Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 2ann; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- RNA-binding protein-RNA
- Method
- X-ray (2.3 Å)
- Summary
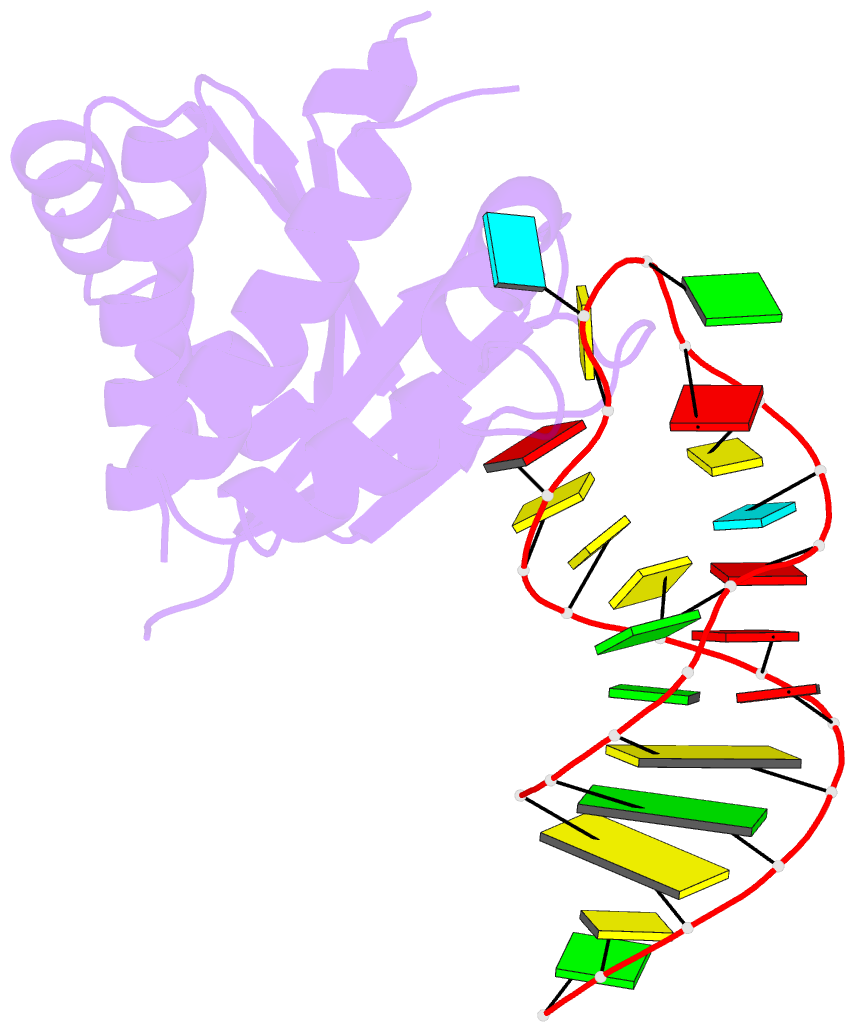
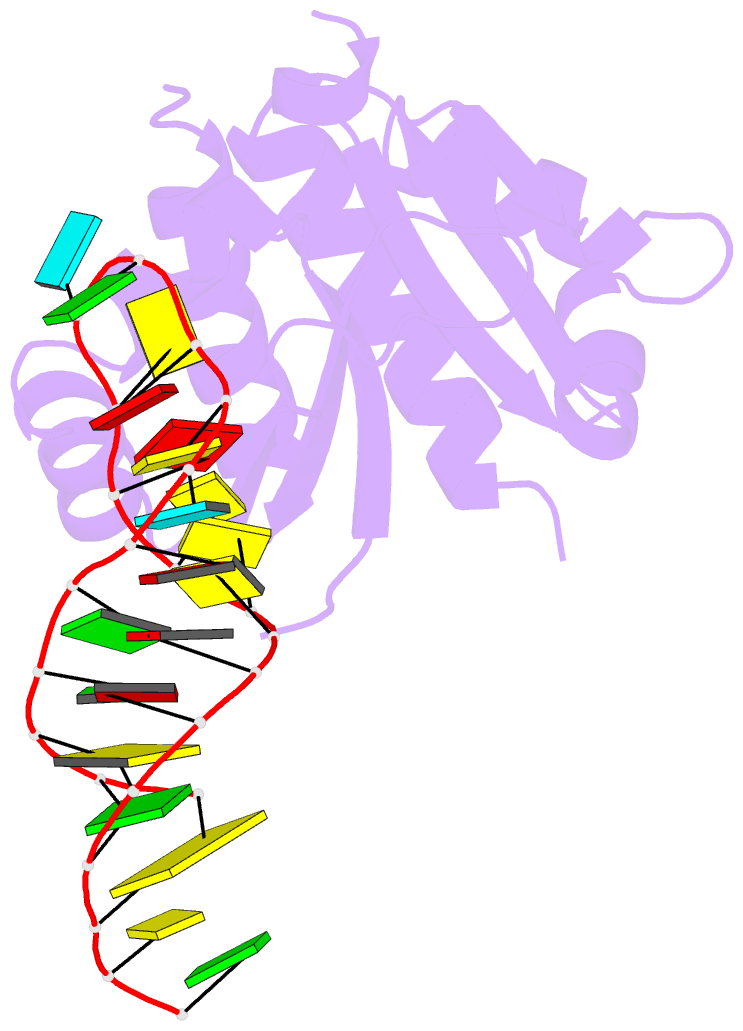
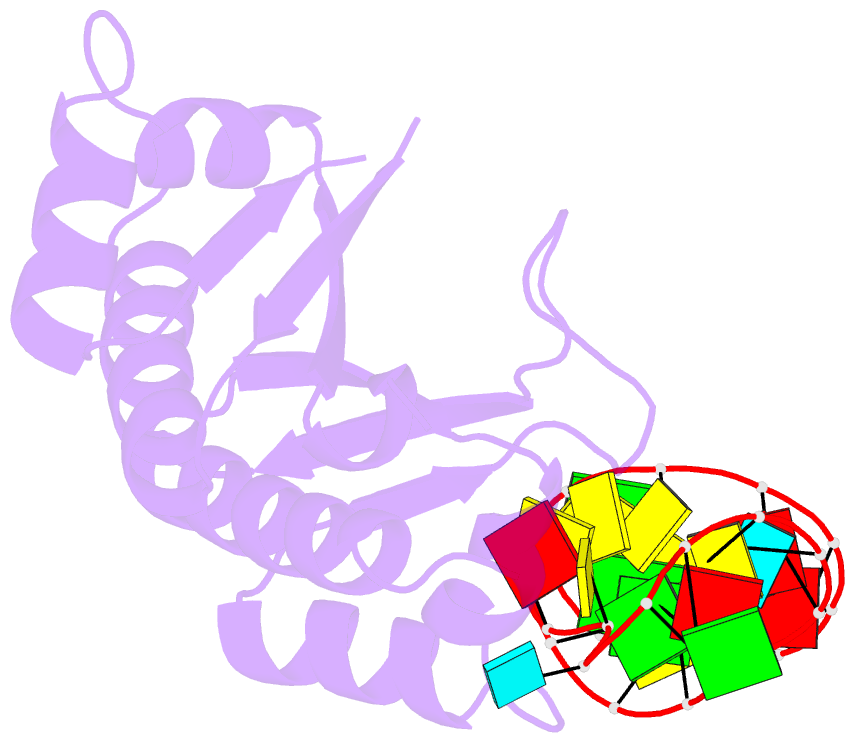
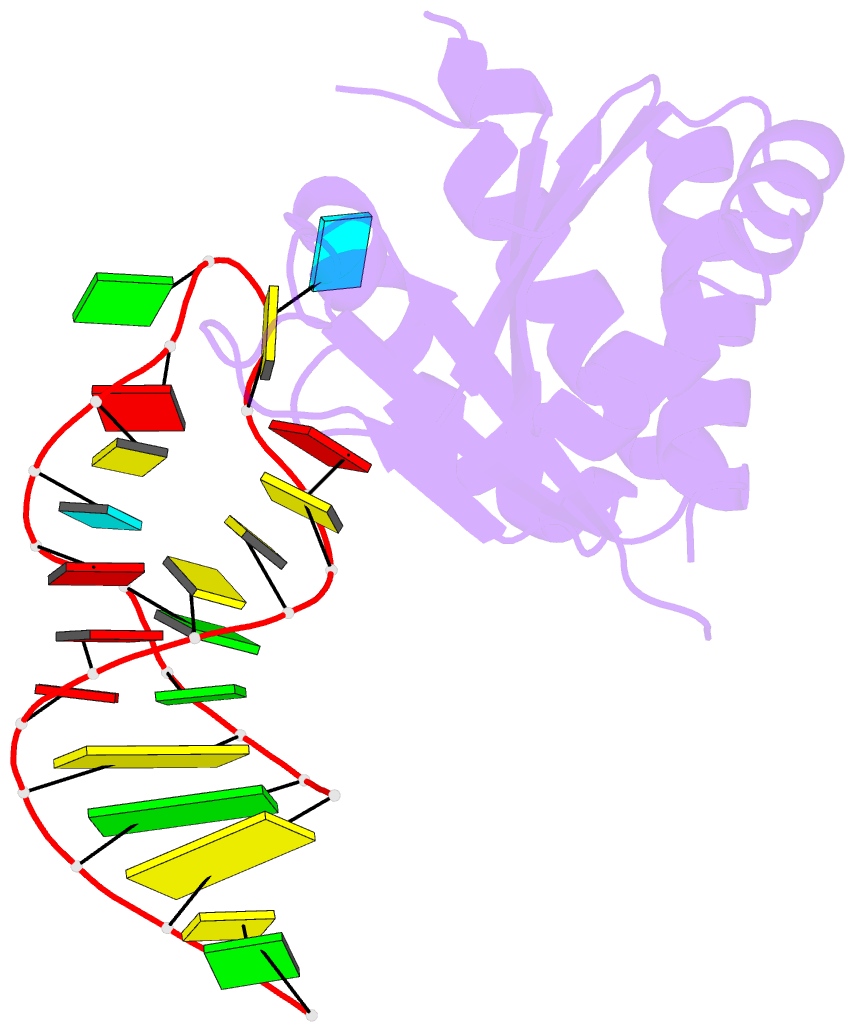
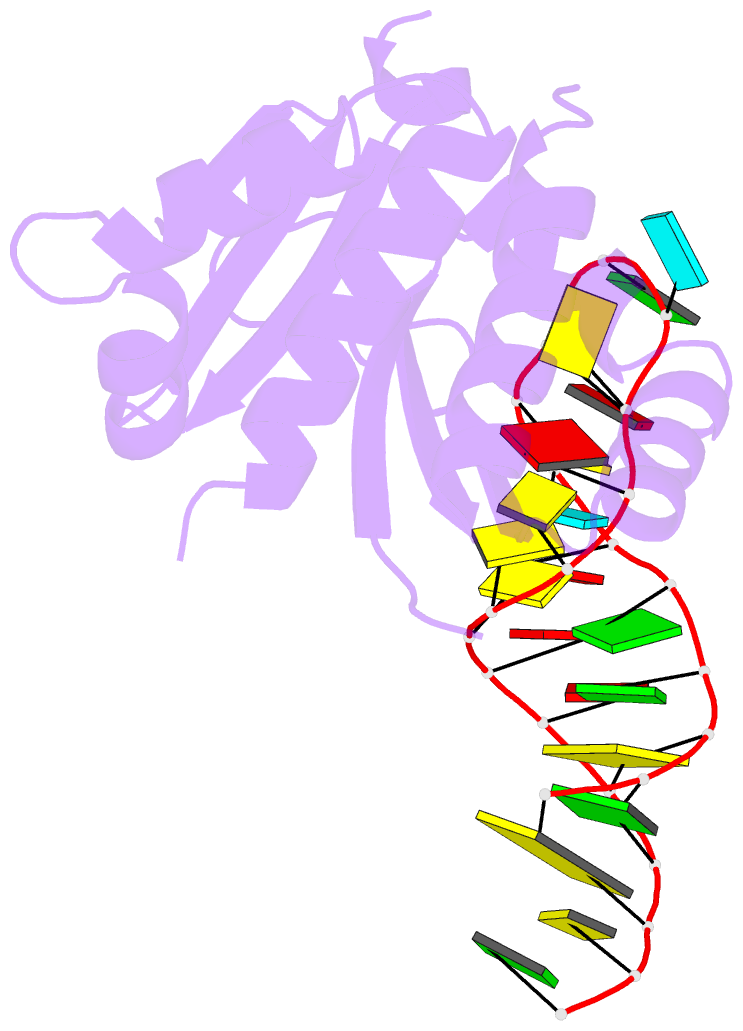
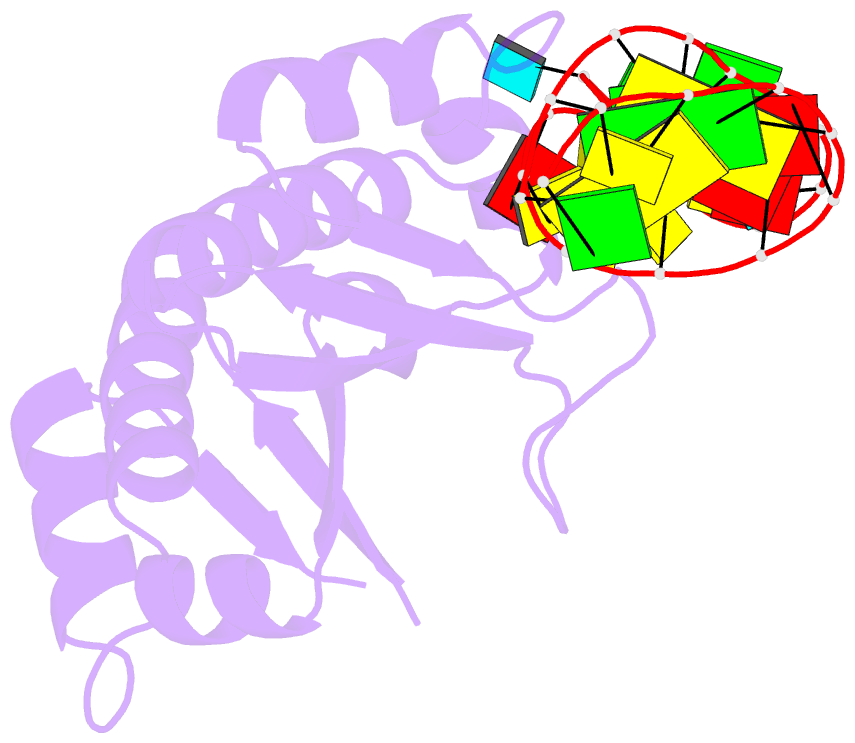
- Crystal structure (i) of nova-1 kh1-kh2 domain tandem with 25 nt RNA hairpin
- Reference
- Teplova M, Malinina L, Darnell JC, Song J, Lu M, Abagyan R, Musunuru K, Teplov A, Burley SK, Darnell RB, Patel DJ (2011): "Protein-RNA and protein-protein recognition by dual KH1/2 domains of the neuronal splicing factor Nova-1." Structure, 19, 930-944. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2011.05.002.
- Abstract
- Nova onconeural antigens are neuron-specific RNA-binding proteins implicated in paraneoplastic opsoclonus-myoclonus-ataxia (POMA) syndrome. Nova harbors three K-homology (KH) motifs implicated in alternate splicing regulation of genes involved in inhibitory synaptic transmission. We report the crystal structure of the first two KH domains (KH1/2) of Nova-1 bound to an in vitro selected RNA hairpin, containing a UCAG-UCAC high-affinity binding site. Sequence-specific intermolecular contacts in the complex involve KH1 and the second UCAC repeat, with the RNA scaffold buttressed by interactions between repeats. Whereas the canonical RNA-binding surface of KH2 in the above complex engages in protein-protein interactions in the crystalline state, the individual KH2 domain can sequence-specifically target the UCAC RNA element in solution. The observed antiparallel alignment of KH1 and KH2 domains in the crystal structure of the complex generates a scaffold that could facilitate target pre-mRNA looping on Nova binding, thereby potentially explaining Nova's functional role in splicing regulation.