Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 2du5; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- ligase-RNA
- Method
- X-ray (3.2 Å)
- Summary
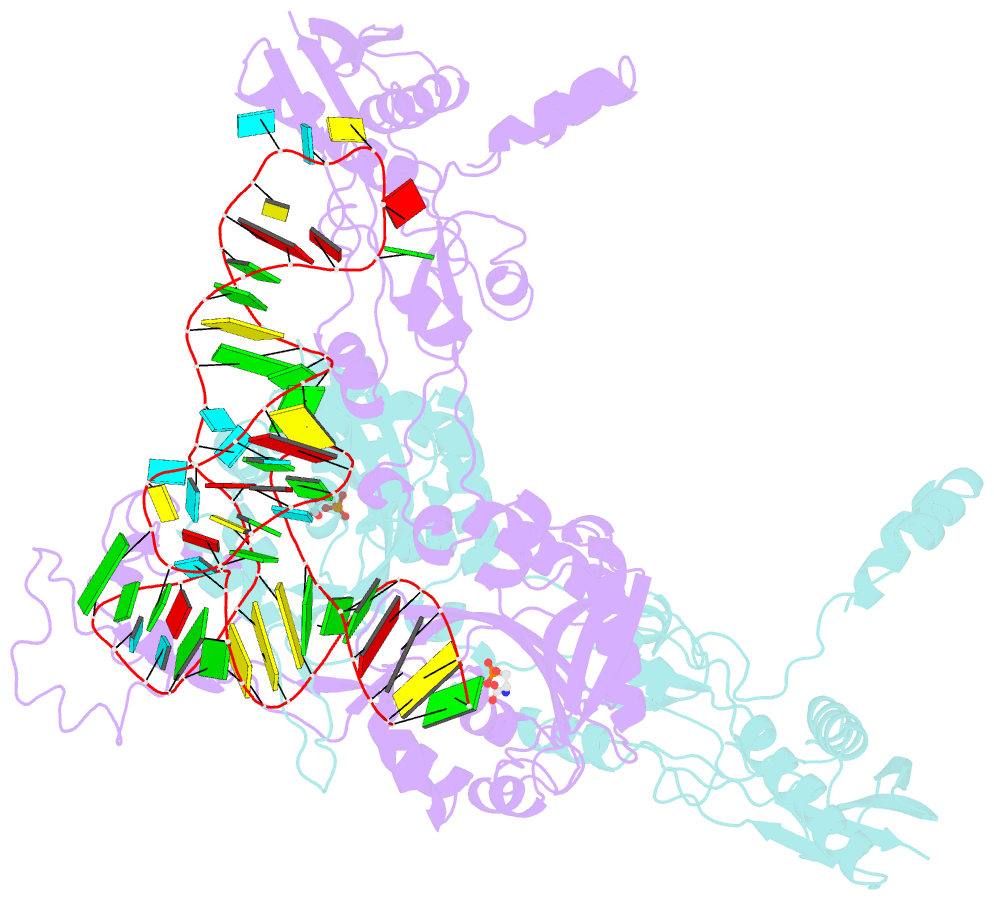
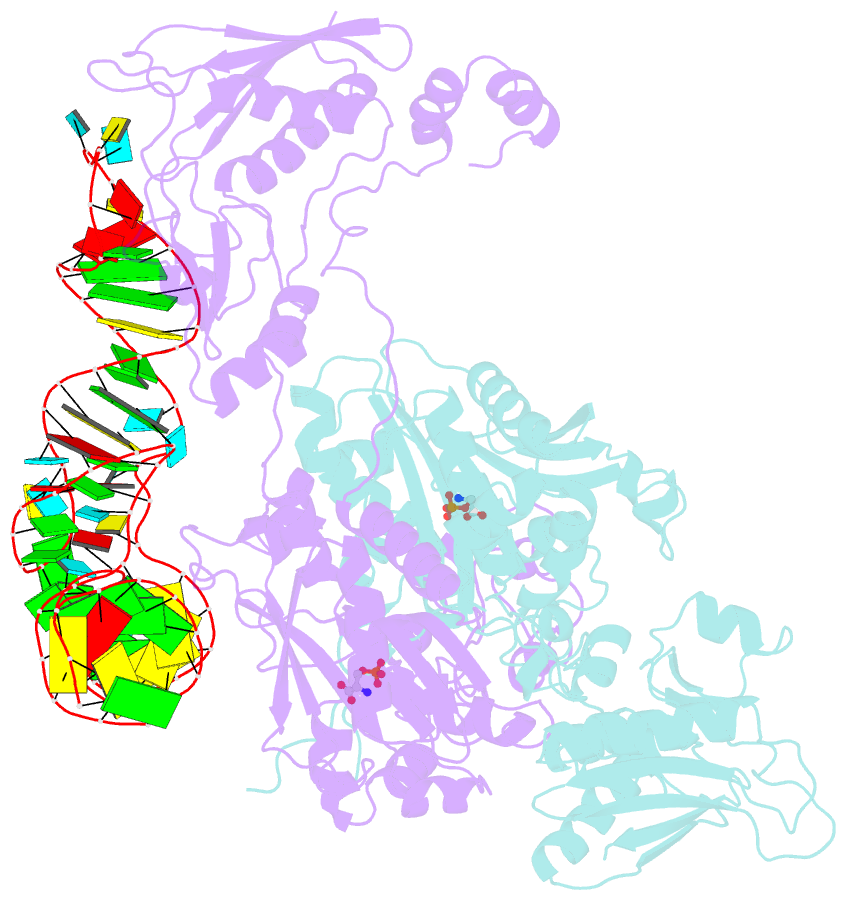
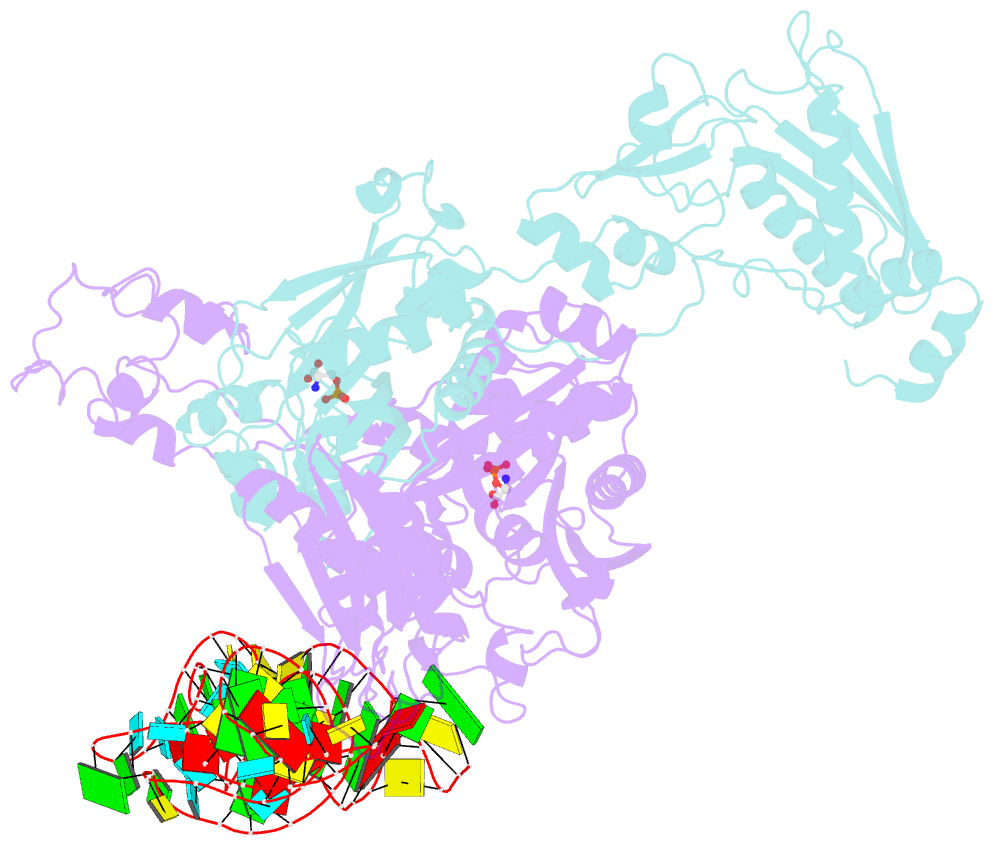
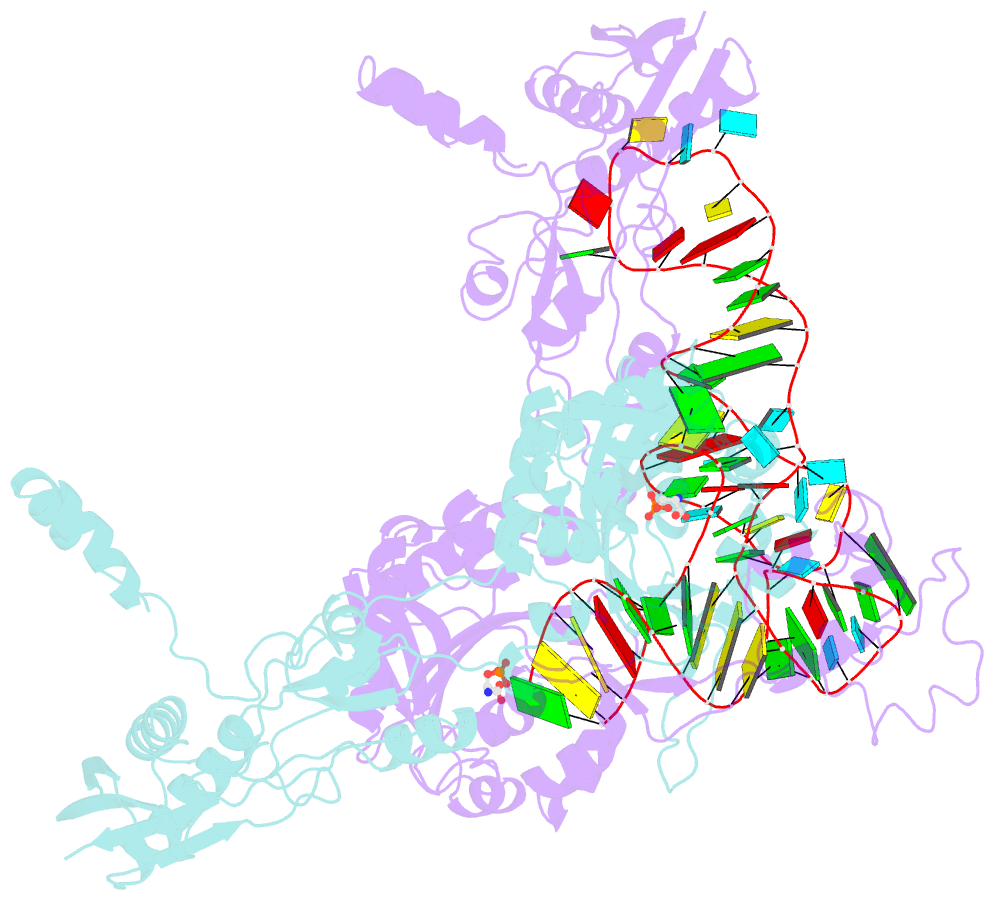
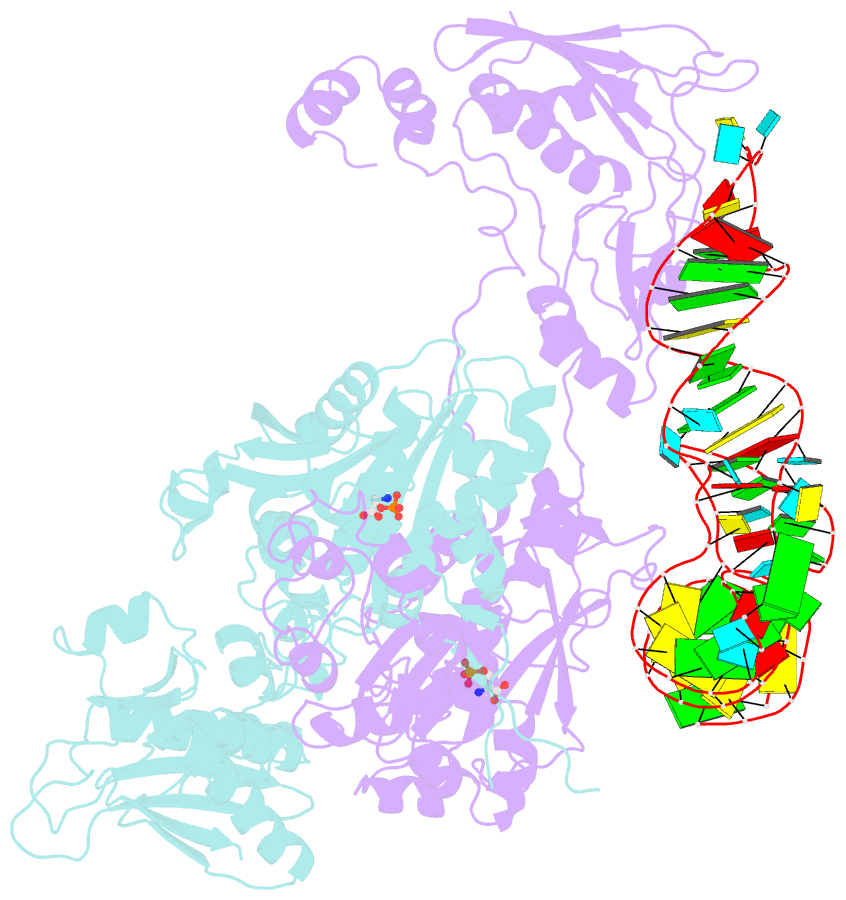
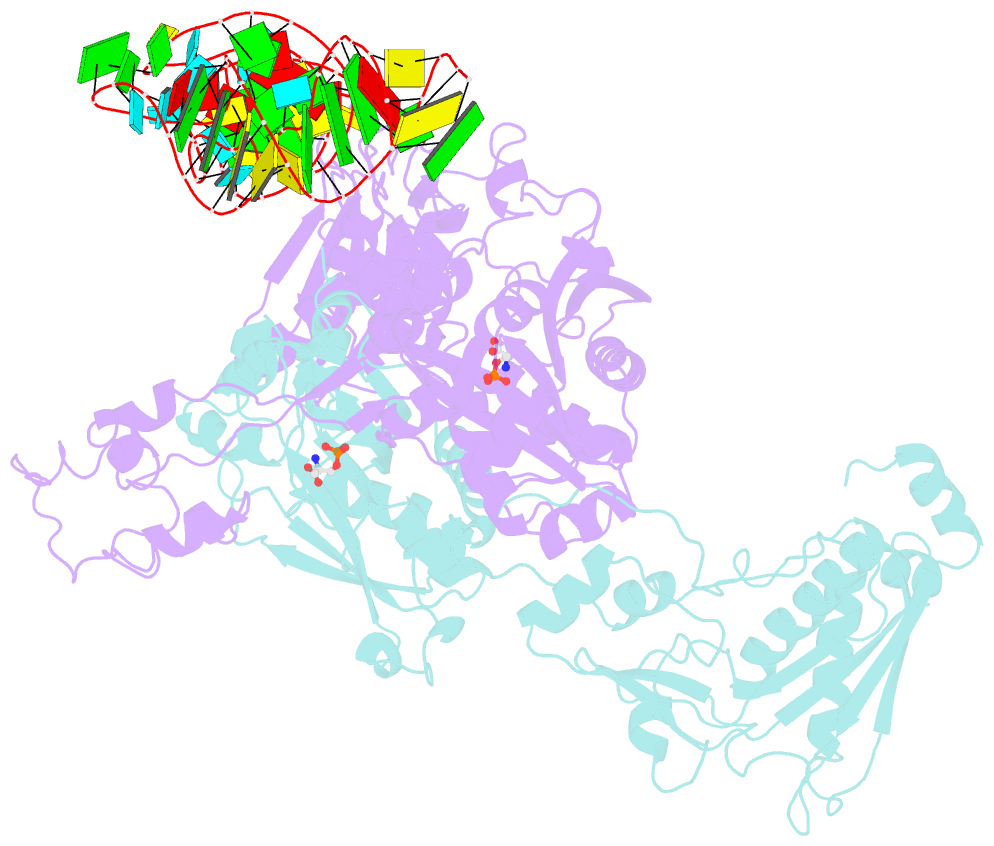
- Crystal structure of archaeoglobus fulgidus o-phosphoseryl-trna synthetase e418n-e420n mutant complexed with trnaopal and o-phosphoserine ("opal complex")
- Reference
- Fukunaga R, Yokoyama S (2007): "Structural insights into the first step of RNA-dependent cysteine biosynthesis in archaea." Nat.Struct.Mol.Biol., 14, 272-279. doi: 10.1038/nsmb1219.
- Abstract
- Cysteine is ligated to tRNA(Cys) by cysteinyl-tRNA synthetase in most organisms. However, in methanogenic archaea lacking cysteinyl-tRNA synthetase, O-phosphoserine is ligated to tRNA(Cys) by O-phosphoseryl-tRNA synthetase (SepRS), and the phosphoseryl-tRNA(Cys) is converted to cysteinyl-tRNA(Cys). In this study, we determined the crystal structure of the SepRS tetramer in complex with tRNA(Cys) and O-phosphoserine at 2.6-A resolution. The catalytic domain of SepRS recognizes the negatively charged side chain of O-phosphoserine at a noncanonical site, using the dipole moment of a conserved alpha-helix. The unique C-terminal domain specifically recognizes the anticodon GCA of tRNA(Cys). On the basis of the structure, we engineered SepRS to recognize tRNA(Cys) mutants with the anticodons UCA and CUA and clarified the anticodon recognition mechanism by crystallography. The mutant SepRS-tRNA pairs may be useful for translational incorporation of O-phosphoserine into proteins in response to the stop codons UGA and UAG.