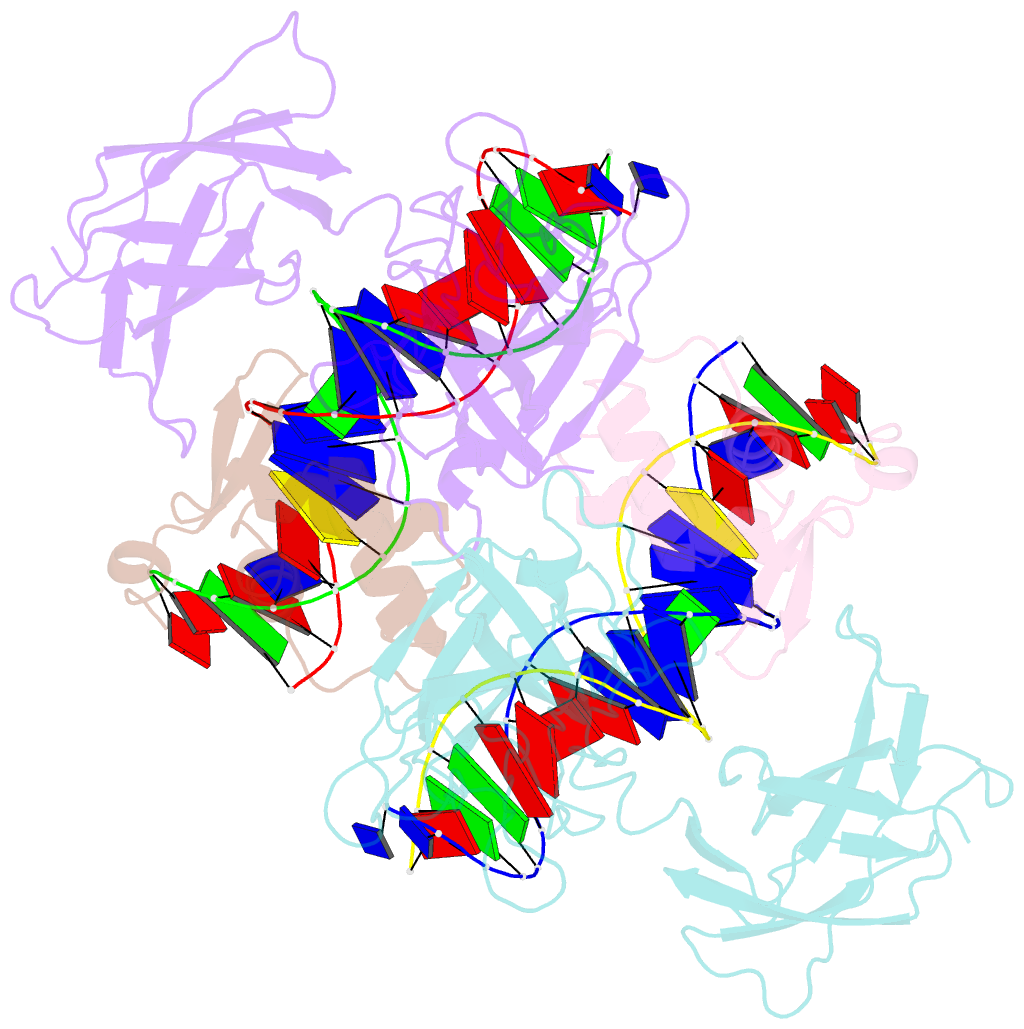
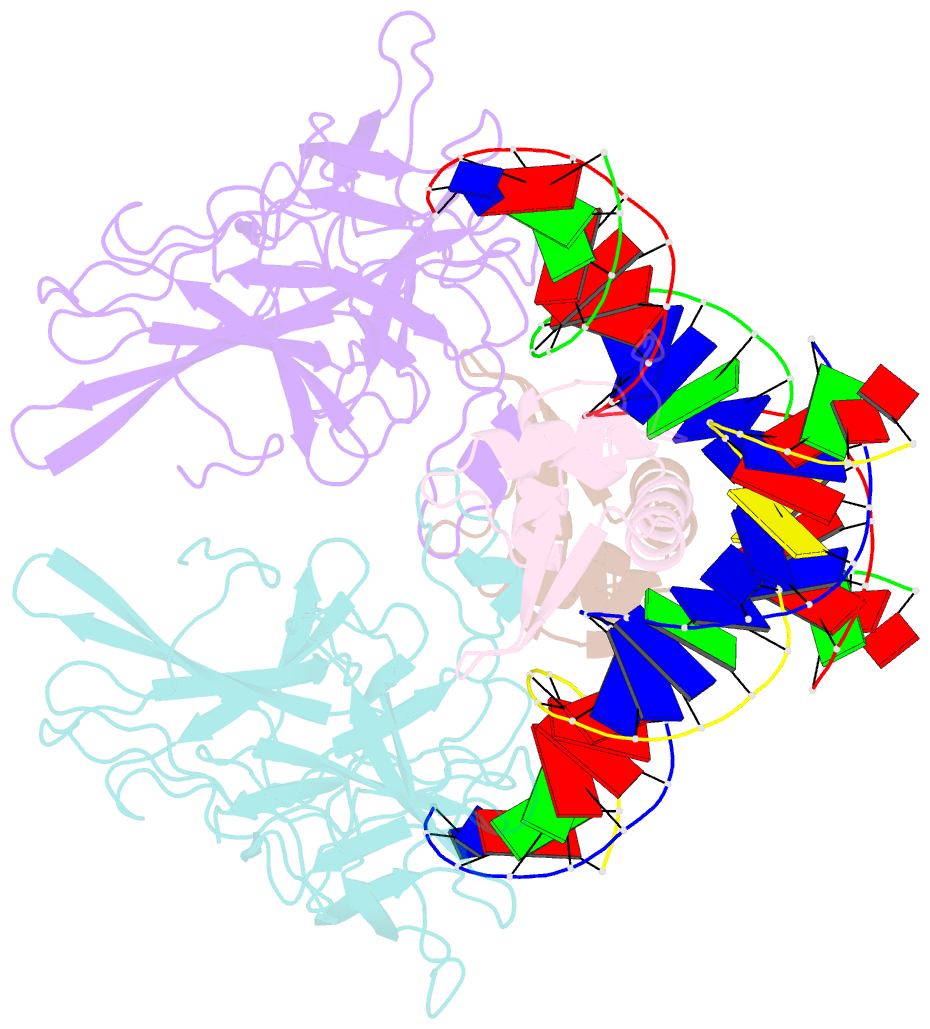
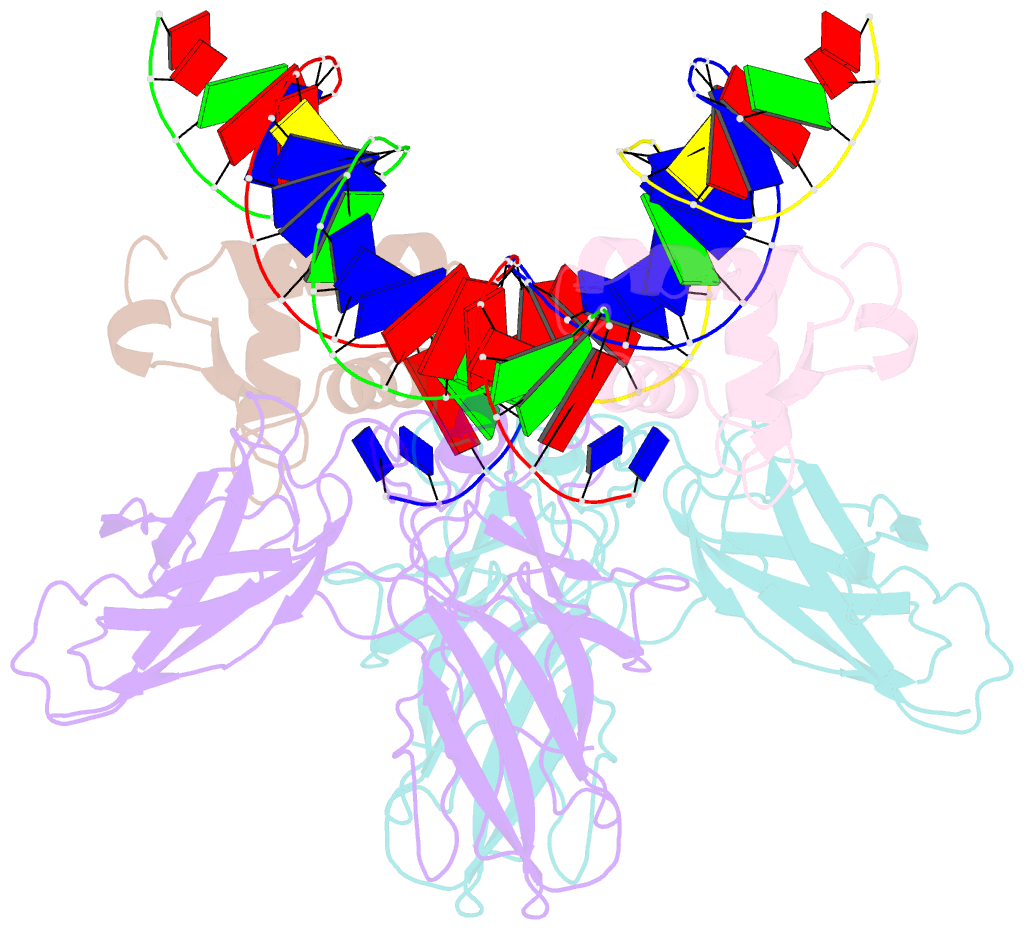
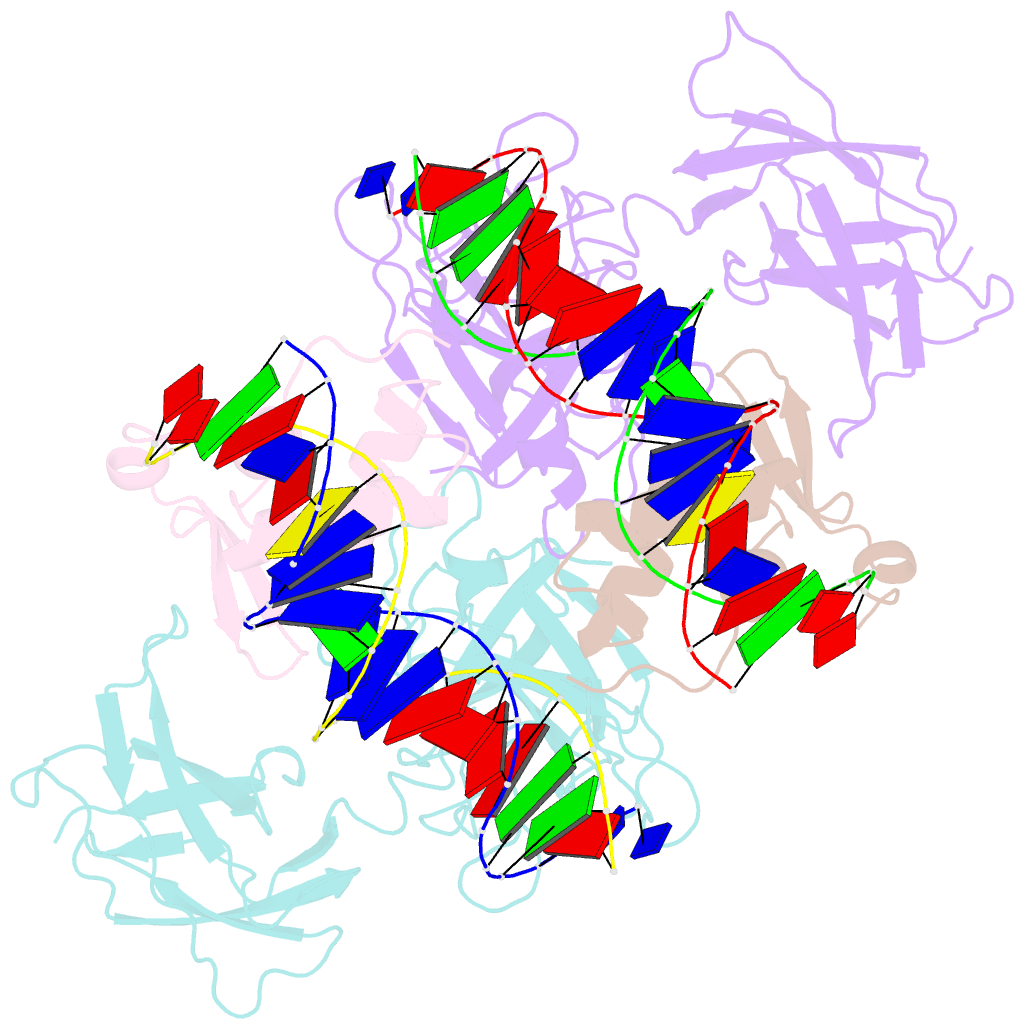
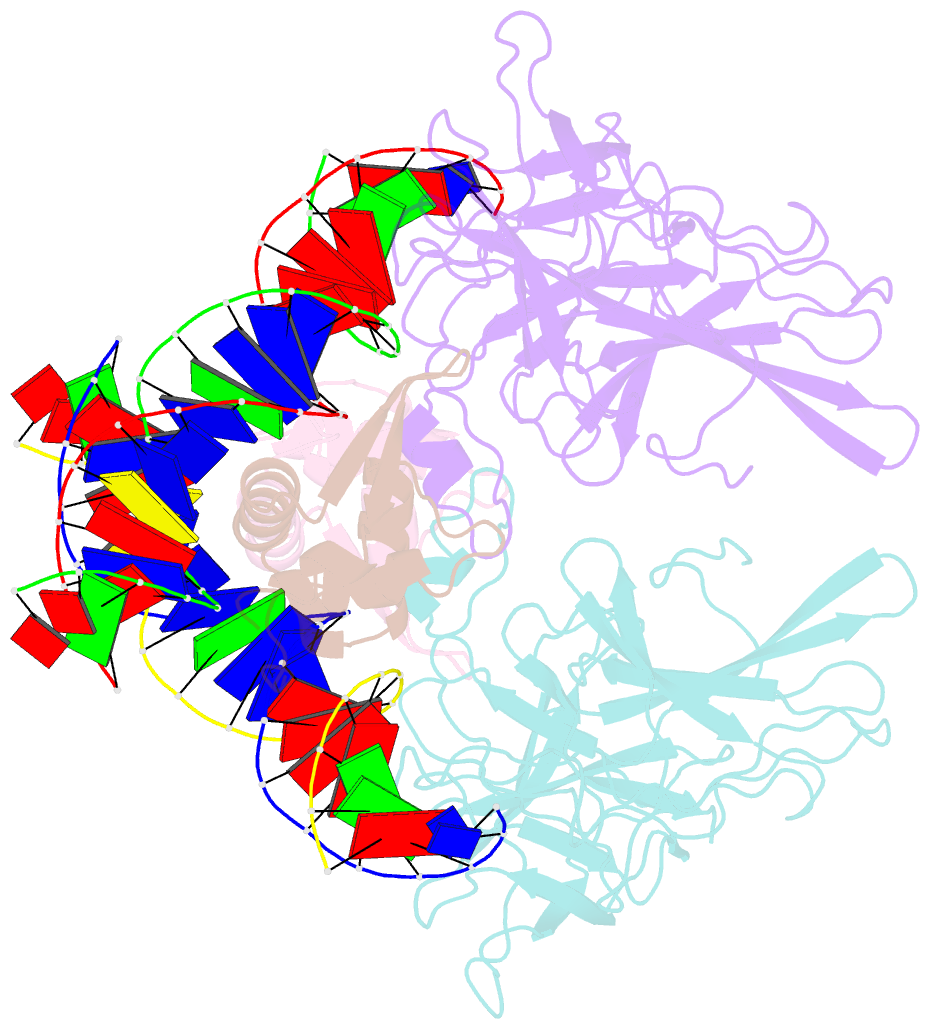
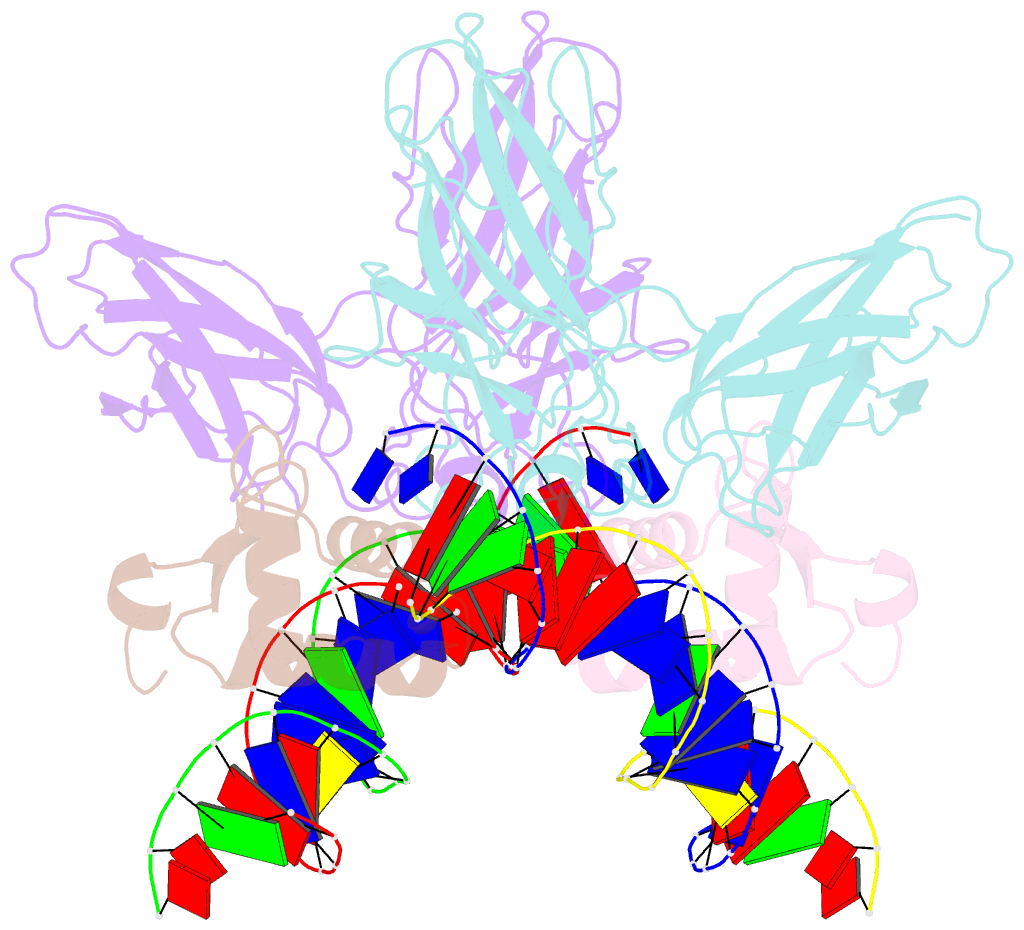
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 2as5; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- transcription-DNA
- Method
- X-ray (2.7 Å)
- Summary
- Structure of the DNA binding domains of nfat and foxp2 bound specifically to DNA.
- Reference
- Wu Y, Borde M, Heissmeyer V, Feuerer M, Lapan AD, Stroud JC, Bates DL, Guo L, Han A, Ziegler SF, Mathis D, Benoist C, Chen L, Rao A (2006): "FOXP3 Controls Regulatory T Cell Function through Cooperation with NFAT." Cell(Cambridge,Mass.), 126, 375-387. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2006.05.042.
- Abstract
- Antigen stimulation of immune cells activates the transcription factor NFAT, a key regulator of T cell activation and anergy. NFAT forms cooperative complexes with the AP-1 family of transcription factors and regulates T cell activation-associated genes. Here we show that regulatory T cell (Treg) function is mediated by an analogous cooperative complex of NFAT with the forkhead transcription factor FOXP3, a lineage specification factor for Tregs. The crystal structure of an NFAT:FOXP2:DNA complex reveals an extensive protein-protein interaction interface between NFAT and FOXP2. Structure-guided mutations of FOXP3, predicted to progressively disrupt its interaction with NFAT, interfere in a graded manner with the ability of FOXP3 to repress expression of the cytokine IL2, upregulate expression of the Treg markers CTLA4 and CD25, and confer suppressor function in a murine model of autoimmune diabetes. Thus by switching transcriptional partners, NFAT converts the acute T cell activation program into the suppressor program of Tregs.