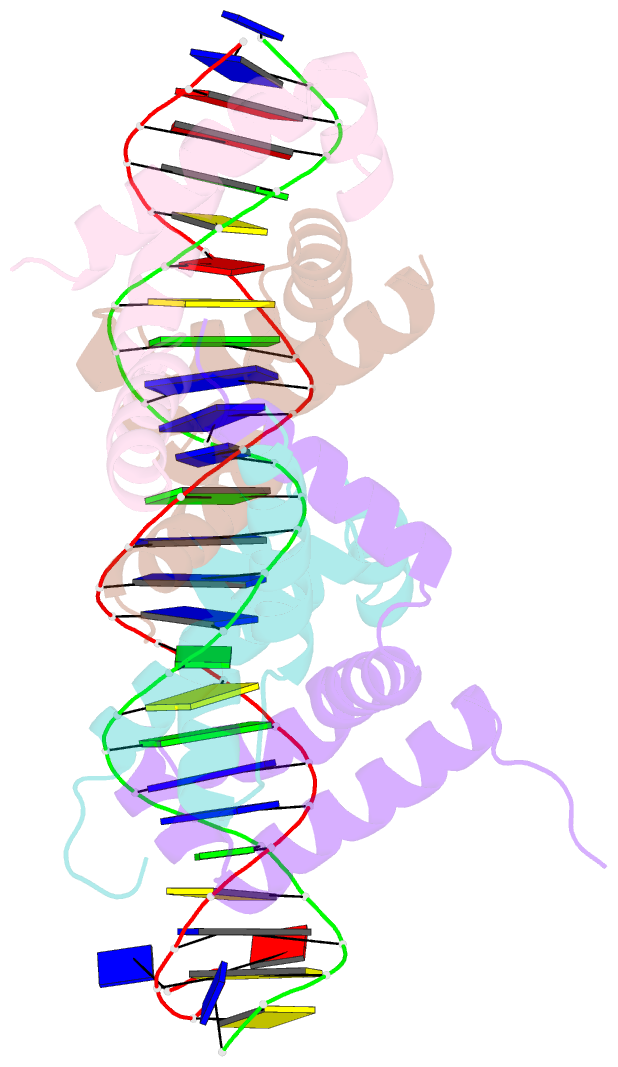
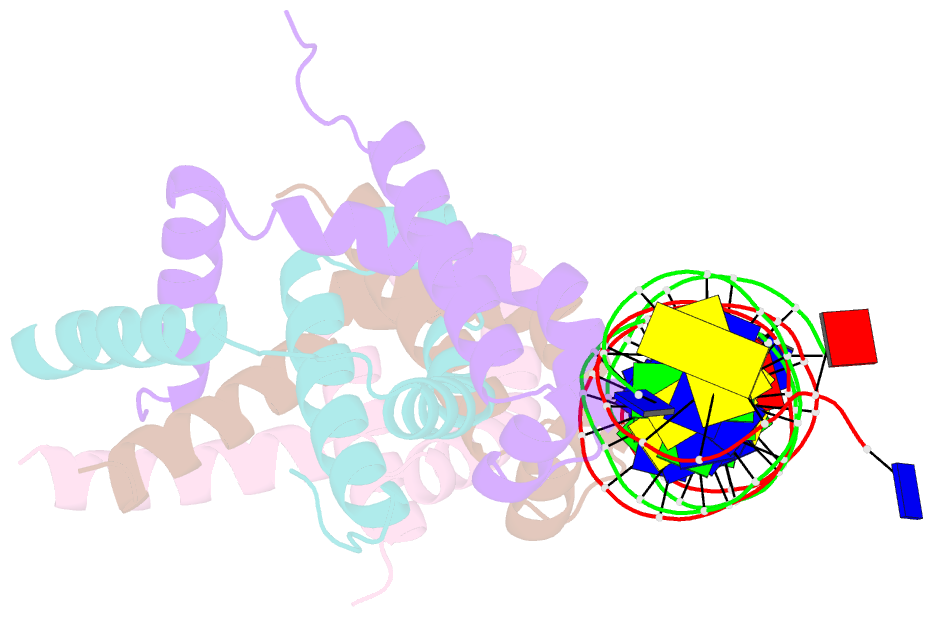
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 1zs4; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- transcription-DNA
- Method
- X-ray (1.7 Å)
- Summary
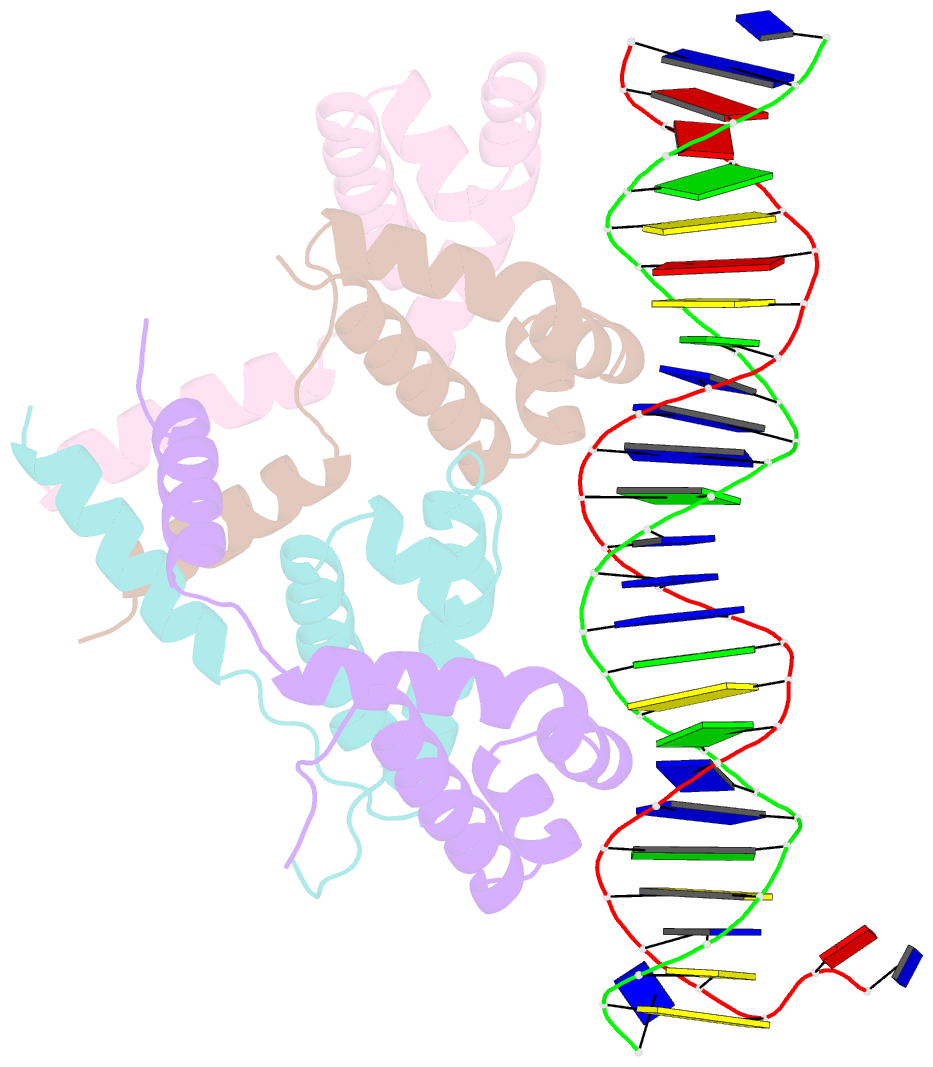
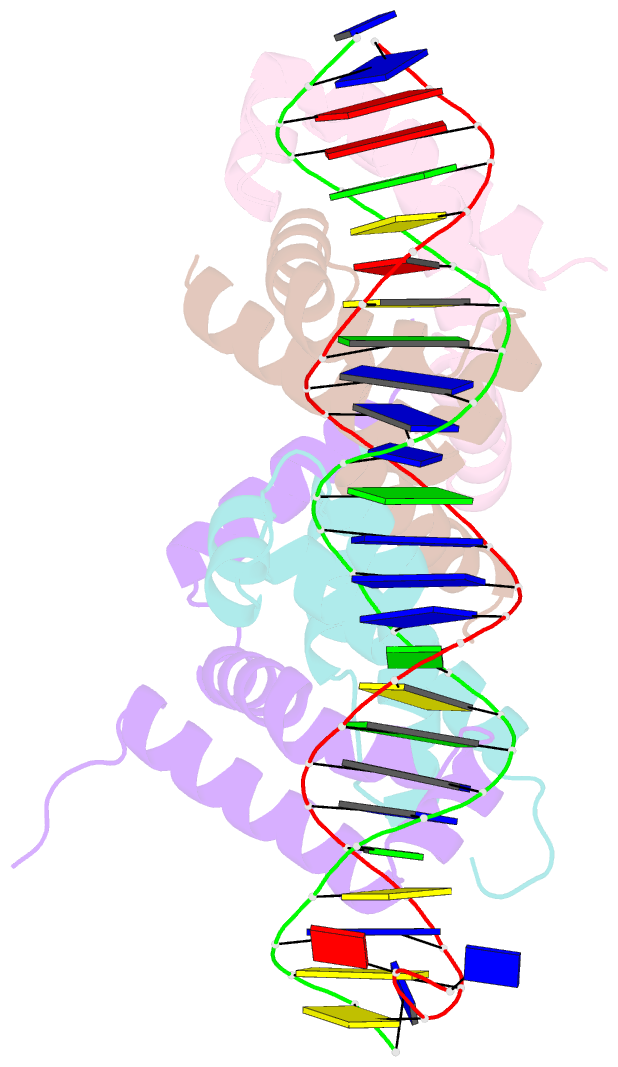
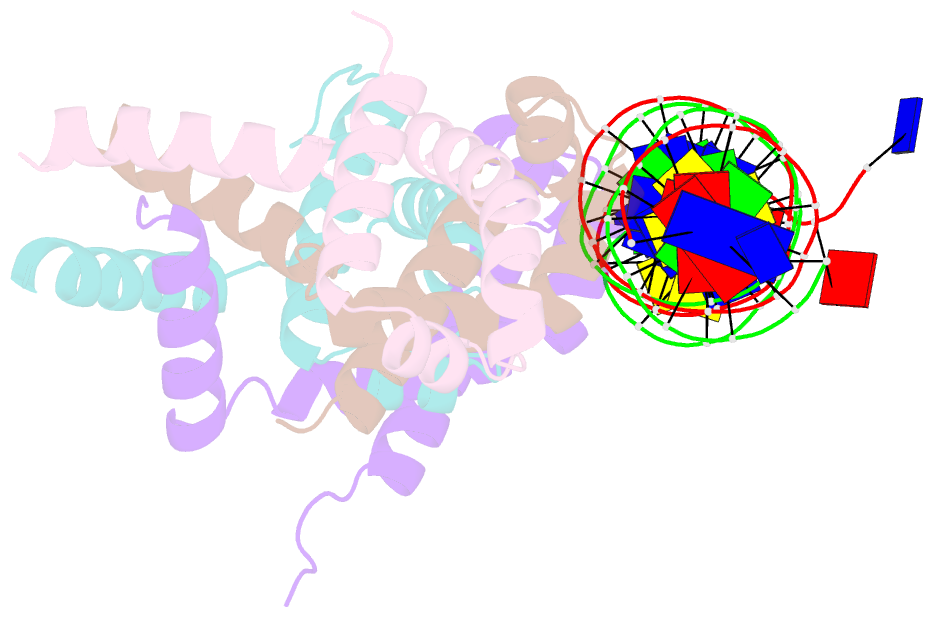
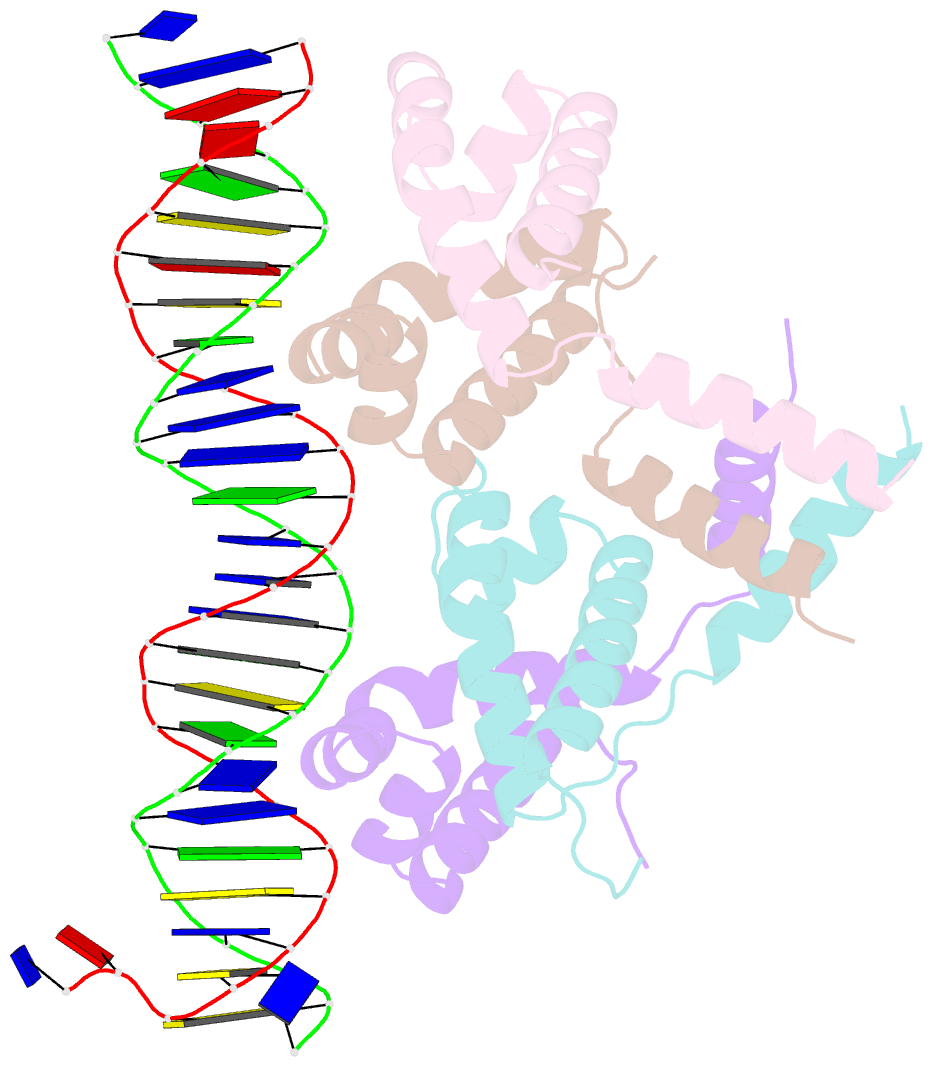
- Structure of bacteriophage lambda cii protein in complex with DNA
- Reference
- Jain D, Kim Y, Maxwell KL, Beasley S, Zhang R, Gussin GN, Edwards AM, Darst SA (2005): "Crystal Structure of Bacteriophage lambdacII and Its DNA Complex." Mol.Cell, 19, 259-269. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2005.06.006.
- Abstract
- The tetrameric cII protein from bacteriophage lambda activates transcription from the phage promoters P(RE), P(I), and P(AQ) by binding to two direct repeats that flank the promoter -35 element. Here, we present the X-ray crystal structure of cII alone (2.8 A resolution) and in complex with its DNA operator from P(RE) (1.7 A resolution). The structures provide a basis for modeling of the activation complex with the RNA polymerase holoenzyme, and point to the key role for the RNA polymerase alpha subunit C-terminal domain (alphaCTD) in cII-dependent activation, which forms a bridge of protein/protein interactions between cII and the RNA polymerase sigma subunit. The model makes specific predictions for protein/protein interactions between cII and alphaCTD, and between alphaCTD and sigma, which are supported by previous genetic studies.