Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 2fj7; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- structural protein-DNA
- Method
- X-ray (3.2 Å)
- Summary
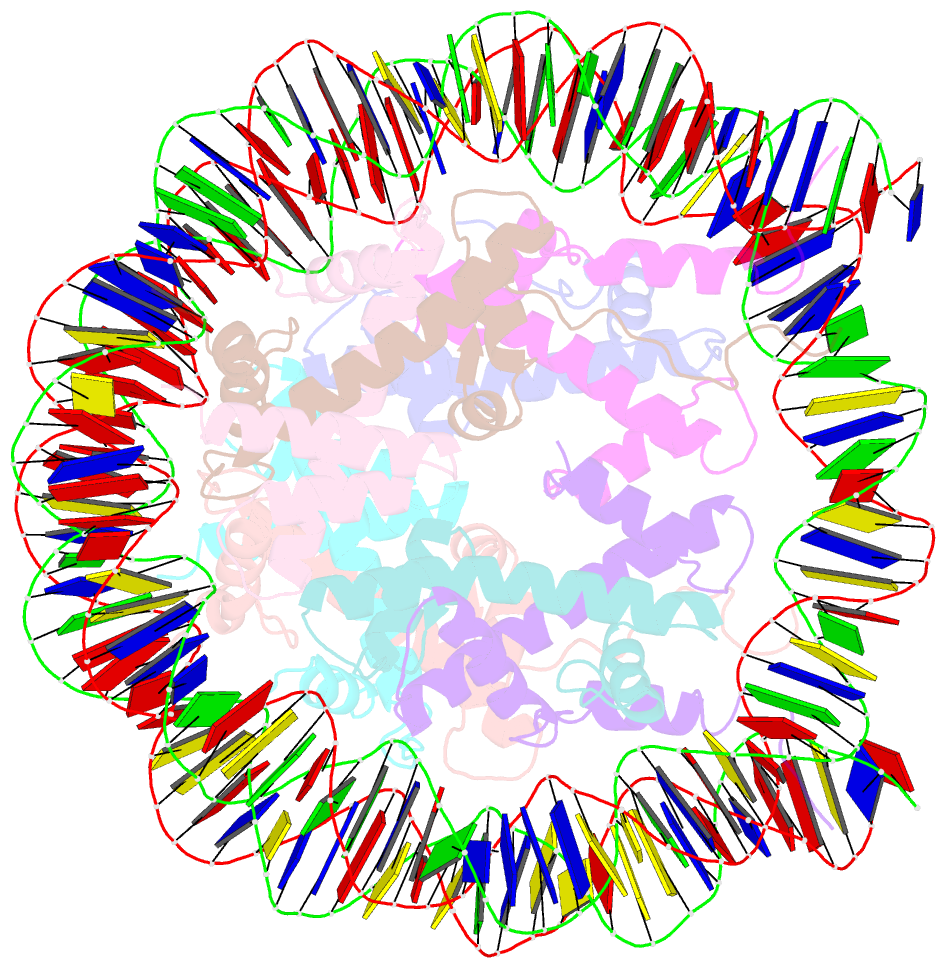
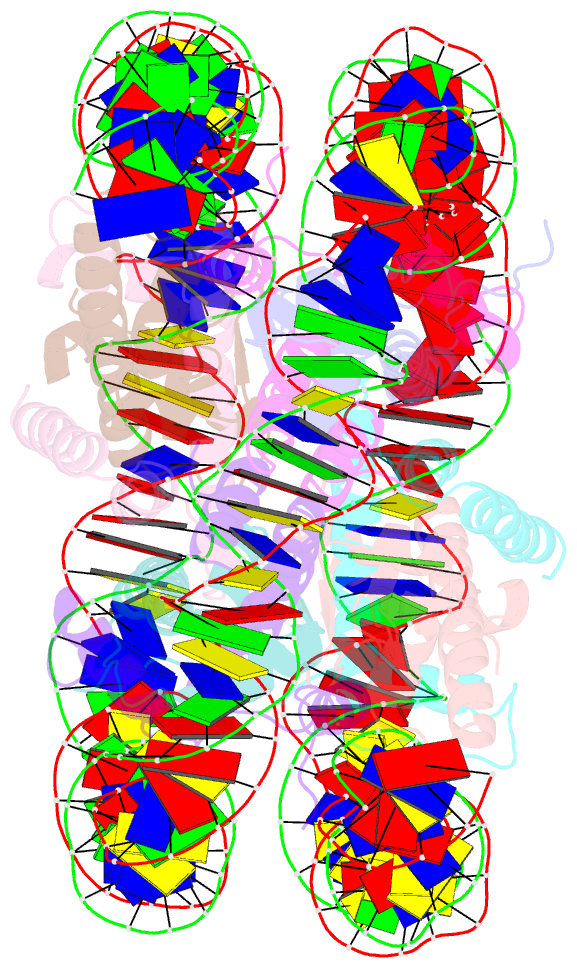
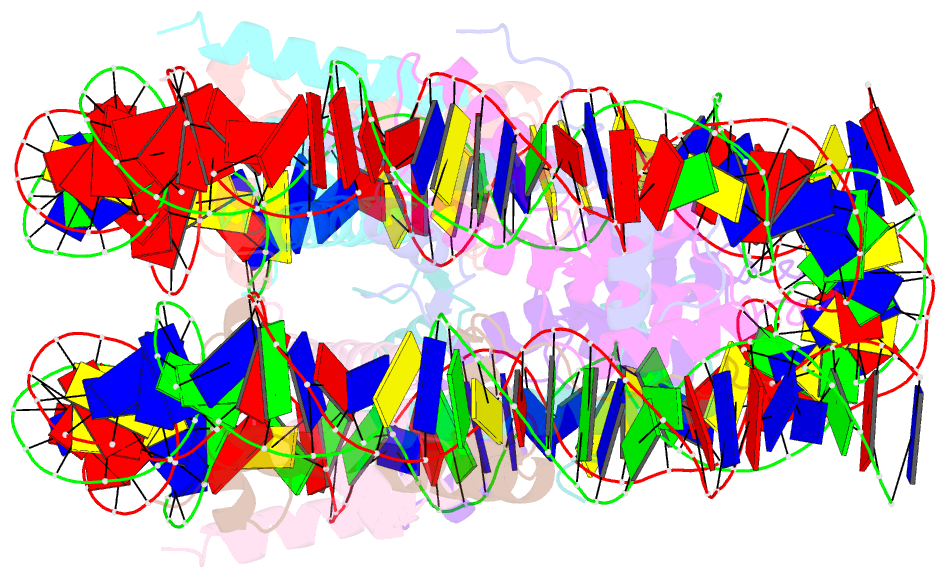
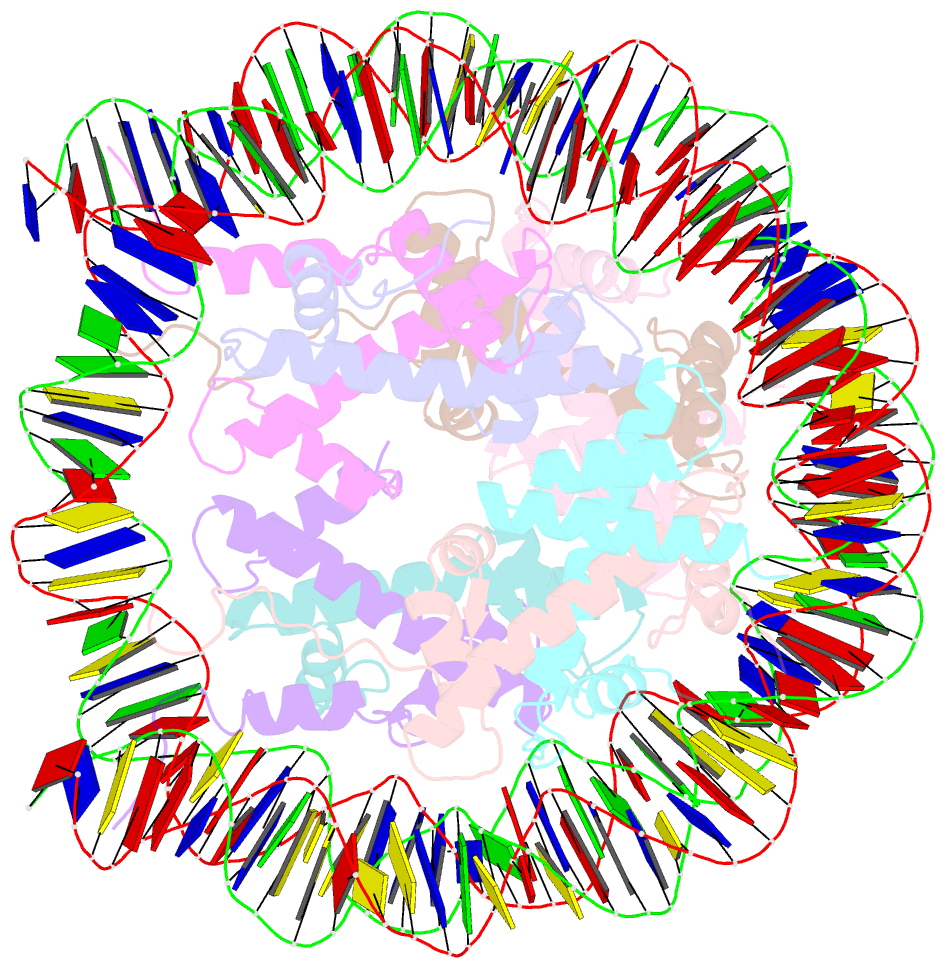
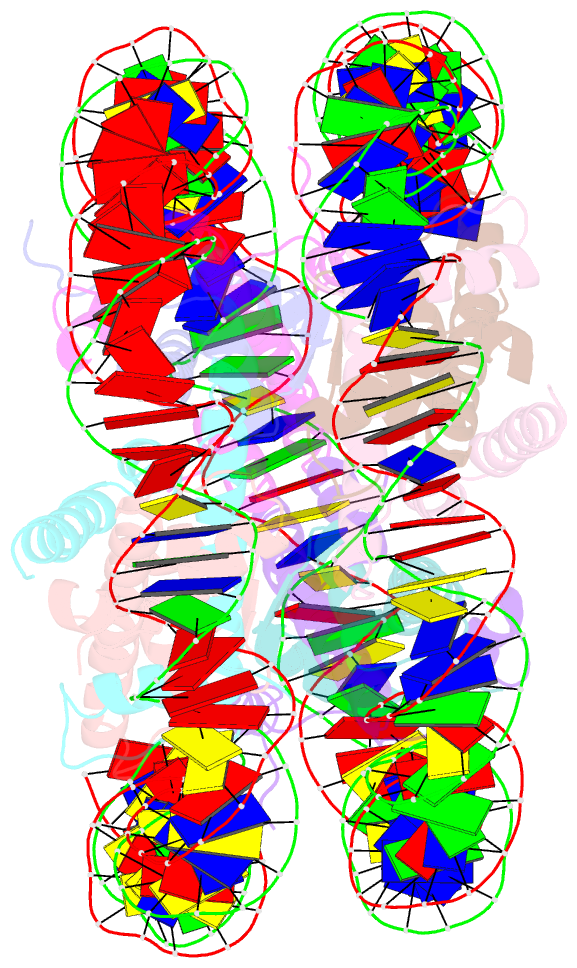
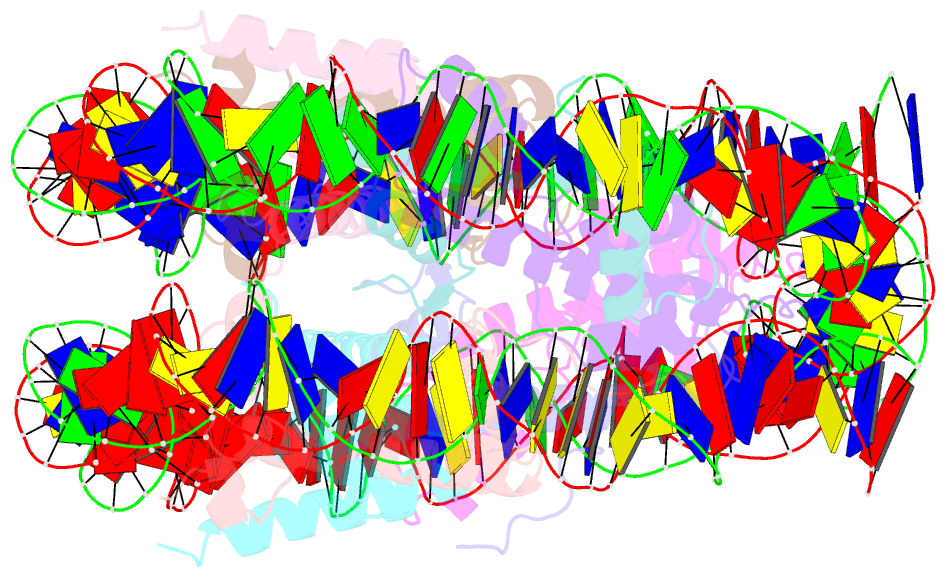
- Crystal structure of nucleosome core particle containing a poly (da.dt) sequence element
- Reference
- Bao Y, White CL, Luger K (2006): "Nucleosome Core Particles Containing a Poly(dA.dT) Sequence Element Exhibit a Locally Distorted DNA Structure." J.Mol.Biol., 361, 617-624. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2006.06.051.
- Abstract
- Poly(dA.dT) DNA sequence elements are thought to promote transcription by either excluding nucleosomes or by altering their structural or dynamic properties. Here, the stability and structure of a defined nucleosome core particle containing a 16 base-pair poly(dA.dT) element (A16 NCP) was investigated. The A16 NCP requires a significantly higher temperature for histone octamer sliding in vitro compared to comparable nucleosomes that do not contain a poly(dA.dT) element. Fluorescence resonance energy transfer showed that the interactions between the nucleosomal DNA ends and the histone octamer were destabilized in A16 NCP. The crystal structure of A16 NCP was determined to a resolution of 3.2 A. The overall structure was maintained except for local deviations in DNA conformation. These results are consistent with previous in vivo and in vitro observations that poly(dA.dT) elements cause only modest changes in DNA accessibility and modest increases in steady-state transcription levels.