Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 1zlk; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- transcription-DNA
- Method
- X-ray (3.1 Å)
- Summary
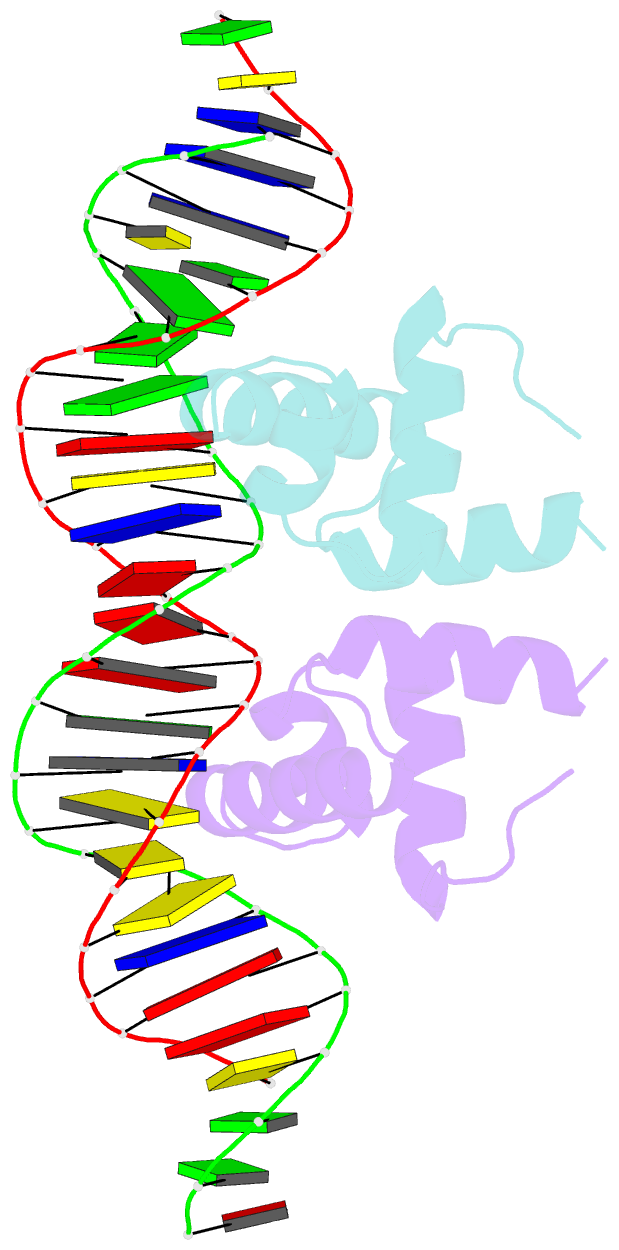
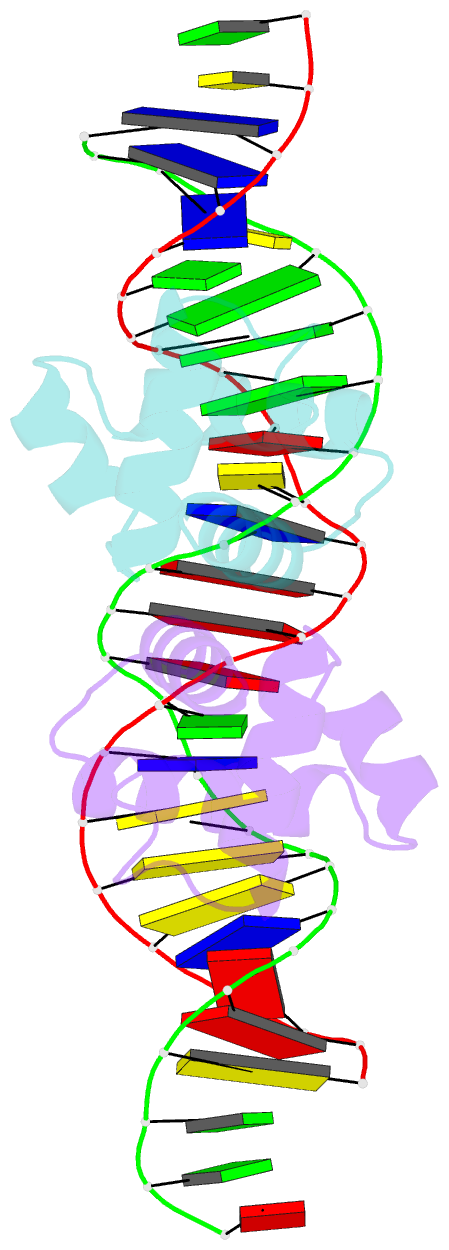
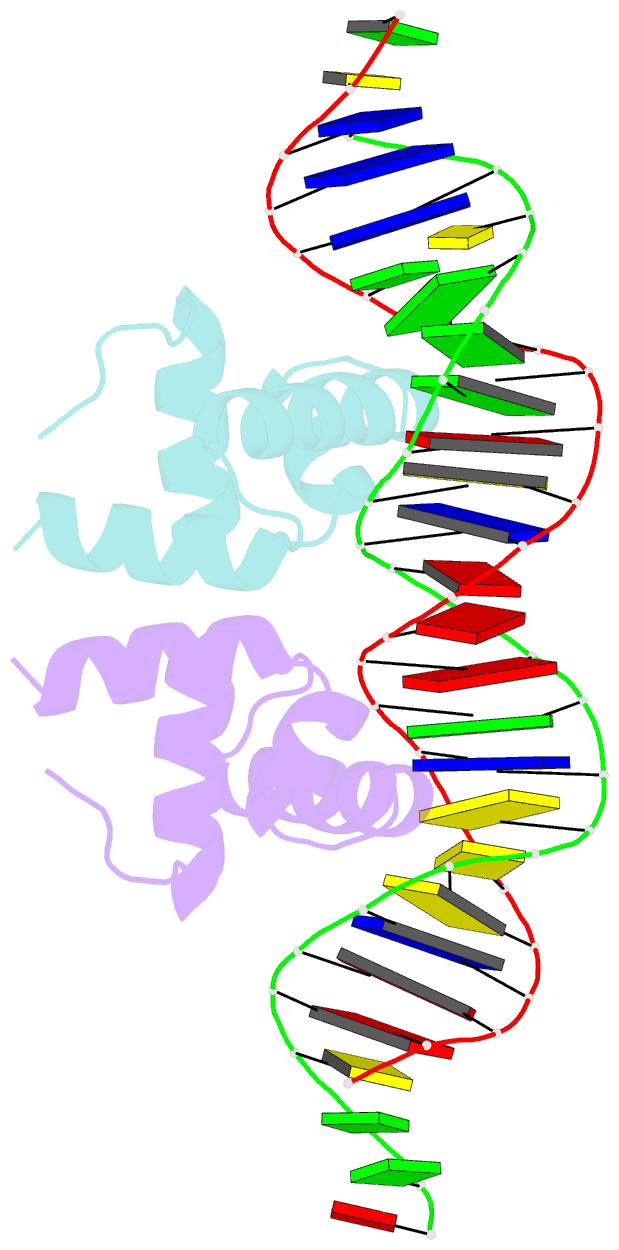
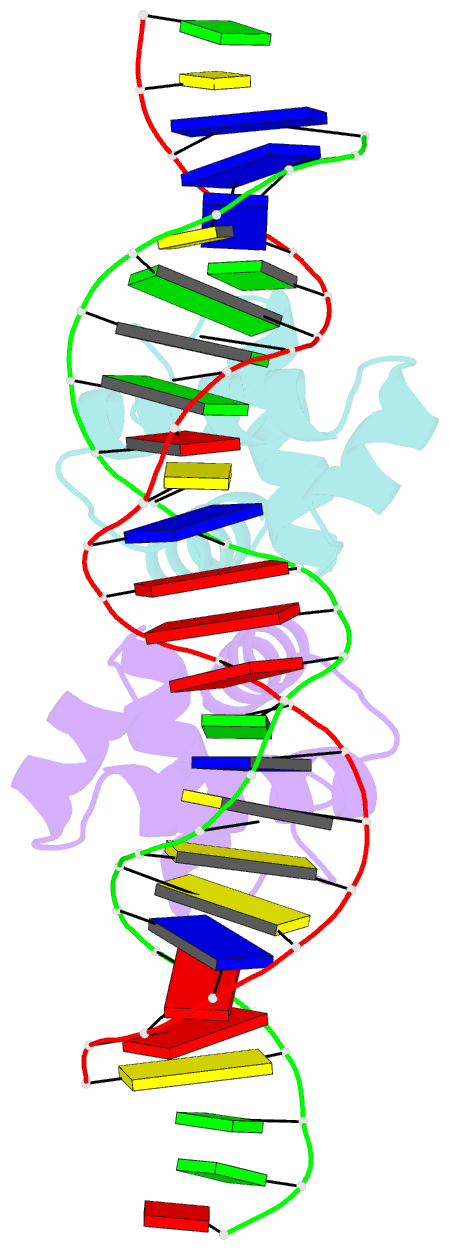
- Crystal structure of the mycobacterium tuberculosis hypoxic response regulator dosr c-terminal domain-DNA complex
- Reference
- Wisedchaisri G, Wu M, Rice AE, Roberts DM, Sherman DR, Hol WGJ (2005): "Structures of Mycobacterium tuberculosis DosR and DosR-DNA complex involved in gene activation during adaptation to hypoxic latency." J.Mol.Biol., 354, 630-641. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2005.09.048.
- Abstract
- On encountering low oxygen conditions, DosR activates the transcription of 47 genes, promoting long-term survival of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in a non-replicating state. Here, we report the crystal structures of the DosR C-terminal domain and its complex with a consensus DNA sequence of the hypoxia-induced gene promoter. The DosR C-terminal domain contains four alpha-helices and forms tetramers consisting of two dimers with non-intersecting dyads. In the DNA-bound structure, each DosR C-terminal domain in a dimer places its DNA-binding helix deep into the major groove, causing two bends in the DNA. DosR makes numerous protein-DNA base contacts using only three amino acid residues per subunit: Lys179, Lys182, and Asn183. The DosR tetramer is unique among response regulators with known structures.