Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 2ezv; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- hydrolase-DNA
- Method
- X-ray (2.4 Å)
- Summary
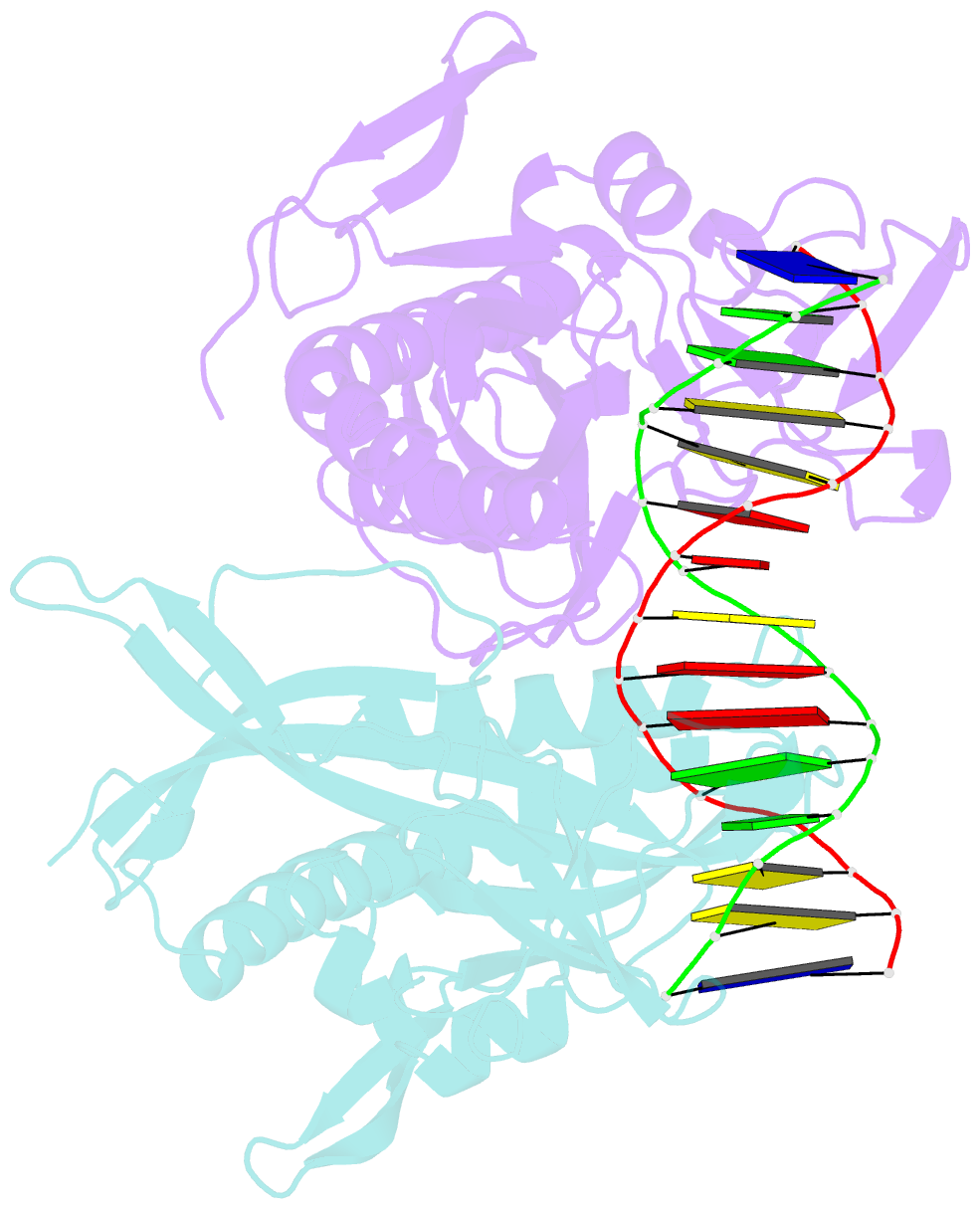
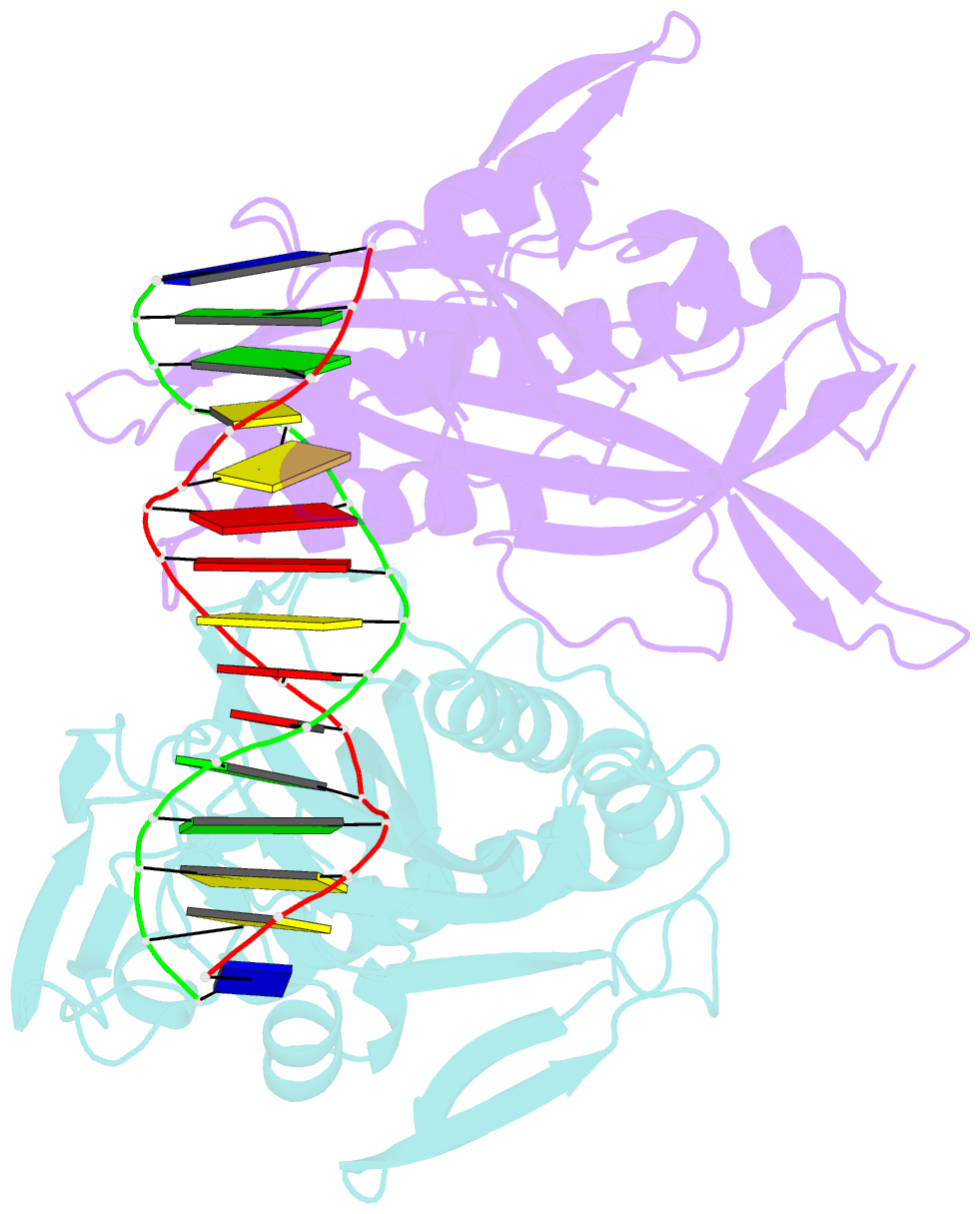
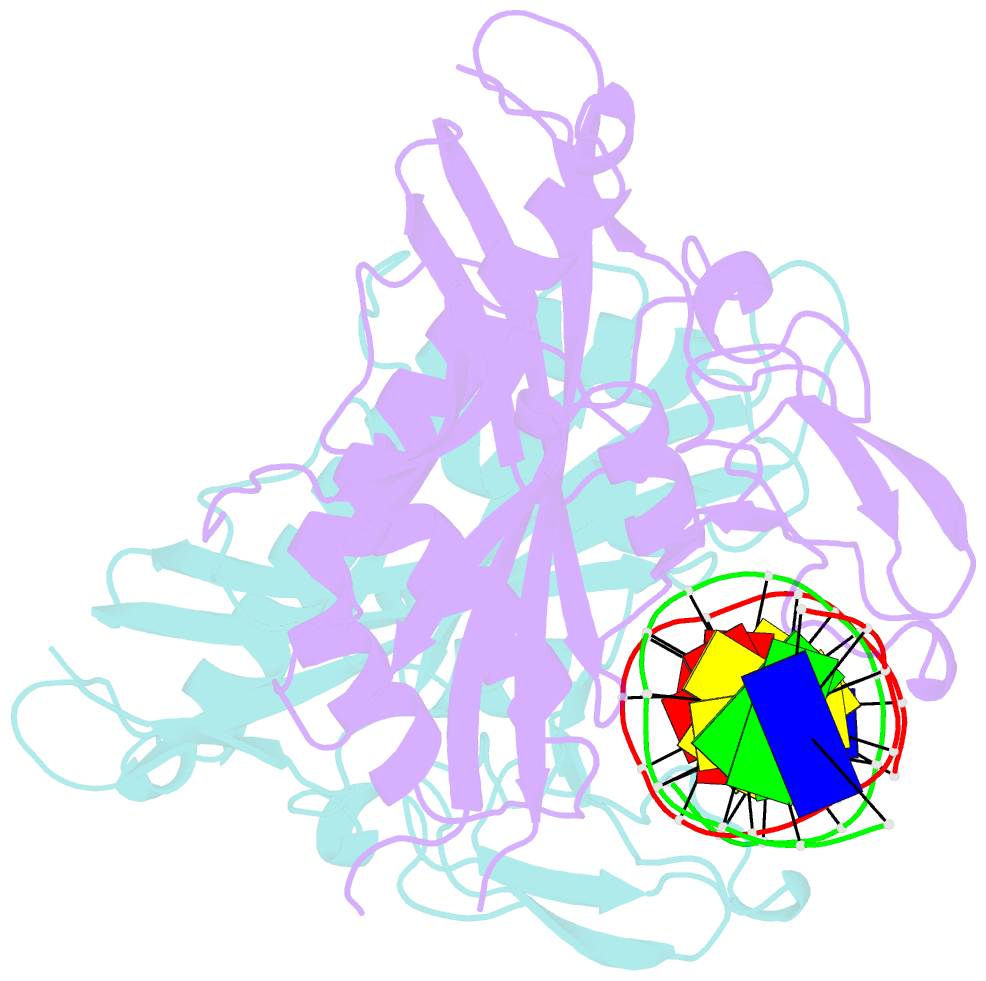
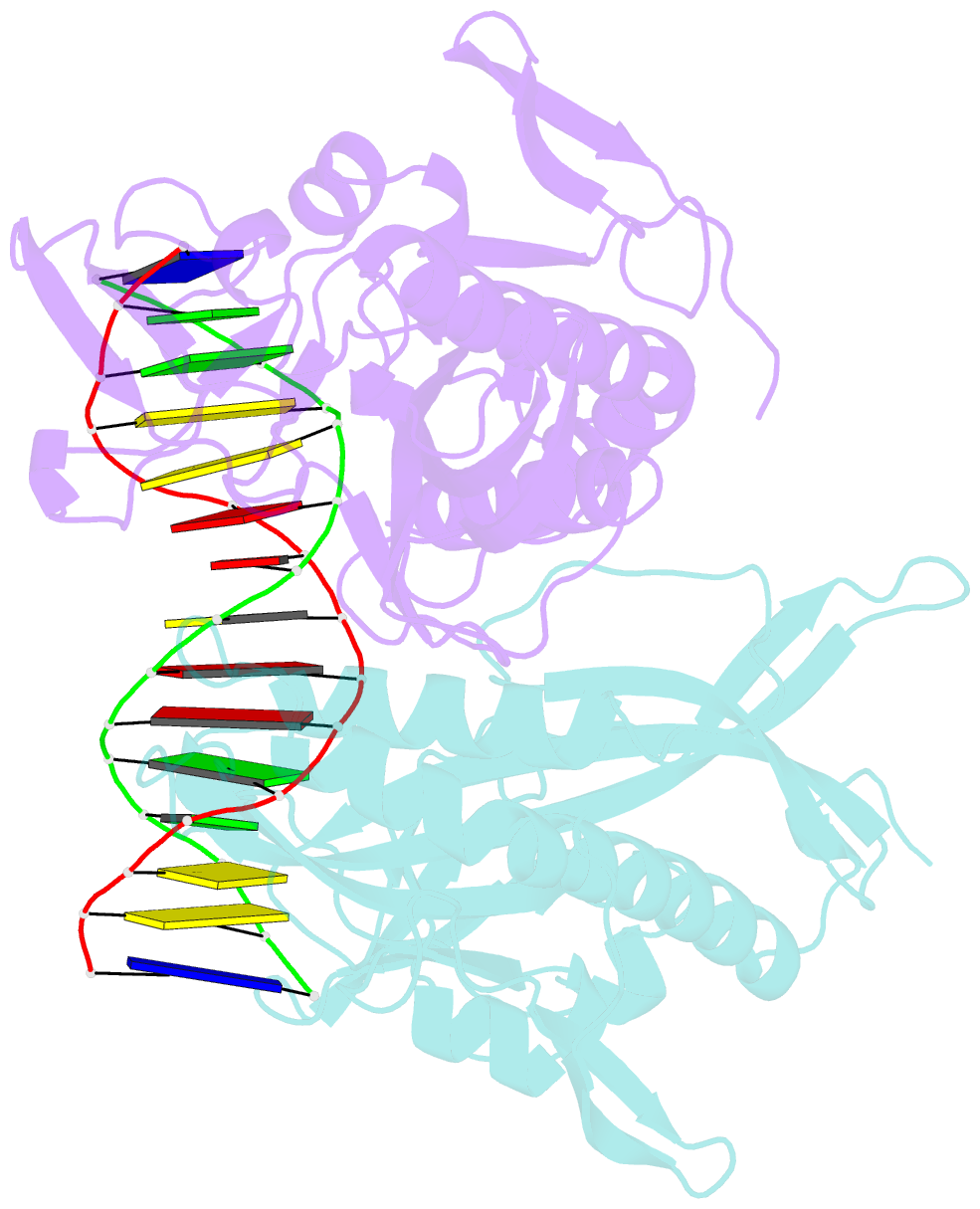
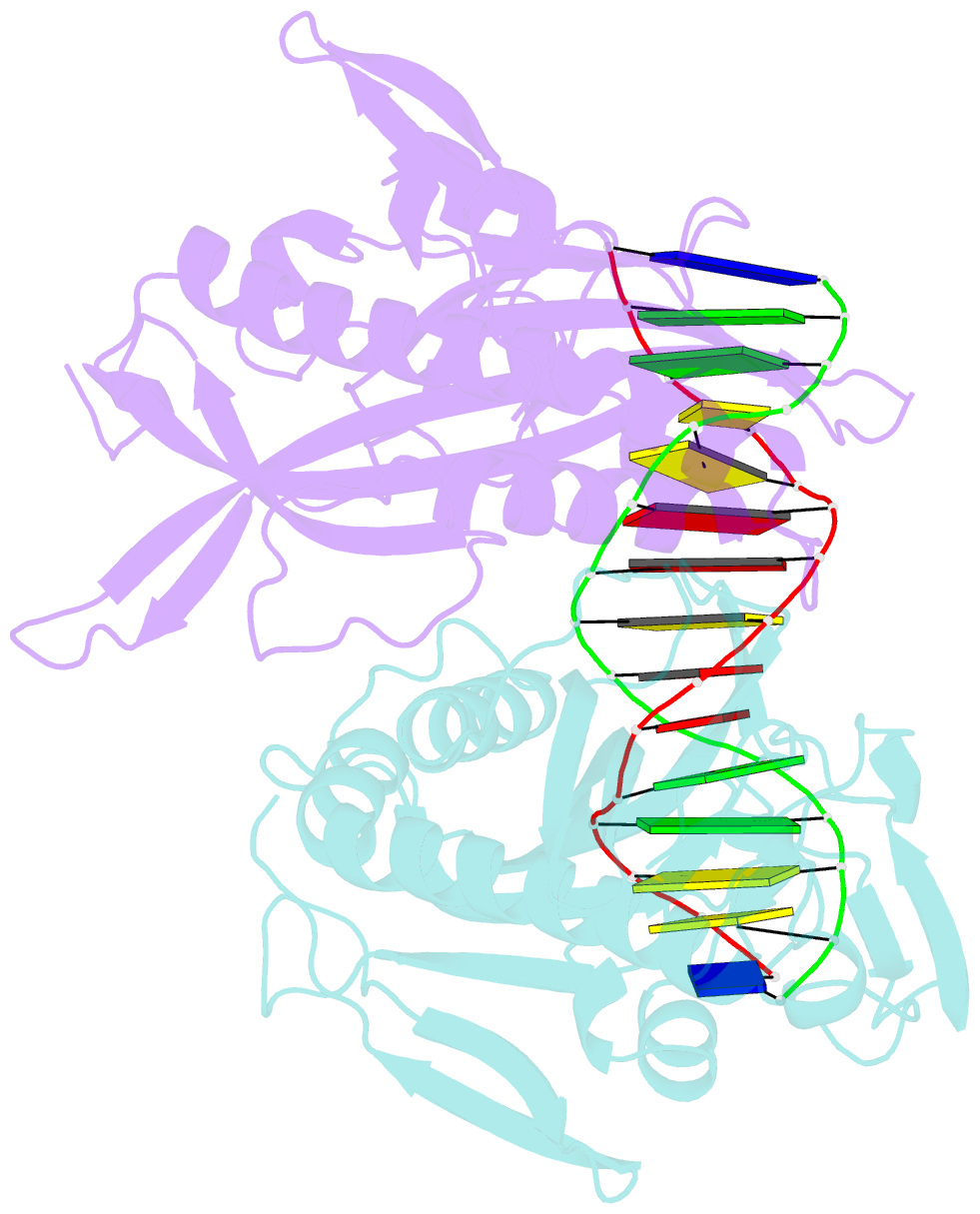
- Crystal structure of tetrameric restriction endonuclease sfii bound to cognate DNA.
- Reference
- Vanamee ES, Viadiu H, Kucera R, Dorner L, Picone S, Schildkraut I, Aggarwal AK (2005): "A view of consecutive binding events from structures of tetrameric endonuclease SfiI bound to DNA." Embo J., 24, 4198-4208. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600880.
- Abstract
- Many reactions in cells proceed via the sequestration of two DNA molecules in a synaptic complex. SfiI is a member of a growing family of restriction enzymes that can bind and cleave two DNA sites simultaneously. We present here the structures of tetrameric SfiI in complex with cognate DNA. The structures reveal two different binding states of SfiI: one with both DNA-binding sites fully occupied and the other with fully and partially occupied sites. These two states provide details on how SfiI recognizes and cleaves its target DNA sites, and gives insight into sequential binding events. The SfiI recognition sequence (GGCCNNNN[downward arrow]NGGCC) is a subset of the recognition sequence of BglI (GCCNNNN[downward arrow]NGGC), and both enzymes cleave their target DNAs to leave 3-base 3' overhangs. We show that even though SfiI is a tetramer and BglI is a dimer, and there is little sequence similarity between the two enzymes, their modes of DNA recognition are unusually similar.