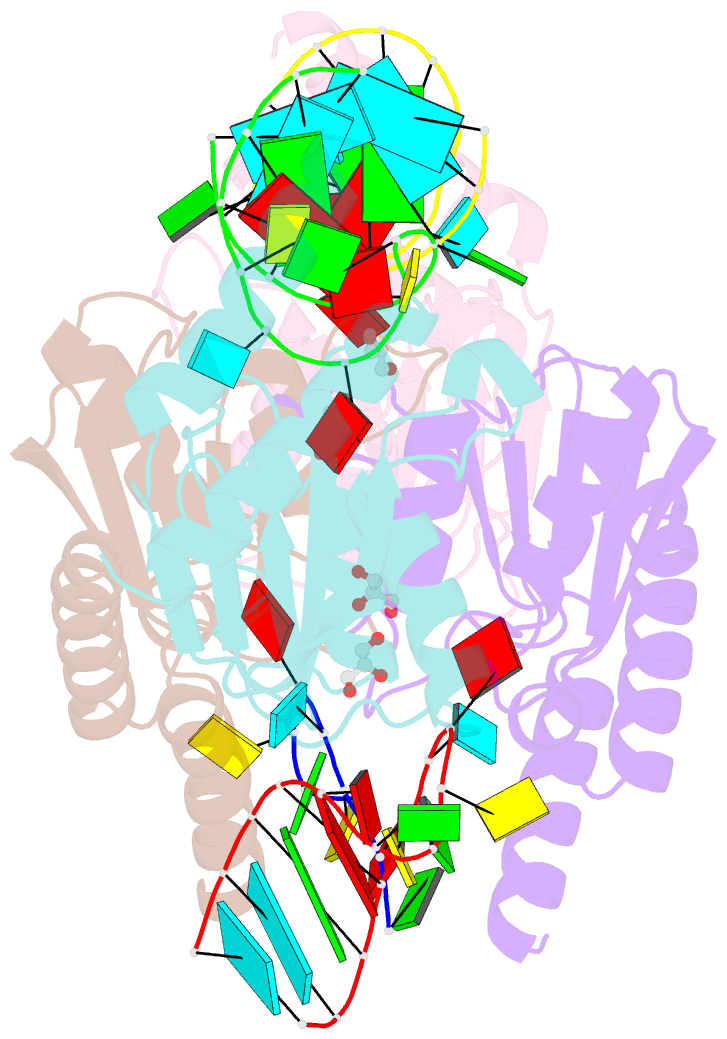
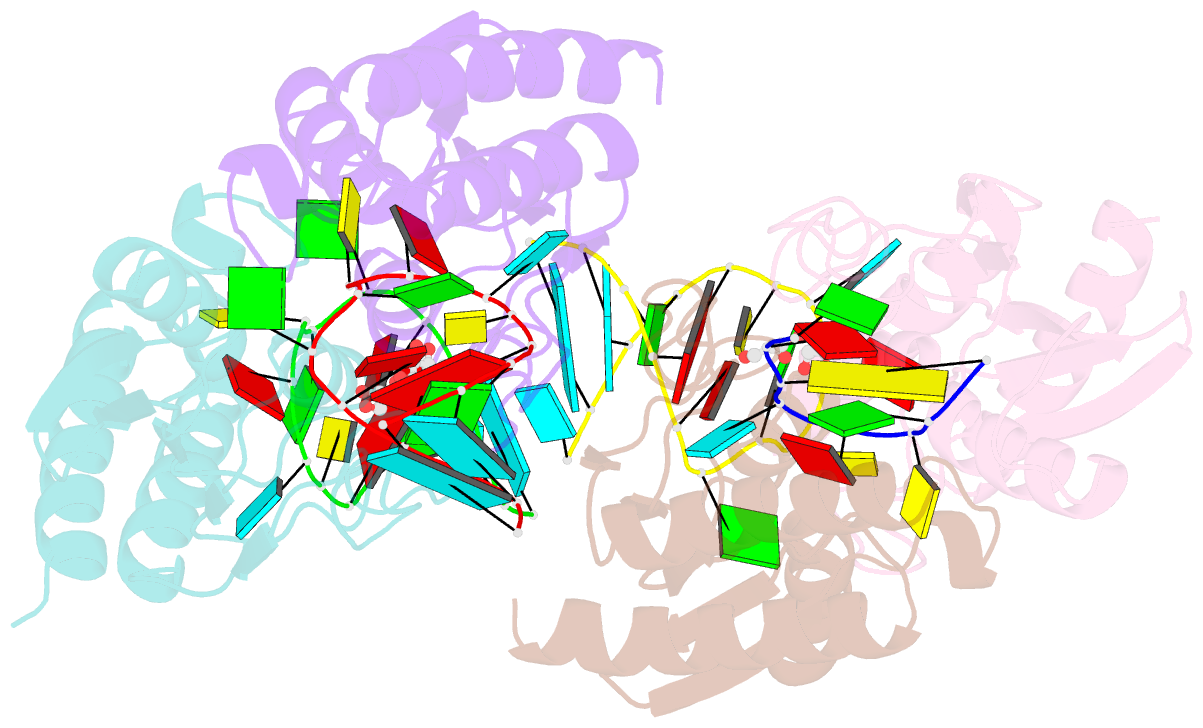
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 2b3j; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- hydrolase-RNA
- Method
- X-ray (2.0 Å)
- Summary
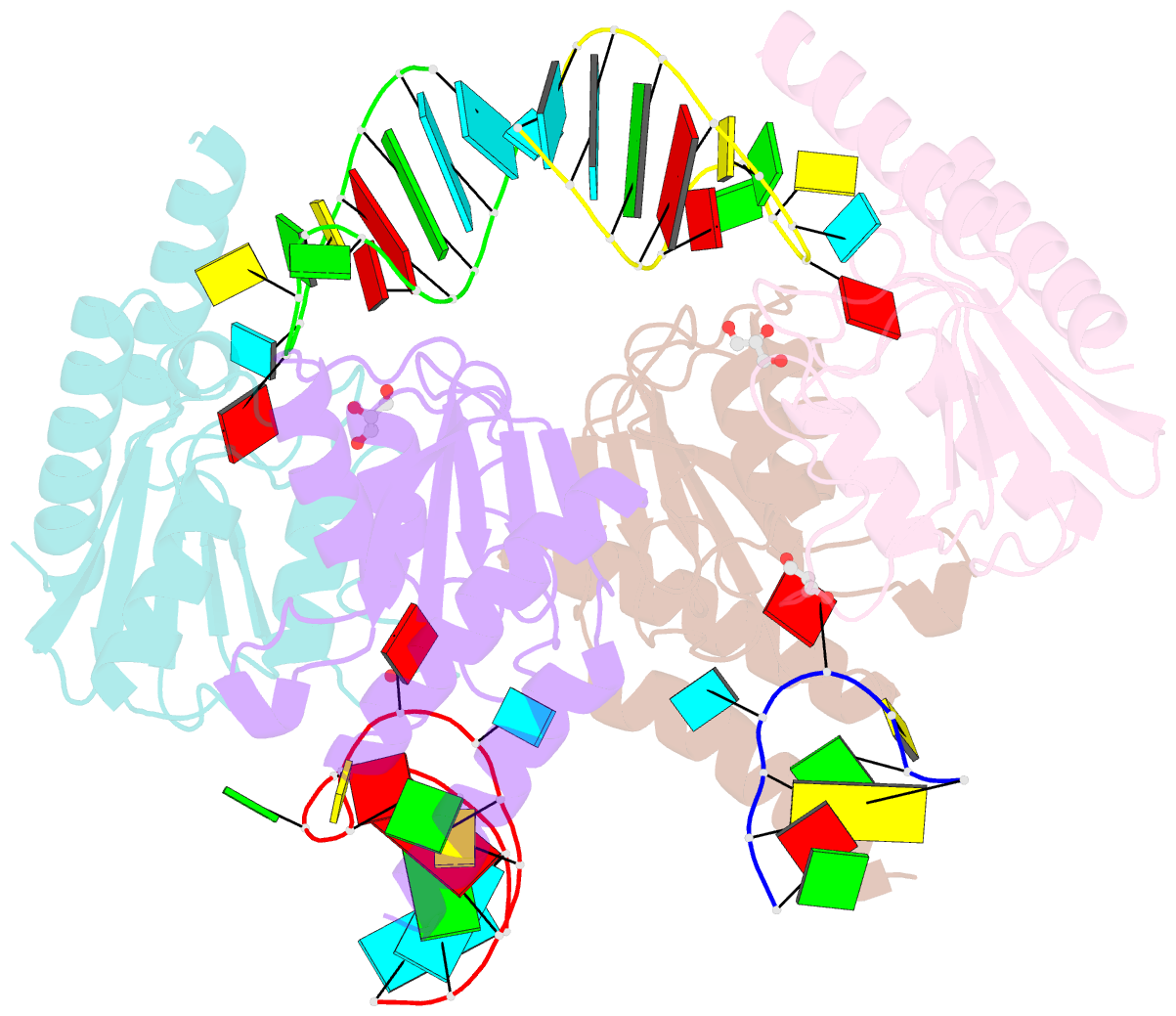
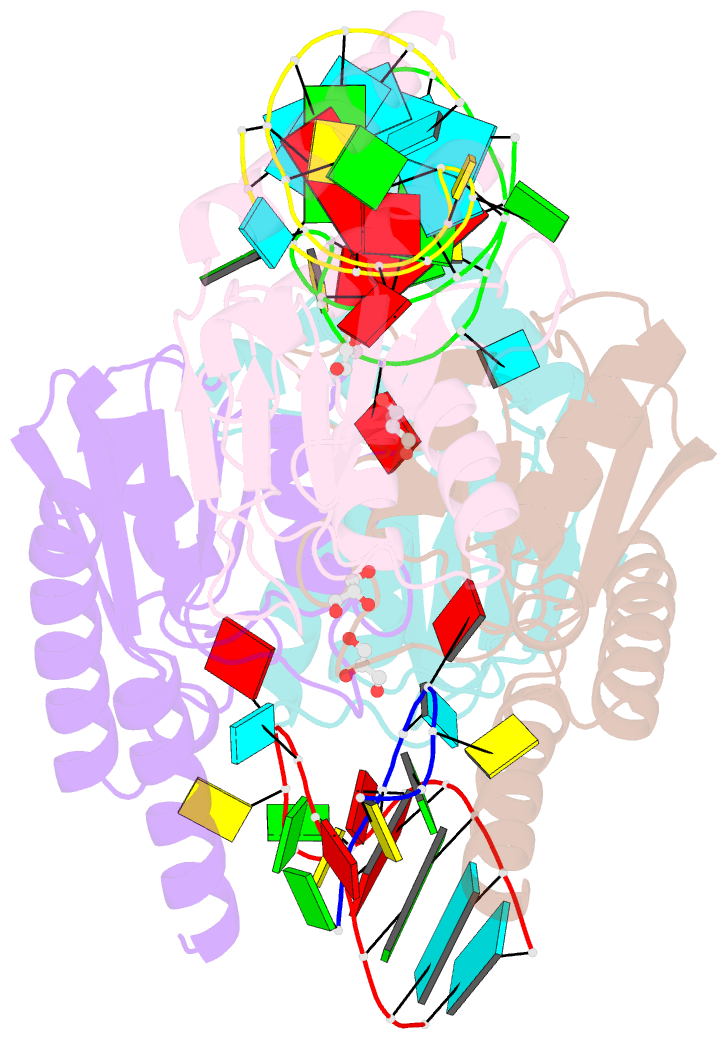
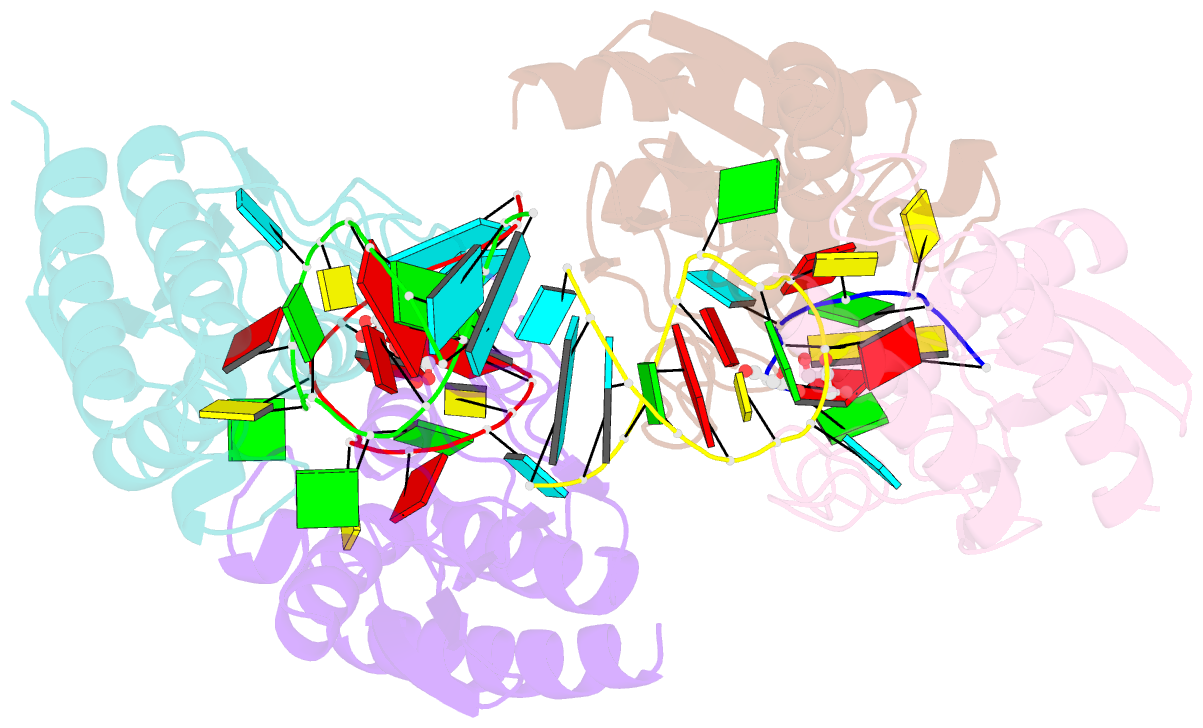
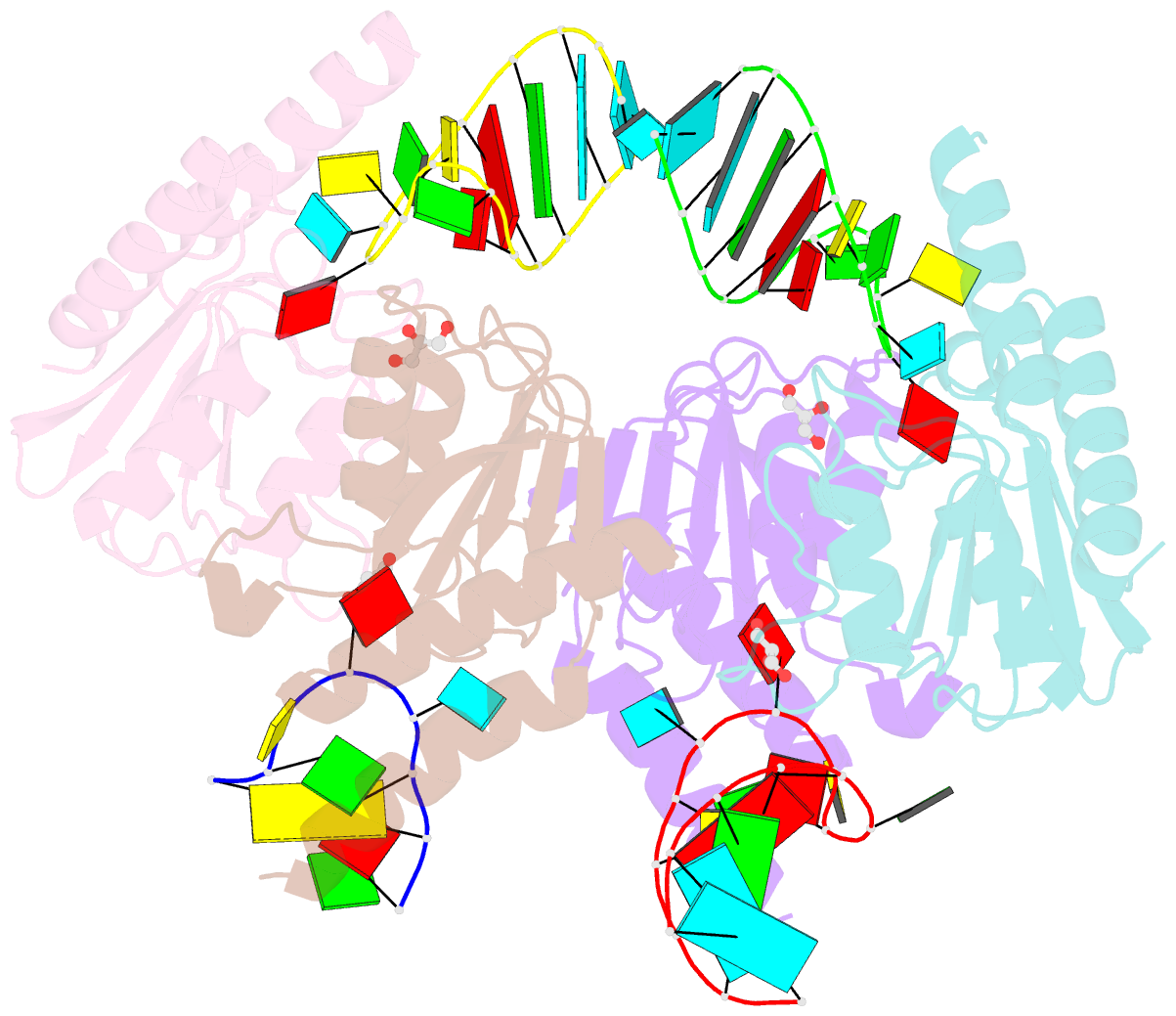
- Crystal structure of staphylococcus aureus trna adenosine deaminase, tada, in complex with RNA
- Reference
- Losey HC, Ruthenburg AJ, Verdine GL (2006): "Crystal structure of Staphylococcus aureus tRNA adenosine deaminase TadA in complex with RNA." Nat.Struct.Mol.Biol., 13, 153-159. doi: 10.1038/nsmb1047.
- Abstract
- Bacterial tRNA adenosine deaminases (TadAs) catalyze the hydrolytic deamination of adenosine to inosine at the wobble position of tRNA(Arg2), a process that enables this single tRNA to recognize three different arginine codons in mRNA. In addition, inosine is also introduced at the wobble position of multiple eukaryotic tRNAs. The genes encoding these deaminases are essential in bacteria and yeast, demonstrating the importance of their biological activity. Here we report the crystallization and structure determination to 2.0 A of Staphylococcus aureus TadA bound to the anticodon stem-loop of tRNA(Arg2) bearing nebularine, a non-hydrolyzable adenosine analog, at the wobble position. The cocrystal structure reveals the basis for both sequence and structure specificity in the interactions of TadA with RNA, and it additionally provides insight into the active site architecture that promotes efficient hydrolytic deamination.