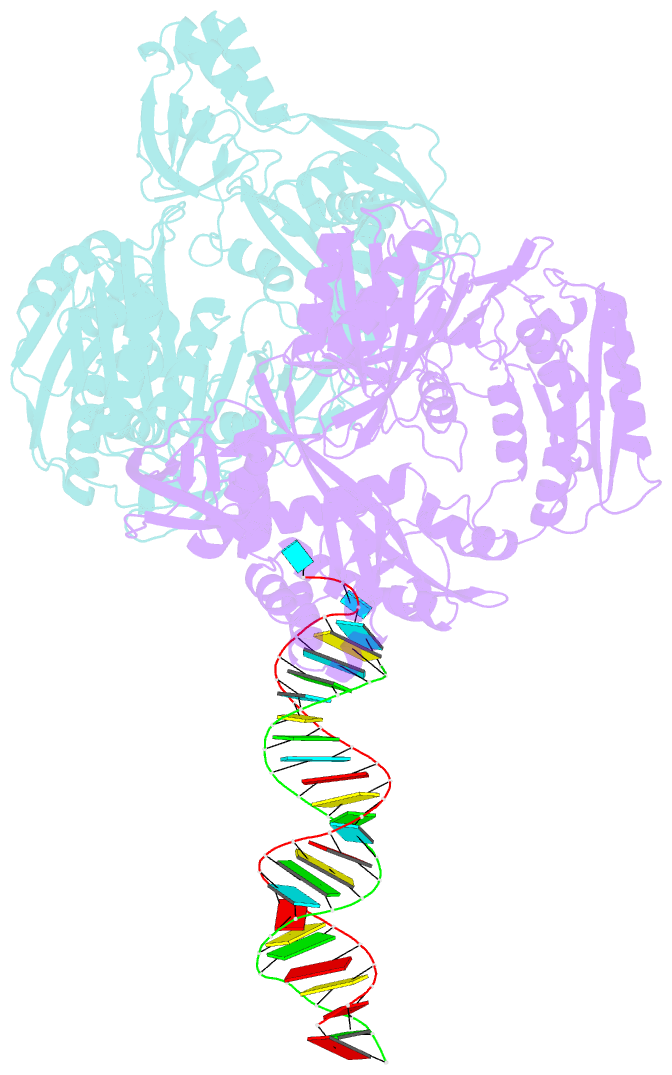
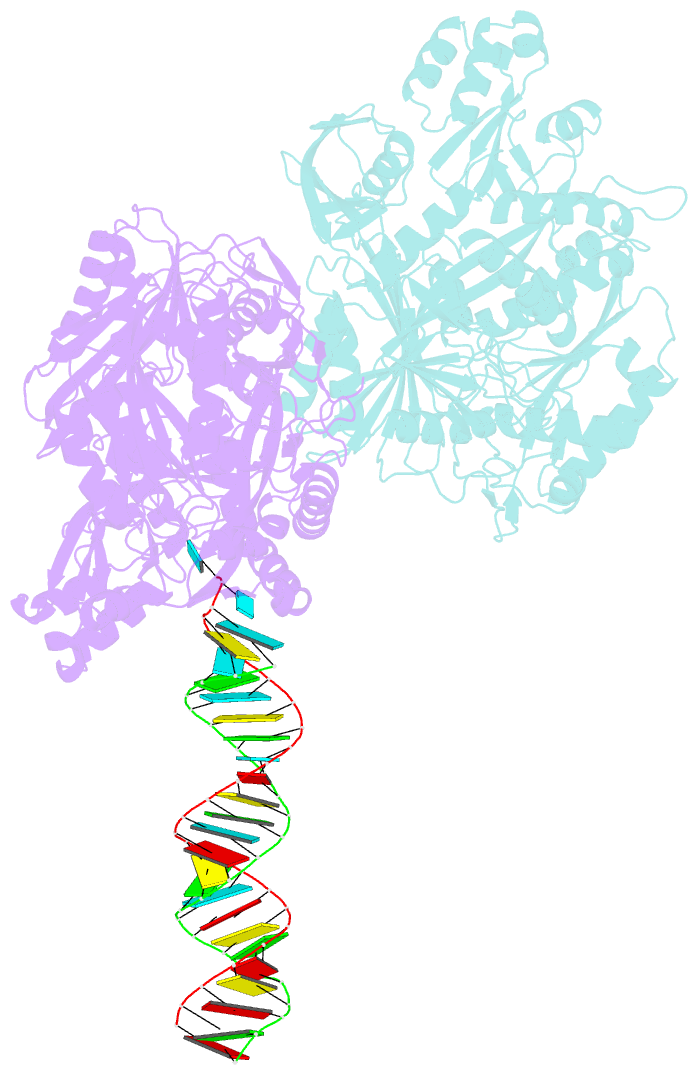
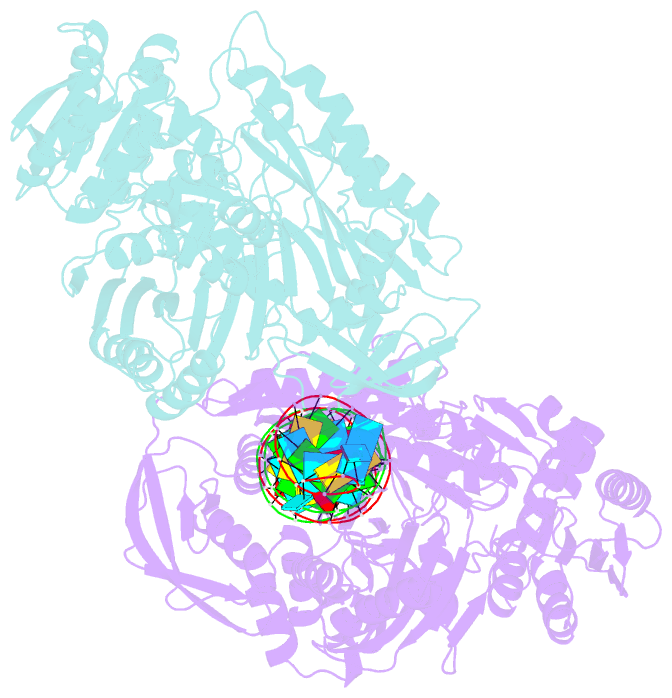
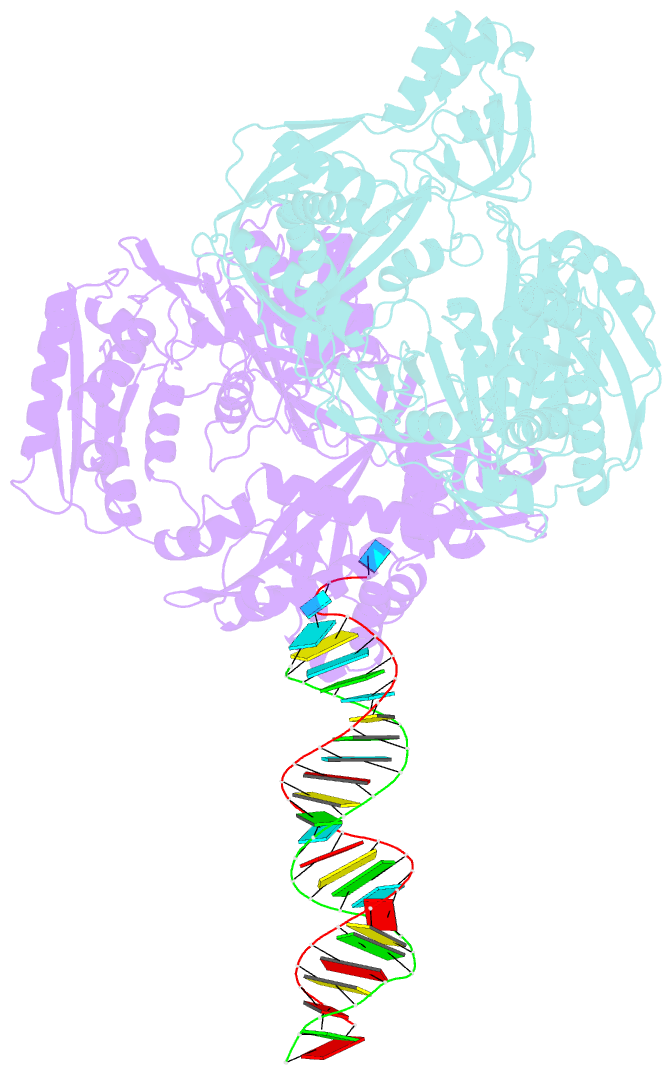
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 2f8t; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- RNA binding protein-RNA
- Method
- X-ray (3.1 Å)
- Summary
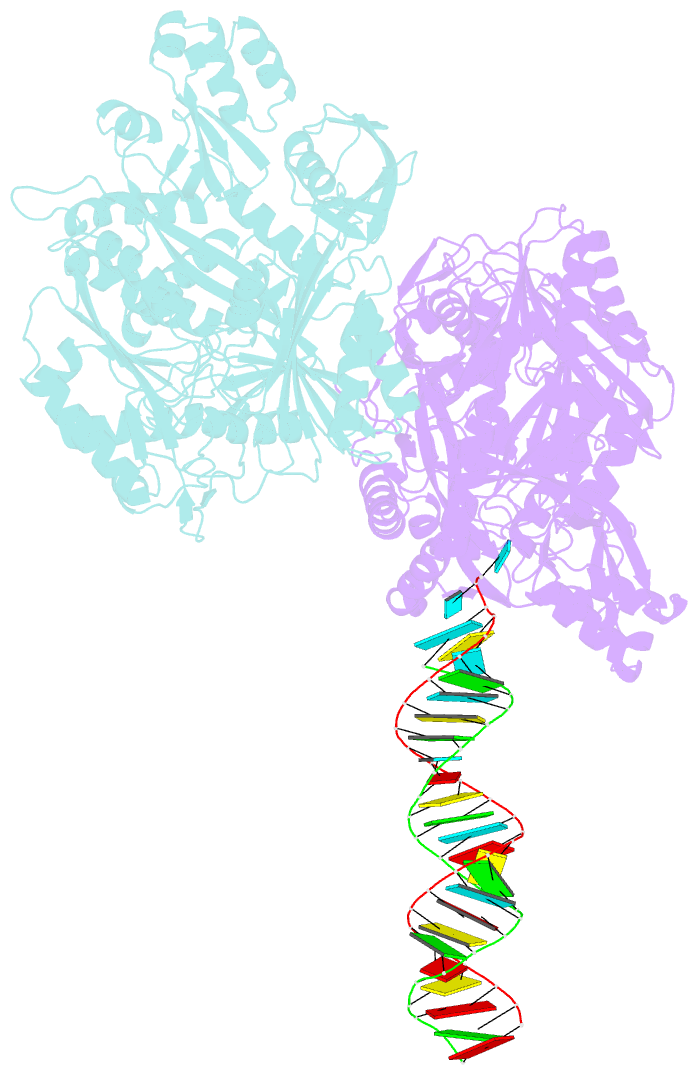
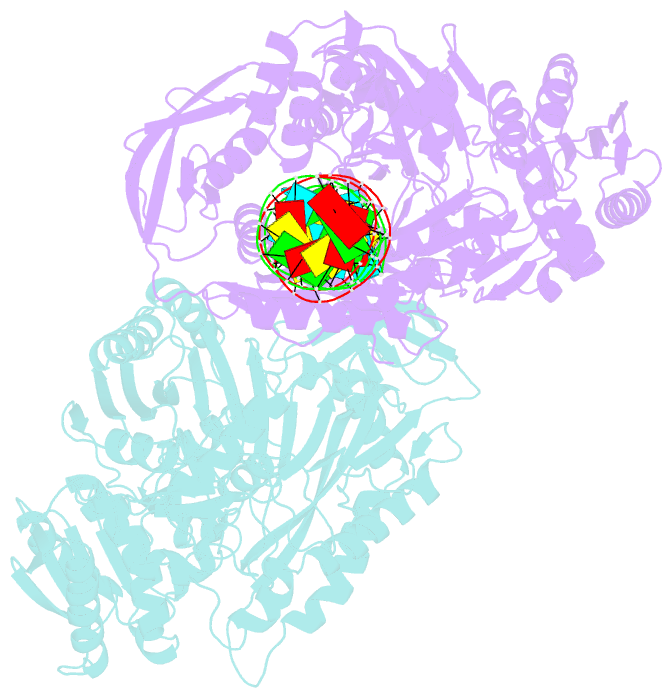
- Crystal structure of aa-ago with externally-bound sirna
- Reference
- Yuan YR, Pei Y, Chen HY, Tuschl T, Patel DJ (2006): "A Potential Protein-RNA Recognition Event along the RISC-Loading Pathway from the Structure of A. aeolicus Argonaute with Externally Bound siRNA." Structure, 14, 1557-1565. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2006.08.009.
- Abstract
- Argonaute proteins are key components of the RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC). They provide both architectural and catalytic functionalities associated with small interfering RNA (siRNA) guide strand recognition and subsequent guide strand-mediated cleavage of complementary mRNAs. We report on the 3.0 A crystal structures of 22-mer and 26-mer siRNAs bound to Aquifex aeolicus Argonaute (Aa-Ago), where one 2 nt 3' overhang of the siRNA inserts into a cavity positioned on the outer surface of the PAZ-containing lobe of the bilobal Aa-Ago architecture. The first overhang nucleotide stacks over a tyrosine ring, while the second overhang nucleotide, together with the intervening sugar-phosphate backbone, inserts into a preformed surface cavity. Photochemical crosslinking studies on Aa-Ago with 5-iodoU-labeled single-stranded siRNA and siRNA duplex provide support for this externally bound siRNA-Aa-Ago complex. The structure and biochemical data together provide insights into a protein-RNA recognition event potentially associated with the RISC-loading pathway.