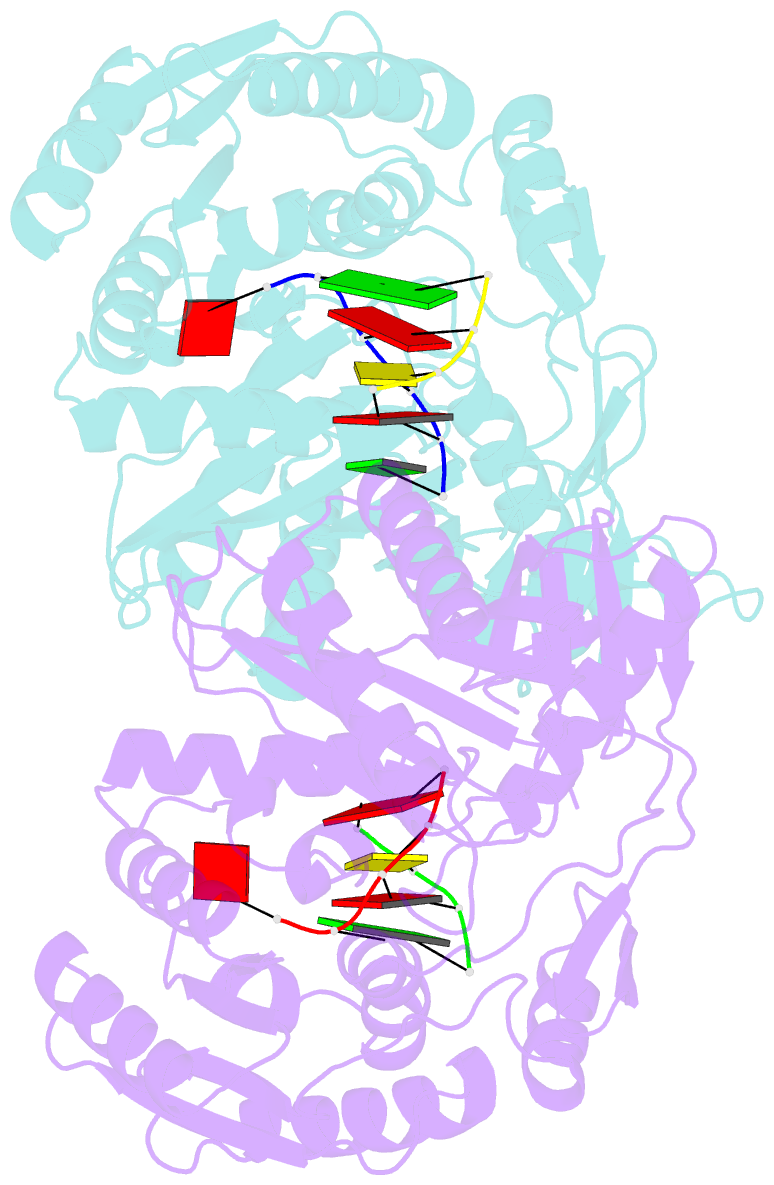
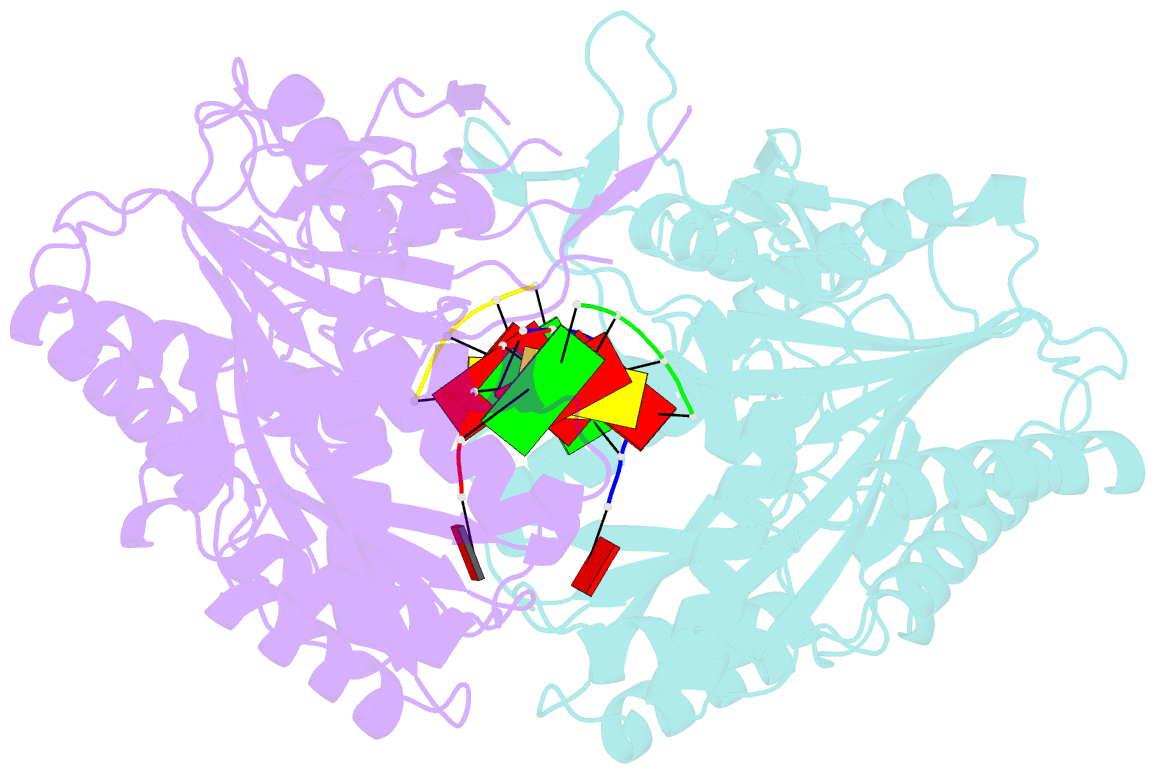
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
-
1ytu;
DSSR-derived features in text and
JSON formats; DNAproDB
- Class
- RNA binding protein-RNA
- Method
- X-ray (2.5 Å)
- Summary
- Structural basis for 5'-end-specific recognition of the
guide RNA strand by the a. fulgidus piwi protein
- Reference
-
Ma JB, Yuan YR, Meister G, Pei Y, Tuschl T, Patel DJ
(2005): "Structural
basis for 5'-end-specific recognition of guide RNA by the
A. fulgidus Piwi protein." Nature,
434, 666-670. doi: 10.1038/nature03514.
- Abstract
- RNA interference (RNAi) is a conserved
sequence-specific gene regulatory mechanism mediated by the
RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC), which is composed of
a single-stranded guide RNA and an Argonaute protein. The
PIWI domain, a highly conserved motif within Argonaute, has
been shown to adopt an RNase H fold critical for the
endonuclease cleavage activity of RISC. Here we report the
crystal structure of Archaeoglobus fulgidus Piwi protein
bound to double-stranded RNA, thereby identifying the
binding pocket for guide-strand 5'-end recognition and
providing insight into guide-strand-mediated messenger RNA
target recognition. The phosphorylated 5' end of the guide
RNA is anchored within a highly conserved basic pocket,
supplemented by the carboxy-terminal carboxylate and a
bound divalent cation. The first nucleotide from the 5' end
of the guide RNA is unpaired and stacks over a conserved
tyrosine residue, whereas successive nucleotides form a
four-base-pair RNA duplex. Mutation of the corresponding
amino acids that contact the 5' phosphate in human Ago2
resulted in attenuated mRNA cleavage activity. Our
structure of the Piwi-RNA complex, and that determined
elsewhere, provide direct support for the 5' region of the
guide RNA serving as a nucleation site for pairing with
target mRNA and for a fixed distance separating the
RISC-mediated mRNA cleavage site from the anchored 5' end
of the guide RNA.