Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 2d55; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- DNA-antibiotic
- Method
- X-ray (3.0 Å)
- Summary
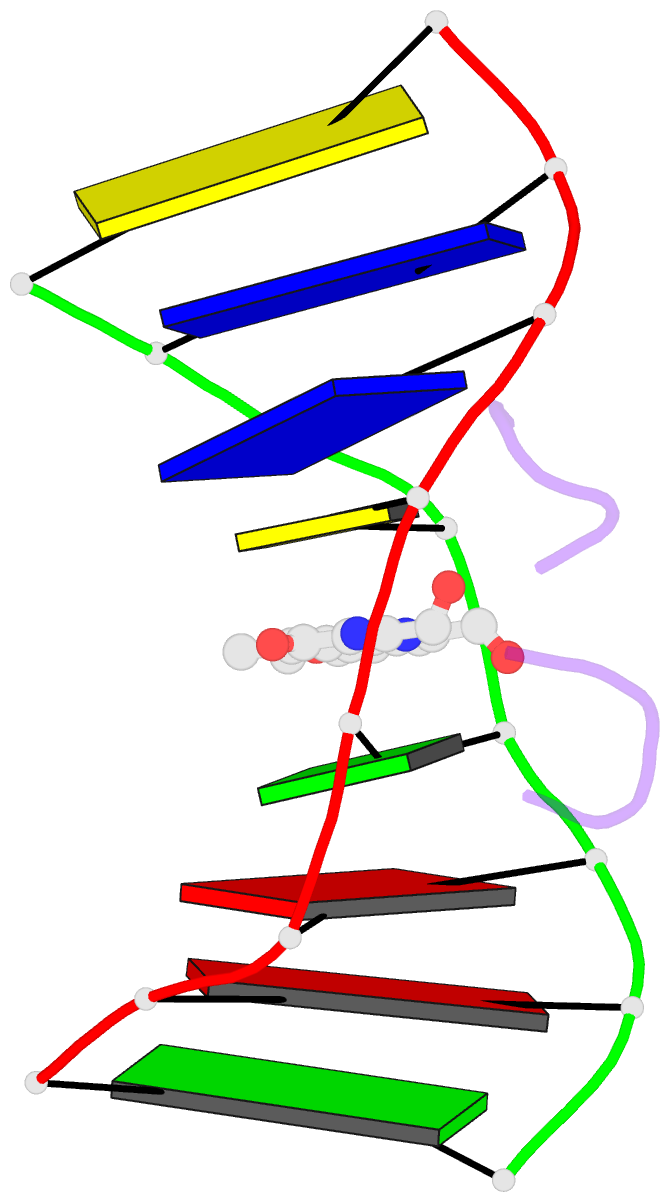
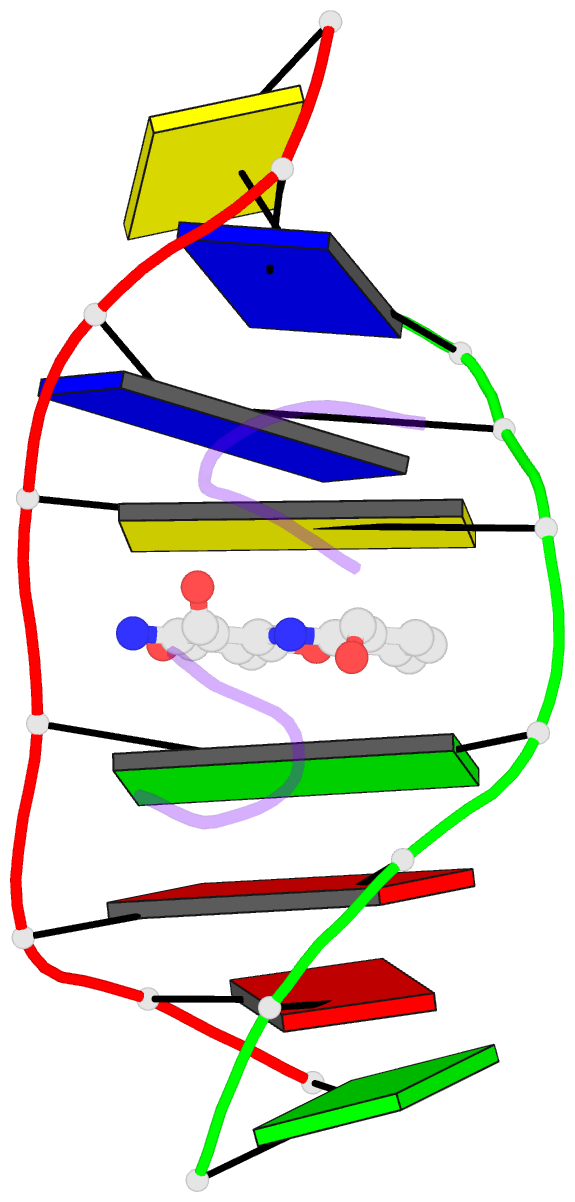
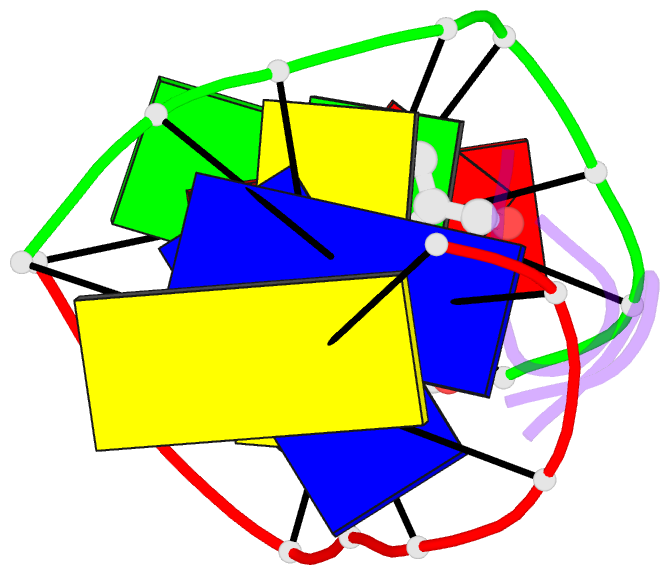
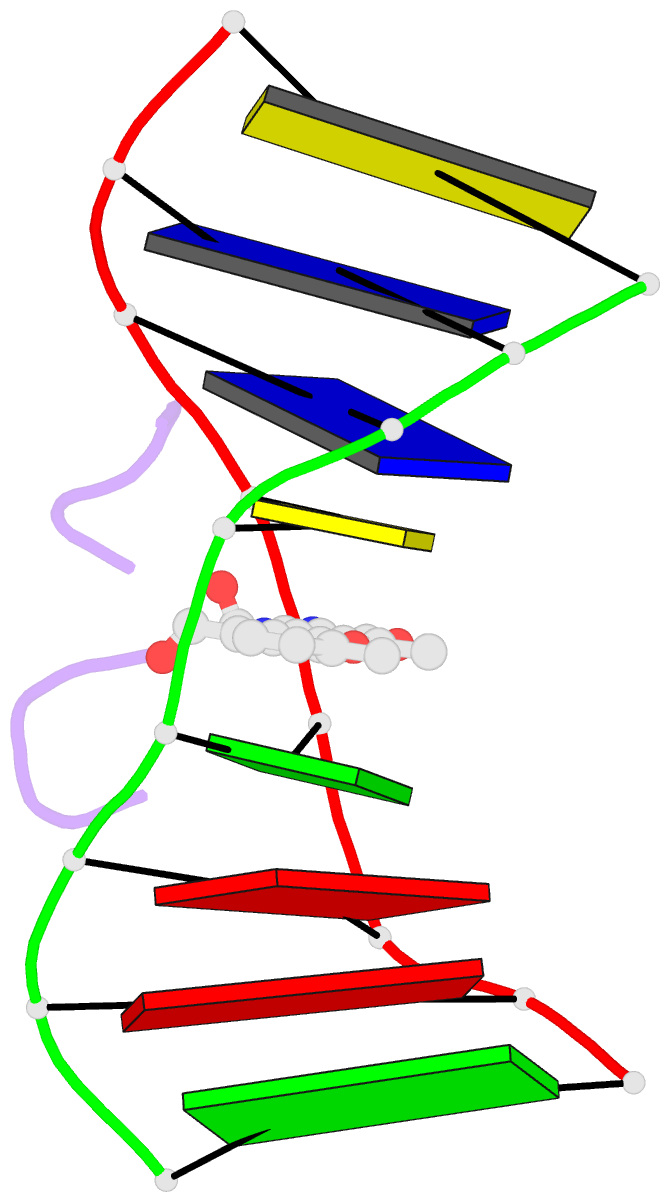
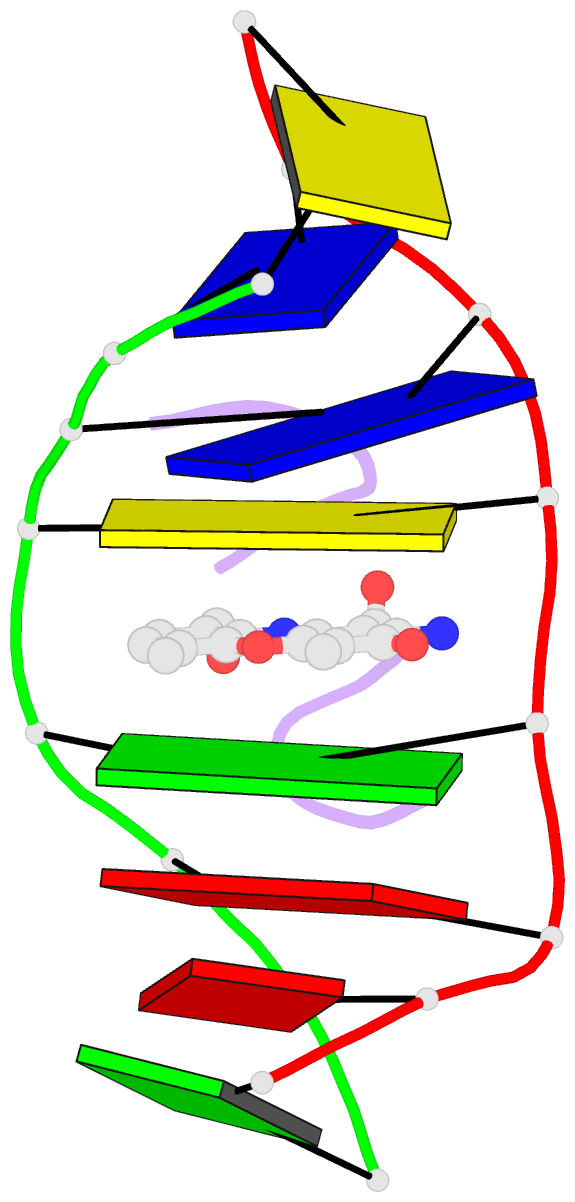
- Structural, physical and biological characteristics of RNA.DNA binding agent n8-actinomycin d
- Reference
- Kamitori S, Takusagawa F (1992): "Crystal Structure of the 2:1 Complex between D(Gaagcttc) and the Anticancer Drug Actinomycin D." J.Mol.Biol., 225, 445. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90931-9.
- Abstract
- The crystal structures of the 2:1 complex of the self-complementary DNA octamer d(GAAGCTTC) with actinomycin D has been determined at 3.0 A resolution. This is the first example of a crystal structure of a DNA-drug complex in which the drug intercalates into the middle of a relatively long DNA segment. The results finally confirmed the DNA-actinomycin intercalation model proposed by Sobell & co-workers in 1971. The DNA molecule adopts a severely distorted and slightly kinked B-DNA-like structure with an actinomycin D molecule intercalated in the middle sequence, GC. The two cyclic depsipeptides, which differ from each other in overall conformation, lie in the minor groove. The complex is further stabilized by forming base-peptide and chromophore-backbone hydrogen bonds. The DNA helix appears to be unwound by rotating one of the base-pairs at the intercalation site. This single base-pair unwinding motion generates a unique asymmetrically wound helix at the binding site of the drug, i.e. the helix is loosened at one end of the intercalation site and tightened at the other end. The large unwinding of the DNA by the drug intercalation is absorbed mostly in a few residues adjacent to the intercalation site. The asymmetrical twist of the DNA helix, the overall conformation of the two cyclic depsipeptides and their interaction mode with DNA are correlated to each other and rationally explained.