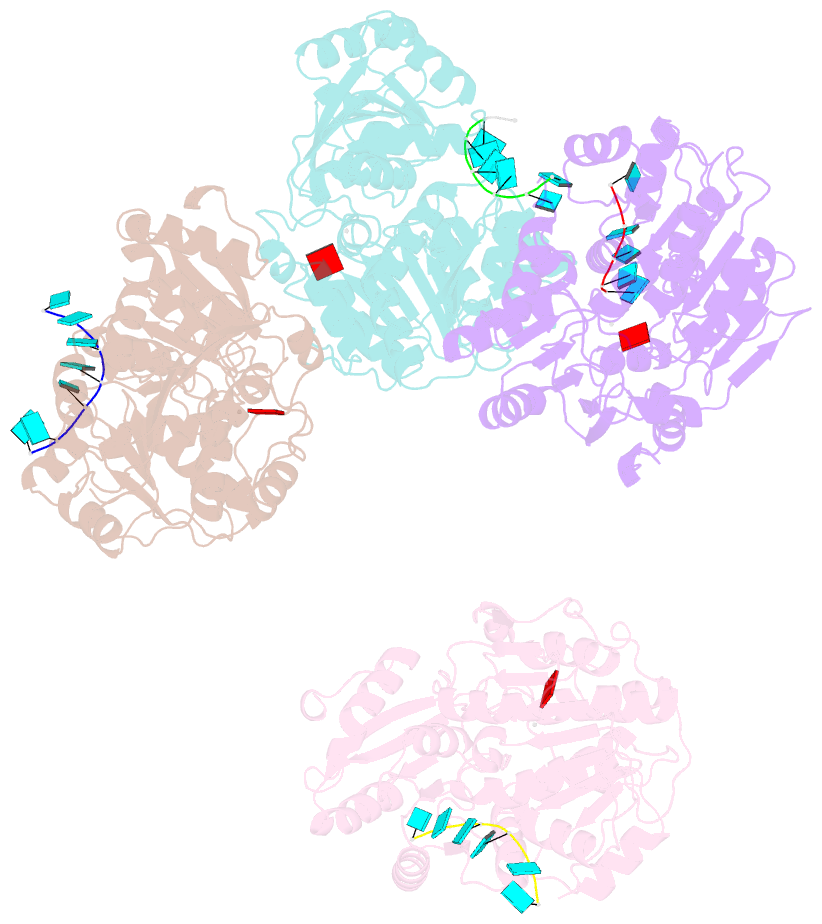
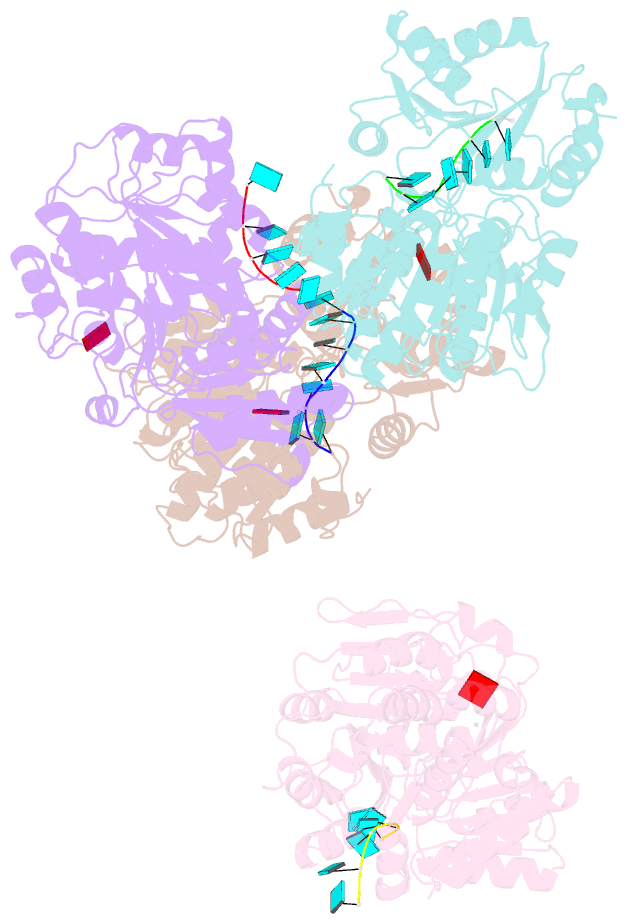
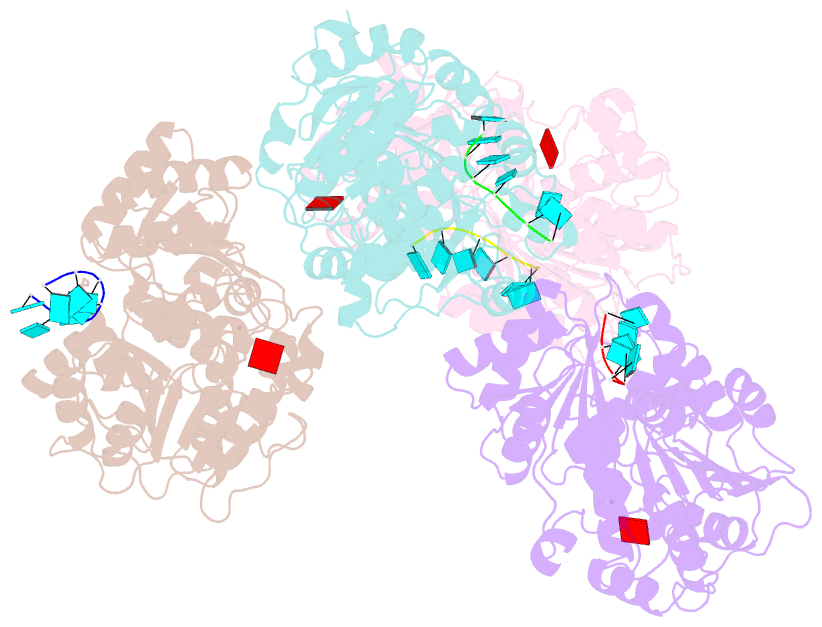
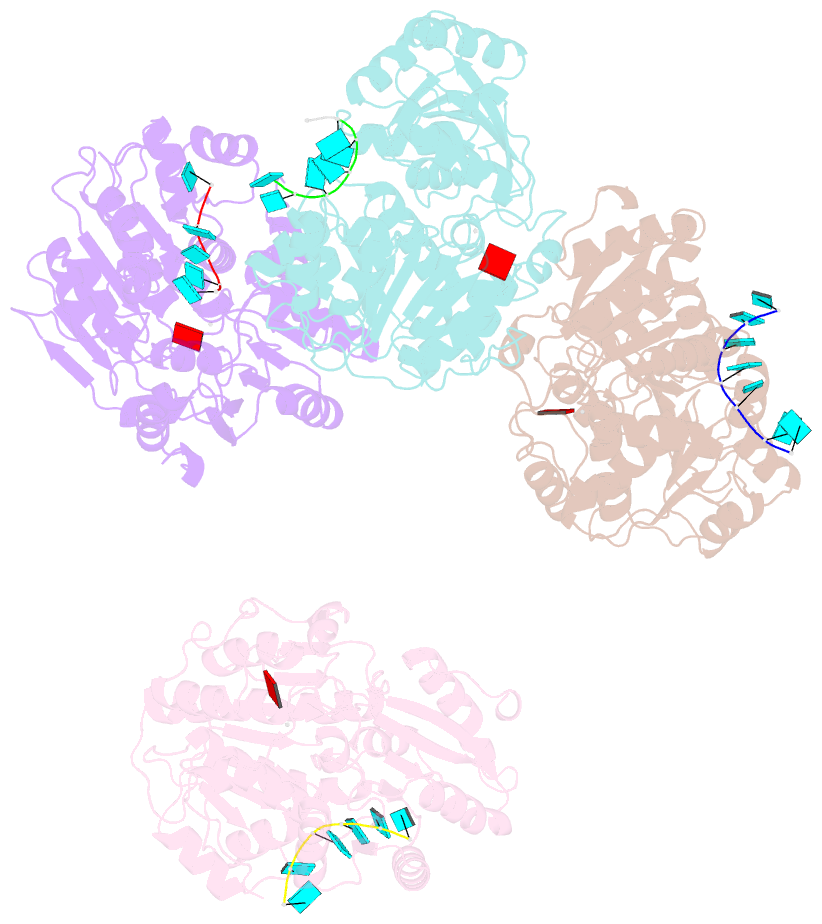
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 2db3; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- hydrolase-RNA
- Method
- X-ray (2.2 Å)
- Summary
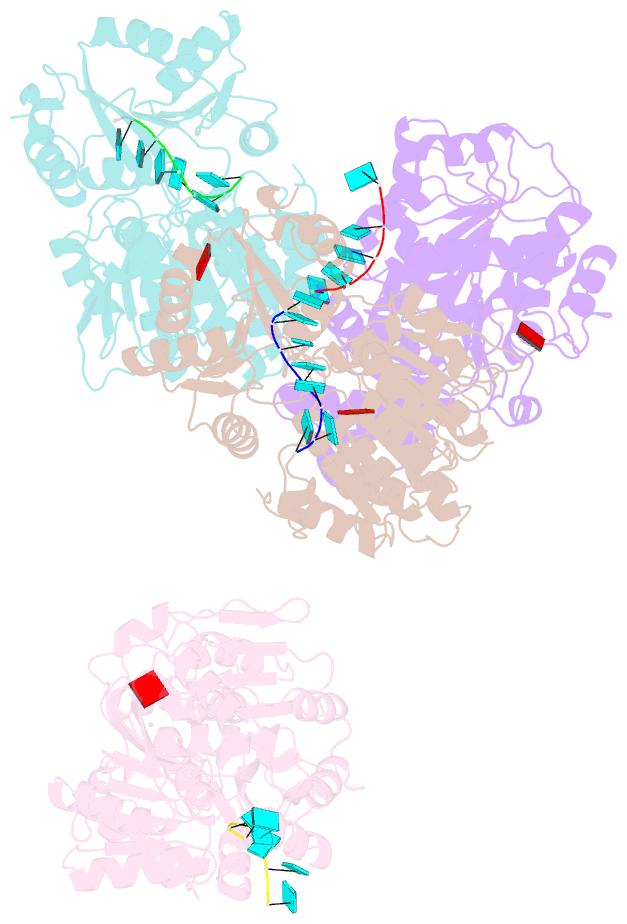
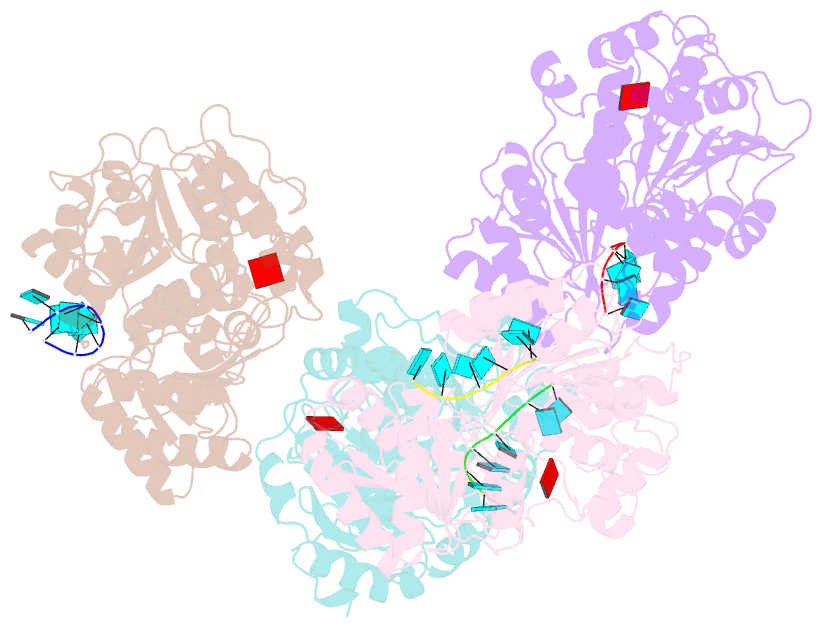
- Structural basis for RNA unwinding by the dead-box protein drosophila vasa
- Reference
- Sengoku T, Nureki O, Nakamura A, Kobayashi S, Yokoyama S (2006): "Structural basis for RNA unwinding by the DEAD-box protein Drosophila Vasa." Cell(Cambridge,Mass.), 125, 287-300. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2006.01.054.
- Abstract
- DEAD-box RNA helicases, which regulate various processes involving RNA, have two RecA-like domains as a catalytic core to alter higher-order RNA structures. We determined the 2.2 A resolution structure of the core of the Drosophila DEAD-box protein Vasa in complex with a single-stranded RNA and an ATP analog. The ATP analog intensively interacts with both of the domains, thereby bringing them into the closed form, with many interdomain interactions of conserved residues. The bound RNA is sharply bent, avoiding a clash with a conserved alpha helix in the N-terminal domain. This "wedge" helix should disrupt base pairs by bending one of the strands when a duplex is bound. Mutational analyses indicated that the interdomain interactions couple ATP hydrolysis to RNA unwinding, probably through fine positioning of the duplex relative to the wedge helix. This mechanism, which differs from those for canonical translocating helicases, may enable the targeted modulation of intricate RNA structures.