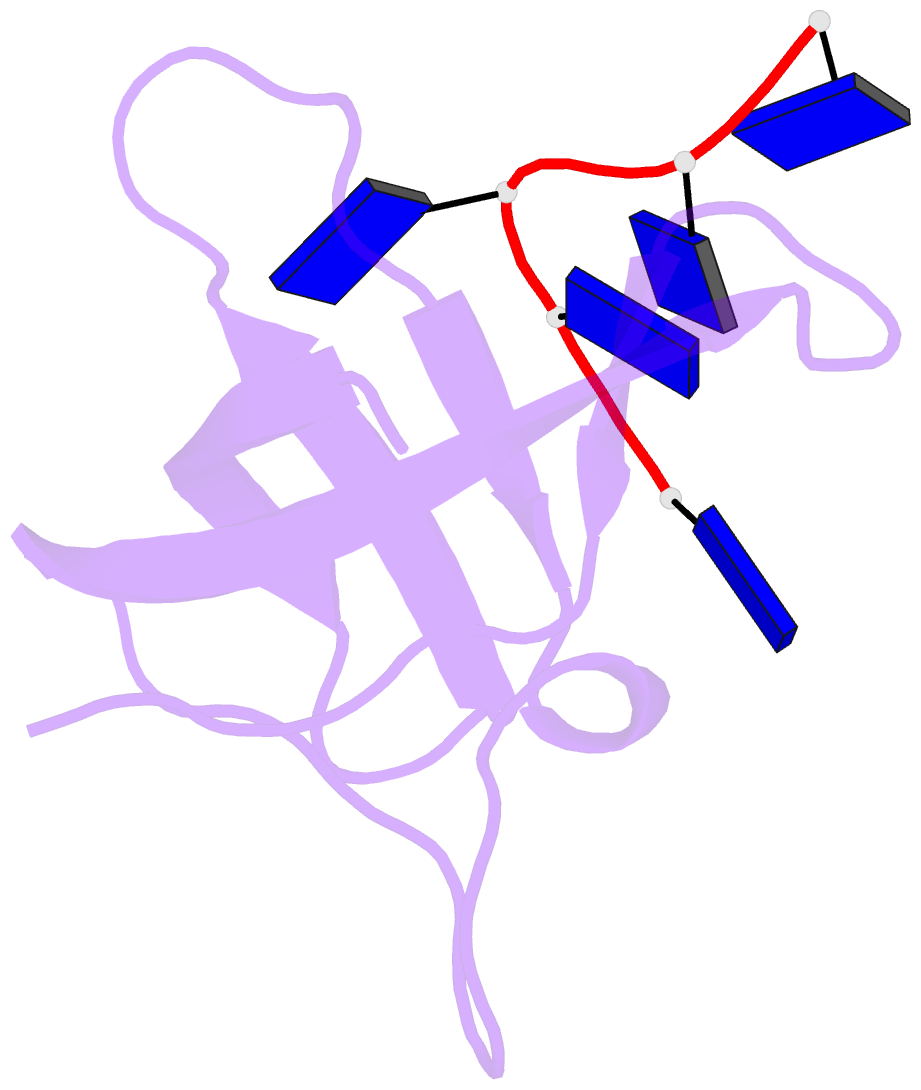
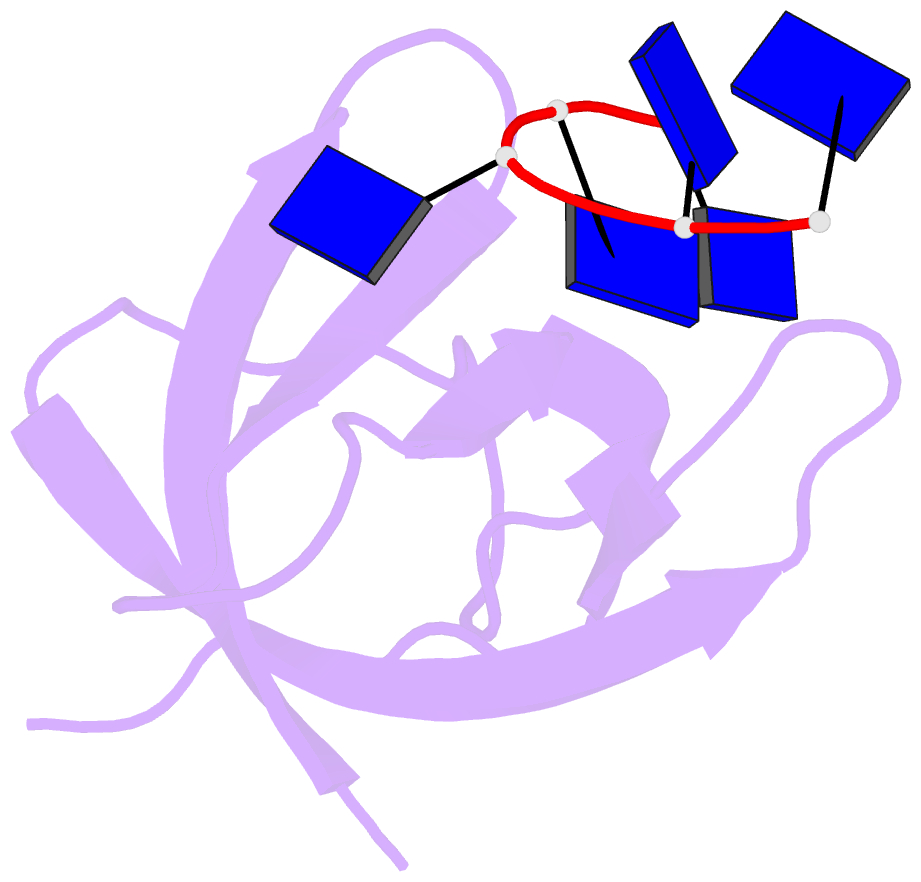
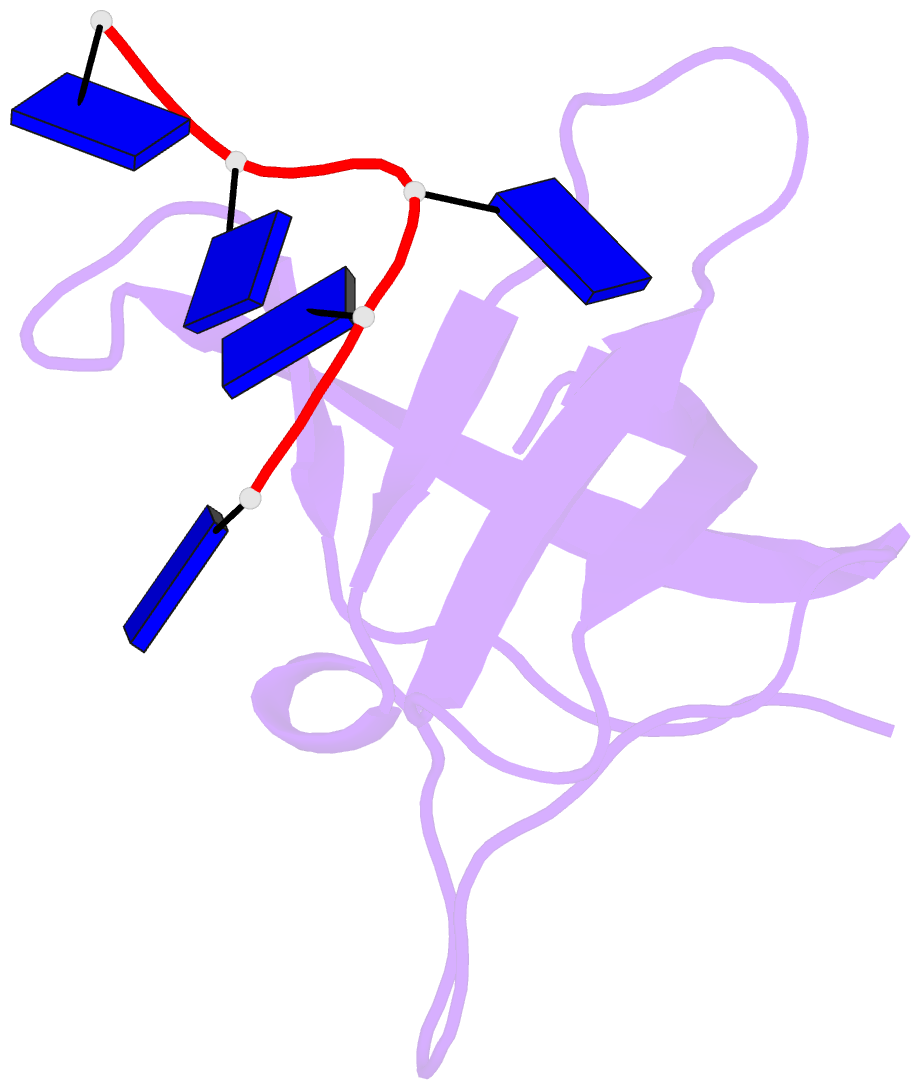
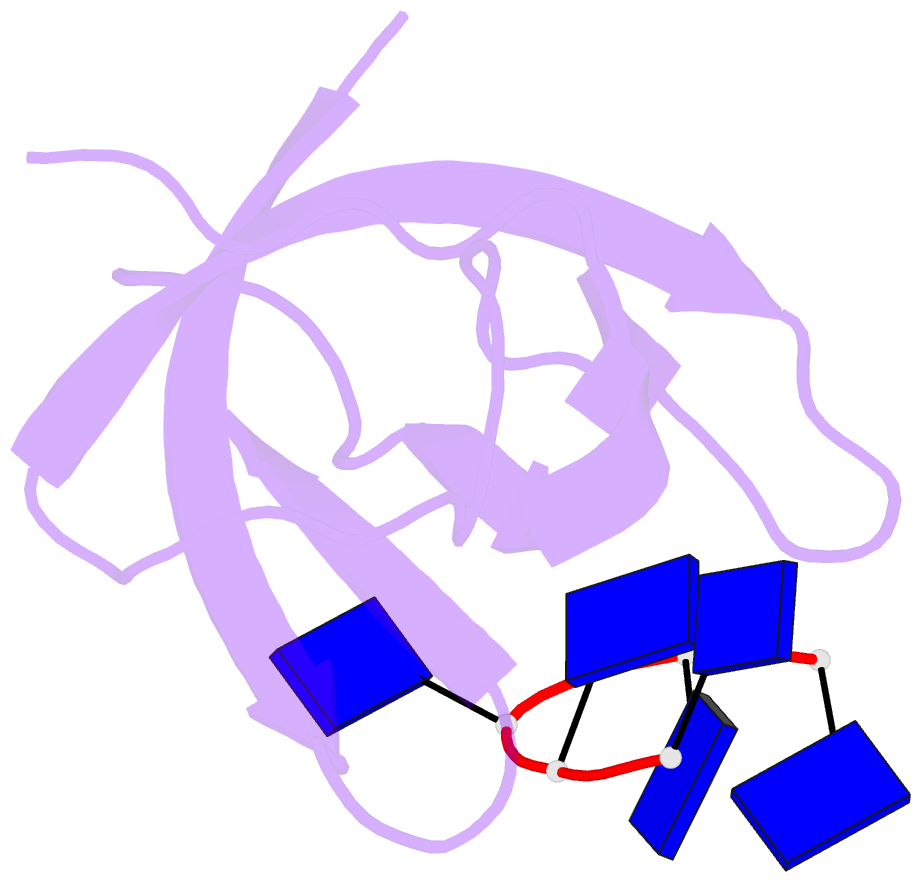
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 2es2; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- gene regulation
- Method
- X-ray (1.78 Å)
- Summary
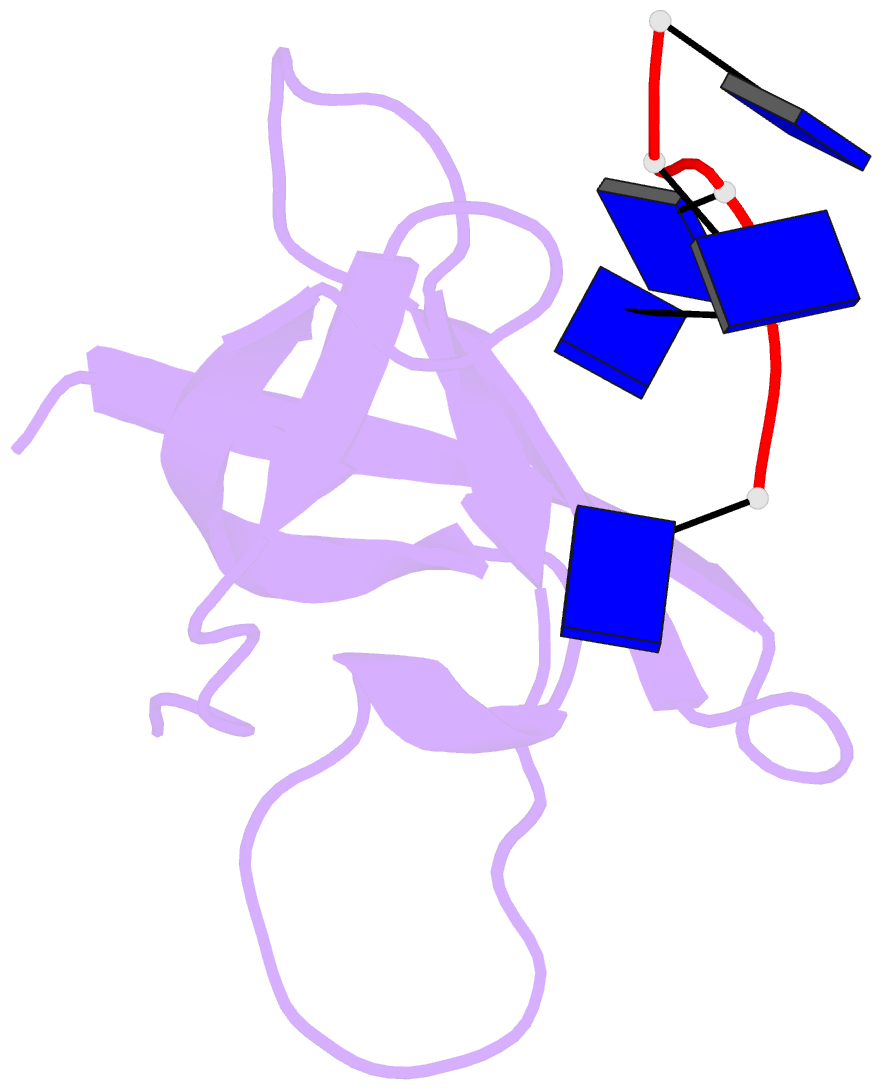
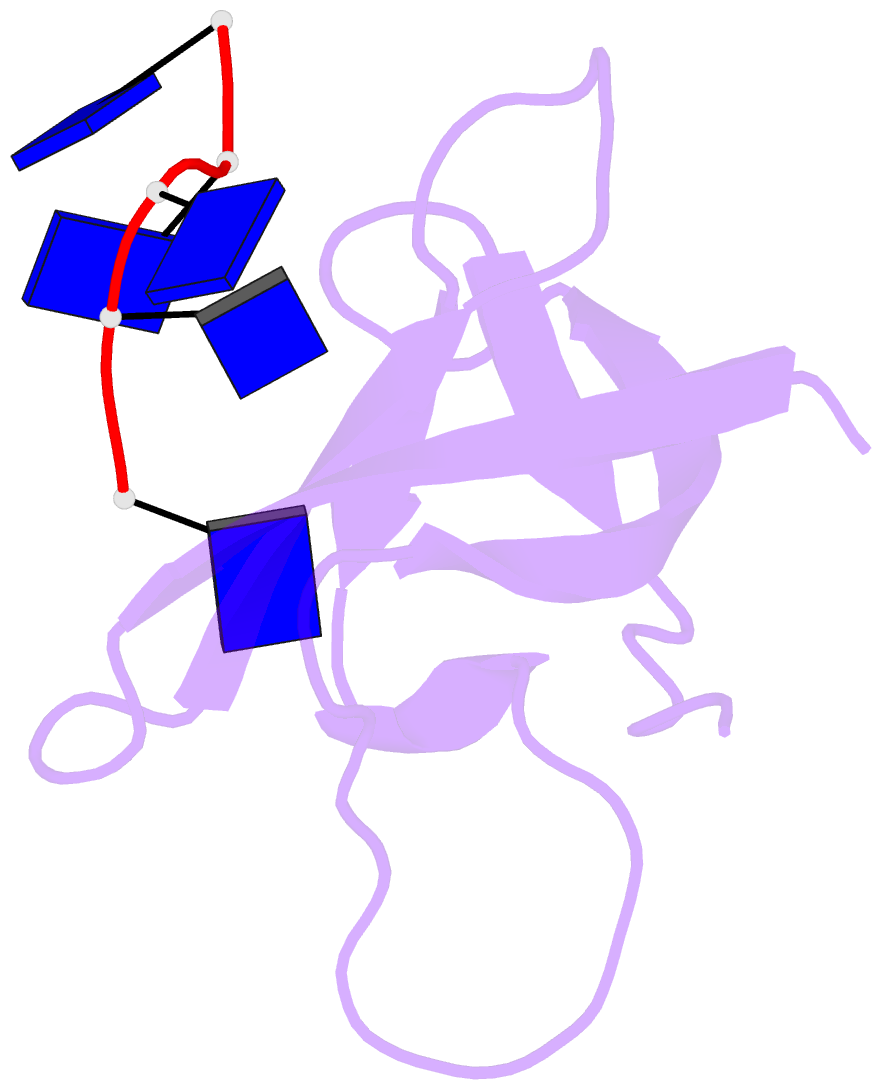
- Crystal structure analysis of the bacillus subtilis cold shock protein bs-cspb in complex with hexathymidine
- Reference
- Max KE, Zeeb M, Bienert R, Balbach J, Heinemann U (2006): "T-rich DNA single strands bind to a preformed site on the bacterial cold shock protein Bs-CspB." J.Mol.Biol., 360, 702-714. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2006.05.044.
- Abstract
- Bacterial cold shock proteins (CSPs) are involved in cellular adaptation to cold stress. They bind to single-stranded nucleic acids with a KD value in the micro- to nanomolar range. Here we present the structure of the Bacillus subtilis CspB (Bs-CspB) in complex with hexathymidine (dT6) at a resolution of 1.78 A. Bs-CspB binds to dT6 with nanomolar affinity via an amphipathic interface on the protein surface. Individual binding subsites interact with single nucleobases through stacking interactions and hydrogen bonding. The sugar-phosphate backbone and the methyl groups of the thymine nucleobases remain solvent exposed and are not contacted by protein groups. Fluorescence titration experiments monitoring the binding of oligopyrimidines to Bs-CspB reveal binding preferences at individual subsites and allow the design of an optimised heptapyrimidine ligand, which is bound with sub-nanomolar affinity. This study reveals the stoichiometry and sequence determinants of the binding of single-stranded nucleic acids to a preformed site on Bs-CspB and thus provides the structural basis of the RNA chaperone and transcription antitermination activities of the CSP.